編輯:關於Android編程
多點觸控是指多個手指同時觸摸屏幕的情況。這節課主要學習如何檢測多點觸控手勢。
當多根手指同時觸碰到屏幕時,系統會產生以下觸摸事件:
ACTION_DOWN -第一個觸碰到屏幕的點。它是手勢的起始事件。這個觸控點的指針數據在MotionEvent對象中的索引總是0。 ACTION_POINTER_DOWN -除第一個觸控點之外的其它點。這個觸控點的指針數據的索引由getActionIndex()方法返回。 ACTION_MOVE -屏幕上的手指位置發生變化時。 ACTION_POINTER_UP -除最開始按下的其它觸控點離開屏幕時。 ACTION_UP -最後一個觸控點離開屏幕時。我們可以通過每一個觸控點對應的索或ID來追蹤MotionEvent對象中的每一個觸控點:
Index: MotionEvent對象將觸控點的相關信息存儲於一個數組中。每一個觸控點的索引則是這個觸控點在數組中的相對位置。MotionEvent對象的大多數方法都可以使用這些索引來與這些點產生交互。 ID: 每一個觸控點也含有一個ID映射,這個映射關系在手勢事件的整個生命周期內與相對應的觸控點一直保持相對關系。每個觸控點的出現順序是不固定的。因此,觸控點的索引可以由事件轉移到下一個索引,但是觸控點的ID始終保持為一個常量。使用getPointerId()方法可以獲得指定觸控點的ID,因此可以在余下的手勢事件中還可以繼續保持與這個觸控點的聯系。使用findPointerIndex()方法可以根據指定的ID獲得觸控點的索引:
private int mActivePointerId;
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
....
// Get the pointer ID
mActivePointerId = event.getPointerId(0);
// ... Many touch events later...
// Use the pointer ID to find the index of the active pointer
// and fetch its position
int pointerIndex = event.findPointerIndex(mActivePointerId);
// Get the pointer's current position
float x = event.getX(pointerIndex);
float y = event.getY(pointerIndex);
}
使用getActionMasked()方法可以獲取MotionEvent的活動。與getAction()方法不同,getActionMasked()適用於多個觸控點。它會返回正在執行的活動。你可以使用getActionIndex()方法獲得與之相關聯的觸控點的索引。下面的代碼演示了這個過程:
Note: 示例中使用了MotionEventCompat類。這個類位於支持庫中。你應該使用該類以便提供良好的向後兼容性。注意,MotionEventCompat類並不可以替代MotionEvent類。這個類提供了一個實用的靜態方法,可以將MotionEvent對象所關聯的活動提取出來。
int action = MotionEventCompat.getActionMasked(event);
// Get the index of the pointer associated with the action.
int index = MotionEventCompat.getActionIndex(event);
int xPos = -1;
int yPos = -1;
Log.d(DEBUG_TAG,"The action is " + actionToString(action));
if (event.getPointerCount() > 1) {
Log.d(DEBUG_TAG,"Multitouch event");
// The coordinates of the current screen contact, relative to
// the responding View or Activity.
xPos = (int)MotionEventCompat.getX(event, index);
yPos = (int)MotionEventCompat.getY(event, index);
} else {
// Single touch event
Log.d(DEBUG_TAG,"Single touch event");
xPos = (int)MotionEventCompat.getX(event, index);
yPos = (int)MotionEventCompat.getY(event, index);
}
...
// Given an action int, returns a string description
public static String actionToString(int action) {
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: return "Down";
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: return "Move";
case MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN: return "Pointer Down";
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: return "Up";
case MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_UP: return "Pointer Up";
case MotionEvent.ACTION_OUTSIDE: return "Outside";
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL: return "Cancel";
}
return "";
}
有關多點觸控的更多信息,可以參見課程Dragging and Scaling.
原文地址:http://android.xsoftlab.net/training/gestures/multi.html
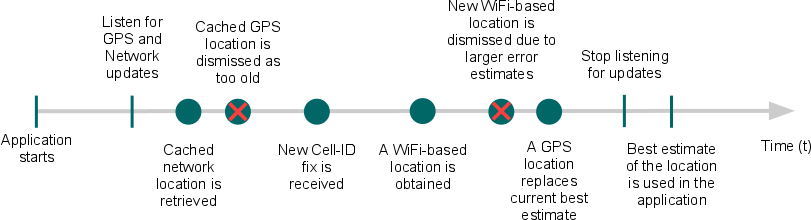 Android官方文檔之Location and Sensors APIs(上)
Android官方文檔之Location and Sensors APIs(上)
定位(Location) 和 傳感器(Sensors)API充分發揮了移動設備的優勢,您可以調用這些API,制作出交互性較高的應用程序,比如使用設備自帶的GPS模塊定位、
 [Android] 使用Include布局+Fragment滑動切換屏幕
[Android] 使用Include布局+Fragment滑動切換屏幕
前面的文章已經講述了隨手拍項目圖像處理的技術部分,該篇文章主要是主界面的布局及屏幕滑動切換,並結合鴻洋大神的視頻和郭神的第一行代碼(強推兩人Android博客),完成了下
 Android[安卓] 版Air Video 遠程播放電腦視頻
Android[安卓] 版Air Video 遠程播放電腦視頻
在蘋果的iOS下面,有個應用Air Video,可以在iOS下通過Wifi遠程直接播放電腦裡的視頻,而不需要把視頻復制到手機上再看。非常好用!最近用了Android的手
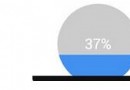 Android實現自定義圓形進度條
Android實現自定義圓形進度條
今天無意中發現一個圓形進度,想想自己實現一個,如下圖:基本思路是這樣的:1.首先繪制一個實心圓2.繪制一個白色實心的正方形,遮住實心圓3.在圓的中心動態繪制當前進度的百分