編輯:關於Android編程
}
例題
/*
定義一個數組,輸出該數組的名稱和數組元素值。
給數組元素賦值,再次輸出該數組的名稱和數組元素值。
*/
class ArrayDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定義一個數組
int[] arr = new int[3];
//輸出數組名稱
System.out.println(arr);
//輸出數組元素值
System.out.println(arr[0]);
System.out.println(arr[1]);
System.out.println(arr[2]);
System.out.println("----");
//給數組元素賦值
arr[0] = 100;
arr[2] = 200;
//輸出數組名稱
System.out.println(arr);
//輸出數組元素值
System.out.println(arr[0]);
System.out.println(arr[1]);
System.out.println(arr[2]);
}
}
/*
數組操作的兩個常見小問題:
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:數組索引越界異常
原因:你訪問了不存在的索引。
NullPointerException:空指針異常
原因:數組已經不在指向堆內存了。而你還用數組名去訪問元素。
作用:請自己把所有的場景Exception結尾的問題總結一下。以後遇到就記錄下來。
現象,原因,解決方案。
*/
class ArrayDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定義數組
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
//System.out.println(arr[3]);
//引用類型的常量:空常量 null
arr = null;
System.out.println(arr[0]);
}
}
/*
數組的靜態初始化:
格式:數據類型[] 數組名 = new 數據類型[]{元素1,元素2,…};
簡化格式:
數據類型[] 數組名 = {元素1,元素2,…};
舉例:
int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,3};
簡化後:
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
注意事項:
不要同時動態和靜態進行。
如下格式:
int[] arr = new int[3]{1,2,3}; //錯誤
*/
class ArrayDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定義數組
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
System.out.println(arr);
System.out.println(arr[0]);
System.out.println(arr[1]);
System.out.println(arr[2]);
}
}
/*
數組獲取最值(獲取數組中的最大值最小值)
分析:
A:定義一個數組,並對數組的元素進行靜態初始化。
B:從數組中任意的找一個元素作為參照物(一般取第一個),默認它就是最大值。
C:然後遍歷其他的元素,依次獲取和參照物進行比較,如果大就留下來,如果小,就離開。
D:最後參照物裡面保存的就是最大值。
*/
class ArrayTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定義一個數組
int[] arr = {34,98,10,25,67};
//請獲取數組中的最大值
/*
//從數組中任意的找一個元素作為參照物
int max = arr[0];
//然後遍歷其他的元素
for(int x=1; x //依次獲取和參照物進行比較,如果大就留下來,如果小,就離開。
if(arr[x] > max) {
max = arr[x];
}
}
//最後參照物裡面保存的就是最大值。
System.out.println("max:"+max);
*/
//把這個代碼用方法改進
//調用方法
int max = getMax(arr);
System.out.println("max:"+max);
//請獲取數組中的最小值
int min = getMin(arr);
System.out.println("min:"+min);
}
/*
需求:獲取數組中的最大值
兩個明確:
返回值類型:int
參數列表:int[] arr
*/
public static int getMax(int[] arr) {
//從數組中任意的找一個元素作為參照物
int max = arr[0];
//然後遍歷其他的元素
for(int x=1; x //依次獲取和參照物進行比較,如果大就留下來,如果小,就離開。
if(arr[x] > max) {
max = arr[x];
}
}
//最後參照物裡面保存的就是最大值。
return max;
}
public static int getMin(int[] arr) {
//從數組中任意的找一個元素作為參照物
int min = arr[0];
//然後遍歷其他的元素
for(int x=1; x //依次獲取和參照物進行比較,如果小就留下來,如果大,就離開。
if(arr[x] < min) {
min = arr[x];
}
}
//最後參照物裡面保存的就是最小值。
return min;
}
}
/*
數組元素逆序 (就是把元素對調)
分析:
A:定義一個數組,並進行靜態初始化。
B:思路
把0索引和arr.length-1的數據交換
把1索引和arr.length-2的數據交換
...
只要做到arr.length/2的時候即可。
*/
class ArrayTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定義一個數組,並進行靜態初始化。
int[] arr = {12,98,50,34,76};
//逆序前
System.out.println("逆序前:");
printArray(arr);
//逆序後
System.out.println("逆序後:");
//reverse(arr);
reverse2(arr);
printArray(arr);
}
/*
需求:數組逆序
兩個明確:
返回值類型:void (有人會想到應該返回的是逆序後的數組,但是沒必要,因為這兩個數組其實是同一個數組)
參數列表:int[] arr
*/
public static void reverse(int[] arr) {
/*
//第一次交換
int temp = arr[0];
arr[0] = arr[arr.length-1-0];
arr[arr.length-1-0] = temp;
//第二次交換
int temp = arr[1];
arr[1] = arr[arr.length-1-1];
arr[arr.length-1-1] = temp;
//第三次交換
int temp = arr[2];
arr[2] = arr[arr.length-1-2];
arr[arr.length-1-2] = temp;
*/
//用循環改進
for(int x=0; x int temp = arr[x];
arr[x] = arr[arr.length-1-x];
arr[arr.length-1-x] = temp;
}
}
public static void reverse2(int[] arr) {
for(int start=0,end=arr.length-1; start<=end; start++,end--) {
int temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
}
}
//遍歷數組
public static void printArray(int[] arr) {
System.out.print("[");
for(int x=0; x if(x == arr.length-1) { //這是最後一個元素
System.out.println(arr[x]+"]");
}else {
System.out.print(arr[x]+", ");
}
}
}
}
/*
數組查表法(根據鍵盤錄入索引,查找對應星期)
意思是:String[] strArray = {"星期一","星期二",...};
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
class ArrayTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定義一個字符串數組
String[] strArray = {"星期一","星期二","星期三","星期四","星期五","星期六","星期日"};
//創建鍵盤錄入對象
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("請輸入一個數據(0-6):");
int index = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("你要查找的日期是:"+strArray[index]);
}
}
/*
需求:數組元素查找(查找指定元素第一次在數組中出現的索引)
分析:
A:定義一個數組,並靜態初始化。
B:寫一個功能實現
遍歷數組,依次獲取數組中的每一個元素,和已知的數據進行比較
如果相等,就返回當前的索引值。
*/
class ArrayTest5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定義一個數組,並靜態初始化
int[] arr = {200,250,38,888,444};
//需求:我要查找250在這個數組中第一次出現的索引
int index = getIndex(arr,250);
System.out.println("250在數組中第一次出現的索引是:"+index);
int index2 = getIndex2(arr,250);
System.out.println("250在數組中第一次出現的索引是:"+index2);
int index3 = getIndex2(arr,2500);
System.out.println("2500在數組中第一次出現的索引是:"+index3);
}
/*
需求:查找指定數據在數組中第一次出現的索引
兩個明確:
返回值類型:int
參數列表:int[] arr,int value
*/
public static int getIndex(int[] arr,int value) {
//遍歷數組,依次獲取數組中的每一個元素,和已知的數據進行比較
for(int x=0; x if(arr[x] == value) {
//如果相等,就返回當前的索引值。
return x;
}
}
//目前的代碼有一個小問題
//就是假如我要查找的數據在數組中不存在,那就找不到,找不到,你就對應的返回嗎?
//所以報錯。
//只要是判斷,就可能是false,所以大家要細心。
//如果找不到數據,我們一般返回一個負數即可,而且是返回-1
return -1;
}
public static int getIndex2(int[] arr,int value) {
//定義一個索引
int index = -1;
//有就修改索引值
for(int x=0; x if(arr[x] == value) {
index = x;
break;
}
}
//返回index
return index;
}
}
 Android 源碼解析View的touch事件分發機制
Android 源碼解析View的touch事件分發機制
概述本篇主要分析的是touch事件的分發機制,網上關於這個知識點的分析文章非常多。但是還是想通過結合自身的總結,來加深自己的理解。對於事件分發機制,我將使用兩篇文章對其進
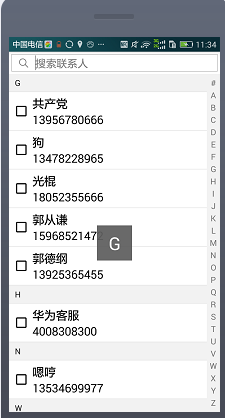 android通訊錄搜索,通過輸入框搜索以及側邊litview的滾動搜索,還有單選,全選以及反選的功能
android通訊錄搜索,通過輸入框搜索以及側邊litview的滾動搜索,還有單選,全選以及反選的功能
由於項目需要做一個仿通訊錄搜索聯系人的功能,並且需要選中聯系人,即推薦好友的功能。所以就想寫一遍blog來介紹它是怎麼實現,以及是怎麼用的。好的,接下來,讓我為大家講解一
 【騰訊TMQ】5小時搞定谷歌原生自動化框架UiAutomator1.0
【騰訊TMQ】5小時搞定谷歌原生自動化框架UiAutomator1.0
前言谷歌對UI測試(UI Tetsting)的概念是:確保用戶在一系列操作過程中(例如鍵盤輸入、點擊菜單、彈出對話框、圖像顯示以及其他UI控件的改變),你的應用程序做出正
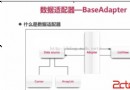 BaseAdapter的使用(筆記)
BaseAdapter的使用(筆記)
適配器模式的應用: 1.降低程序耦合性2.容易擴展 BaseAdapterListView的顯示與緩存機制:需要才顯示,顯示完