編輯:關於Android編程
Android自定義View是程序猿從初級階段進階的必由之路,而自定義View必然會伴隨自定義屬性,本篇先來講講安卓自定義屬性
1、自定義View的屬性,首先在res/values/ 下建立一個attrs.xml , 在裡面定義我們的屬性和聲明我們的整個樣式。
attr子元素:
定義具體的屬性,format表示這個屬性的值的類型,類型有以下幾種:
1.reference:參考指定Theme中資源ID,這個類型意思就是你傳的值可以是引用資源
2.string:字符串,如果你想別人既能直接寫值也可以用類似"@string/test"引用資源的方式,可以寫成format="string|reference"
3.Color:顏色
4.boolean:布爾值
5.dimension:尺寸值
6.float:浮點型
7.integer:整型
8.fraction:百分數
9.enum:枚舉 ,如果你提供的屬性只能讓別人選擇,不能隨便傳入,就可以寫成這樣
10.flag:位或運算
declare-styleable子元素:
定義一個styleable對象,每個styleable對象就是一組attr屬性的集合,注意:這裡的name屬性並不是一定要和自定義類名相同,只是為了好區分對應類的屬性而已
注意:上面的屬性資源文件定義了該屬性之後,至於到底是哪個自定義View組件中來使用該屬性,該屬性到底能發揮什麼作用, 就不歸該屬性資源文件管了,也就是說這個屬性資源文件是個公共的,大家都可以用,但是為了方便管理,一般都是一個自定義View裡的屬性寫成一個declare-styleable集合.屬性資源所定義的屬性到底可以返回什麼作用,取決於自定義組件的代碼實現
2.然後在布局中聲明我們的自定義View
一定要引入 xmlns:swipe="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.huaxun"我們的命名空間,後面的包路徑指的是項目的package,不然組件的屬性設置不了
更新: 對於自定義屬性資源,現在可以不使用http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/
延伸:
3.在View的構造方法中,獲得我們的自定義的屬性信息
TypedArray styled = getContext().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.SwipeListView,defStyle,0);
swipeMode = styled.getInt(R.styleable.SwipeListView_swipeMode, SWIPE_MODE_BOTH);
swipeOffsetLeft = styled.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.SwipeListView_swipeOffsetLeft, 0);
swipeOpenOnLongPress = styled.getBoolean(R.styleable.SwipeListView_swipeOpenOnLongPress, true);
swipeAnimationTime = styled.getInteger(R.styleable.SwipeListView_swipeAnimationTime, 0);
swipeFrontView = styled.getResourceId(R.styleable.SwipeListView_swipeFrontView, 0);
swipeBackView = styled.getResourceId(R.styleable.SwipeListView_swipeBackView, 0);
styled.recycle();
1)先來看看obtainStyledAttributes的四個參數的作用
obtainStyledAttributes這個方法最終調用的的是obtainStyledAttributes(AttributeSet set, int[] attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes);前兩個參數一目了然,來看看第三四個參數
先看第四個參數defStyleRes,其實是用於指定一個style,我們在style.xml裡面編寫
可以看到我們申明了一個style,然後我們修改剛才獲取屬性的代碼
TypedArray styled = getContext().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.SwipeListView,0,R.style.style_swipeListView);
在布局文件中不設置任何屬性
運行後可以看到,swipeOpenOnLongPress=true, swipeAnimationTime=3000, swipeOffsetLeft=278 //139dp
從結果可以明顯看出,如果我們不在布局中設置任何屬性,會從style中讀取相關屬性。
接著看第三個參數defStyleAttr,它是一個引用類型屬性,指向一個style,並且在當前Theme中進行設置,去style.xml裡面,找到我們使用的Theme,添加一條Item:
然後我們再次修改剛才獲取屬性的代碼
TypedArray styled = getContext().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,R.styleable.SwipeListView,R.attr.attrViewStyleRef,0);
運行後可以看到,swipeOpenOnLongPress=false, swipeAnimationTime=5000, swipeOffsetLeft=1776 //888dp
對於第三個參數,實際上用的還是比較多的,比如系統的Button,EditText,它們都會在構造函數指定第三個參數
Public Button(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs, com.android.intenel.R.attr.buttonStyle);}
提供一些參數樣式,比如background,textColor等,所以我們切換不同的主題,會發現控件的樣式會發生一些變化,就是因為不同的主題設置了不同的style。推演到我們自定義View,如果你的屬性非常多,你也可以提供默認style,然後讓用戶去設置到theme裡面即可。
只有defStyleAttr設置為0或者Theme中沒有找到相關屬性時,才會去defStyleRes中讀取,defStyleAttr的優先級更高。
2)構造函數中調用初始化代碼有兩種方式
第一種:
public GifImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
init();
}
public GifImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public GifImageView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
第二種:
public GifImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
init();
}
public GifImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public GifImageView(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
這兩種寫法有什麼區別呢?
二,繼承系統已有控件去實現自定義View,比如繼承Button,第一種方式會覆蓋Button默認在theme裡面的style(默認調用兩個參數的構造函數),相對來說第二種方式更合適。
3)獲取自定義屬性有兩種方式
第一種:
我們上面的寫法
第二種:
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CustomTitleView, defStyle, 0);
int n = a.getIndexCount();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int attr = a.getIndex(i);
switch (attr)
{
case R.styleable.CustomTitleView_titleText:
mTitleText = a.getString(attr);
break;
case R.styleable.CustomTitleView_titleTextColor:
mTitleTextColor = a.getColor(attr, Color.BLACK);
break;
case R.styleable.CustomTitleView_titleTextSize:
mTitleTextSize = a.getDimensionPixelSize(attr, 10);
break;
}
兩種寫法的區別:
第一種寫法,不管你有沒有在布局中使用該屬性,都會執行getXXX方法,第二種只有你布局中使用了該屬性才會執行getXXX
假設有以下場景:
private int attr_mode = 1; //默認為1 attr_mode = a.getInt(attr, 0);
可能你自定義屬性的默認值為1,然而你根本沒有在布局文件中設置這個屬性,這樣運行時它變成了0(而不是默認值),而第二種方法就不存在這個問題了。
還有個場景,假如你是繼承某個View,父類View已經對該成員變量進行了賦值,然後你這邊需要根據用戶的設置去更新這個值,第一種寫法如果用戶沒有設置,你可能就將父類的賦值給覆蓋了。
 服務Service的基本用法
服務Service的基本用法
作為 Android四大組件之一, 服務也少不了有很多非常重要的知識點,那自然要從最基本的用法開始學習了。定義一個服務:public class MyService ex
 android 使用gradle導出jar包,並包含assets資源文件夾
android 使用gradle導出jar包,並包含assets資源文件夾
今天咱們看看android studio的jar打包,但是jar包裡面呢res文件是用不了的,那想用圖片文件怎麼辦呢,這裡可以把圖片文件放進assets文件裡面打進jar
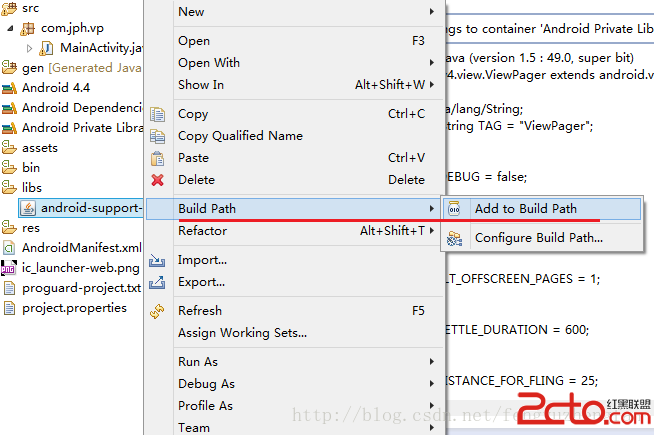 Android關聯源碼support-v4,v7,v13源碼
Android關聯源碼support-v4,v7,v13源碼
在Android實際開發過程中往往會遇到使用v4,v7或v13兼容包中的一些類如ViewPager,Fargment等,但卻無法關聯源碼。 網上有很多解決
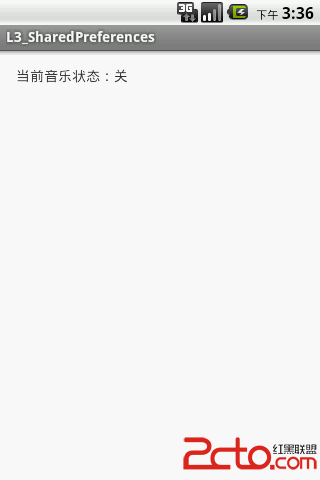 學習Android之SharedPreferences使用
學習Android之SharedPreferences使用
效果圖如下: package com.example.l3_sharedpreferences; import com.example.l3_sharedprefere