編輯:關於Android編程
在Android系統中,有兩種操作會引發Activity的啟動,一種用戶點擊應用程序圖標時,Launcher會為我們啟動應用程序的主Activity;應用程序的默認Activity啟動起來後,它又可以在內部通過調用startActvity接口啟動新的Activity,依此類推,每一個Activity都可以在內部啟動新的Activity。通過這種連鎖反應,按需啟動Activity,從而完成應用程序的功能。
本文主要講點擊應用圖標,啟動應用程序的過程。
在手機屏幕中點擊應用程序圖標的情景就會引發Android應用程序中的默認Activity的啟動,從而把應用程序啟動起來。這種啟動方式的特點是會啟動一個新的進程來加載相應的Activity。這裡,我們以這個例子為例來說明Android應用程序的啟動過程,即MainActivity的啟動過程。
1、Launcher.startActivitySafely
Launcher,也就是Android系統的桌面應用程序。我們自己安裝的應用的圖標會在Launcher上顯示,當點擊應用圖標時,會出發Launcher.startActivitySafely方法的執行。
源碼如下:
public void onClick(View v) {
Object tag = v.getTag();
if (tag instanceof ShortcutInfo) {
// Open shortcut
final Intent intent = ((ShortcutInfo) tag).intent;
int[] pos = new int[2];
v.getLocationOnScreen(pos);
intent.setSourceBounds(new Rect(pos[0], pos[1],
pos[0] + v.getWidth(), pos[1] + v.getHeight()));
startActivitySafely(intent, tag);
} else if (tag instanceof FolderInfo) {
handleFolderClick((FolderInfo) tag);
} else if (v == mHandleView) {
if (isAllAppsVisible()) {
closeAllApps(true);
} else {
showAllApps(true);
}
}
}
void startActivitySafely(Intent intent, Object tag) {
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
try {
startActivity(intent);
} catch (ActivityNotFoundException e) {
Toast.makeText(this, R.string.activity_not_found, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
Log.e(TAG, "Unable to launch. tag=" + tag + " intent=" + intent, e);
} catch (SecurityException e) {
Toast.makeText(this, R.string.activity_not_found, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
Log.e(TAG, "Launcher does not have the permission to launch " + intent +
". Make sure to create a MAIN intent-filter for the corresponding activity " +
"or use the exported attribute for this activity. "
+ "tag="+ tag + " intent=" + intent, e);
}
}
接著startActivitySafely又調用Activity的startActivity方法,並且傳入參數intent,添加FLAG,FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK。然後轉入Activity的startActivity方法。
這裡的intent包含的信息為:action = "android.intent.action.Main",category="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER", cmp="shy.luo.activity/.MainActivity",表示它要啟動的Activity為shy.luo.activity.MainActivity。Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK表示要在一個新的Task中啟動這個Activity,注意,Task是Android系統中的概念,它不同於進程Process的概念。簡單地說,一個Task是一系列Activity的集合,這個集合是以堆棧的形式來組織的,遵循後進先出的原則。
稍微擴展一下:
我們知道,一個應用程序可以有多個Activity,每個Activity是同級別的。那麼在啟動程序時,最先啟動哪個Activity呢?有些程序可能需要顯示在程 序列表裡,有些不需要。怎麼定義呢?android.intent.action.MAIN決定應用程序最先啟動的Activity ,android.intent.category.LAUNCHER決定應用程序是否顯示在程序列表裡。Main和LAUNCHER同時設定才有意義,如果有多個同級的Activity都有過濾器
則只有最前面的Activity的 有 效,啟動該程序時,執行的是該Activity。且在程序列表中有多個圖標,這些Activity都在程序列表中顯示,該Application有多個入 口,執行不同的Activity,但是整個程序的主入口(整個程序最先運行的那個activity)只有最先定義的那個Activity。
如 果一個應用沒有LAUNCHER則該apk仍能安裝到設備上,但是在主程序圖中看不到。如果給那個Activity 設定了LAUNCHER,且同時設定了Main,則這個Activity就可出現在程序圖中;如果沒有Main,則不知啟動哪個Activity,故也不 會有圖標出現。
2、Activity.startActivity
Launcher繼承於Activity類,而Activity類實現了startActivity函數,因此,這裡就調用了Activity.startActivity方法
@Override
public void startActivity(Intent intent) {
this.startActivity(intent, null);
}
@Override
public void startActivity(Intent intent, @Nullable Bundle options) {
if (options != null) {
startActivityForResult(intent, -1, options);
} else {
// Note we want to go through this call for compatibility with
// applications that may have overridden the method.
startActivityForResult(intent, -1);
}
}
3. Activity.startActivityForResult
if (mParent == null) {
Instrumentation.ActivityResult ar =
mInstrumentation.execStartActivity(
this, mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mToken, this,
intent, requestCode, options);
if (ar != null) {
mMainThread.sendActivityResult(
mToken, mEmbeddedID, requestCode, ar.getResultCode(),
ar.getResultData());
}
if (requestCode >= 0) {
mStartedActivity = true;
}
cancelInputsAndStartExitTransition(options);
} else {
if (options != null) {
mParent.startActivityFromChild(this, intent, requestCode, options);
} else {
mParent.startActivityFromChild(this, intent, requestCode);
}
}
}
這裡我們需注意的是,這裡的mMainThread代表的是Launcher應用程序運行的進程。
這裡的mToken也是Activity類的成員變量,它是一個Binder對象的遠程接口。
4. Instrumentation.execStartActivity
public ActivityResult execStartActivity(
Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target,
Intent intent, int requestCode, Bundle options) {
IApplicationThread whoThread = (IApplicationThread) contextThread;
Uri referrer = target != null ? target.onProvideReferrer() : null;
if (referrer != null) {
intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_REFERRER, referrer);
}
if (mActivityMonitors != null) {
synchronized (mSync) {
final int N = mActivityMonitors.size();
for (int i=0; i= 0 ? am.getResult() : null;
}
break;
}
}
}
}
try {
intent.migrateExtraStreamToClipData();
intent.prepareToLeaveProcess();
int result = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()
.startActivity(whoThread, who.getBasePackageName(), intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()),
token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null,
requestCode, 0, null, options);
checkStartActivityResult(result, intent);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failure from system", e);
}
return null;
}
5. ActivityManagerProxy.startActivity
ActivityManagerProxy是ActivityManagerNative中的一個內部類。startActivity方法源碼如下。
public int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage, Intent intent,
String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle options) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(caller != null ? caller.asBinder() : null);
data.writeString(callingPackage);
intent.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeString(resolvedType);
data.writeStrongBinder(resultTo);
data.writeString(resultWho);
data.writeInt(requestCode);
data.writeInt(startFlags);
if (profilerInfo != null) {
data.writeInt(1);
profilerInfo.writeToParcel(data, Parcelable.PARCELABLE_WRITE_RETURN_VALUE);
} else {
data.writeInt(0);
}
if (options != null) {
data.writeInt(1);
options.writeToParcel(data, 0);
} else {
data.writeInt(0);
}
mRemote.transact(START_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
int result = reply.readInt();
reply.recycle();
data.recycle();
return result;
}
這裡的參數比較多,我們先整理一下。從上面的調用可以知道,這裡的參數resolvedType、grantedUriPermissions和resultWho均為null;參數caller為ApplicationThread類型的Binder實體;參數resultTo為一個Binder實體的遠程接口,我們先不關注它;參數grantedMode為0,我們也先不關注它;參數requestCode為-1;參數onlyIfNeeded和debug均空false。
由於ActivityManagerProxy是一個代理類,上面是通過IPC的Binder聯系到ActivityManagerService,最後會調用
ActivityManagerService的startActivity方法。
6. ActivityManagerService.startActivity
startActivity又調用了startActivityAsUser方法。
源碼如下
@Override
public final int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle options) {
return startActivityAsUser(caller, callingPackage, intent, resolvedType, resultTo,
resultWho, requestCode, startFlags, profilerInfo, options,
UserHandle.getCallingUserId());
}
@Override
public final int startActivityAsUser(IApplicationThread caller, String callingPackage,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int startFlags, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle options, int userId) {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startActivity");
userId = handleIncomingUser(Binder.getCallingPid(), Binder.getCallingUid(), userId,
false, ALLOW_FULL_ONLY, "startActivity", null);
// TODO: Switch to user app stacks here.
return mStackSupervisor.startActivityMayWait(caller, -1, callingPackage, intent,
resolvedType, null, null, resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, startFlags,
profilerInfo, null, null, options, false, userId, null, null);
}
7.ActivityStackSupervisor.startActivityMayWait
這個方法代碼比較長,這裡摘抄主要部分代碼
final int startActivityMayWait(IApplicationThread caller, int callingUid,
String callingPackage, Intent intent, String resolvedType,
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, int startFlags,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, WaitResult outResult, Configuration config,
Bundle options, boolean ignoreTargetSecurity, int userId,
IActivityContainer iContainer, TaskRecord inTask) {
.................................
ActivityInfo aInfo =
resolveActivity(intent, resolvedType, startFlags, profilerInfo, userId);
....................................................
int res = startActivityLocked(caller, intent, resolvedType, aInfo,
voiceSession, voiceInteractor, resultTo, resultWho,
requestCode, callingPid, callingUid, callingPackage,
realCallingPid, realCallingUid, startFlags, options, ignoreTargetSecurity,
componentSpecified, null, container, inTask);
...........................................
return res;
}
省略無關代碼。
ActivityInfo resolveActivity(Intent intent, String resolvedType, int startFlags,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, int userId) {
ActivityInfo aInfo;
try {
ResolveInfo rInfo =
AppGlobals.getPackageManager().resolveIntent(
intent, resolvedType,
PackageManager.MATCH_DEFAULT_ONLY
| ActivityManagerService.STOCK_PM_FLAGS, userId);
aInfo = rInfo != null ? rInfo.activityInfo : null;
}
......................................
return aInfo;
}
然後又調用了startActivityLocked方法
8.ActivityStackSupervisor.startActivityLocked
這個方法200多行,截取主要部分代碼
final int startActivityLocked(IApplicationThread caller,
Intent intent, String resolvedType, ActivityInfo aInfo,
IVoiceInteractionSession voiceSession, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode,
int callingPid, int callingUid, String callingPackage,
int realCallingPid, int realCallingUid, int startFlags, Bundle options,
boolean ignoreTargetSecurity, boolean componentSpecified, ActivityRecord[] outActivity,
ActivityContainer container, TaskRecord inTask) {
int err = ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS;
ProcessRecord callerApp = null;
if (caller != null) {
callerApp = mService.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
if (callerApp != null) {
callingPid = callerApp.pid;
callingUid = callerApp.info.uid;
} else {
.........................
}
}
...........................................
ActivityRecord sourceRecord = null;
ActivityRecord resultRecord = null;
if (resultTo != null) {
sourceRecord = isInAnyStackLocked(resultTo);
if (DEBUG_RESULTS) Slog.v(TAG_RESULTS,
"Will send result to " + resultTo + " " + sourceRecord);
if (sourceRecord != null) {
if (requestCode >= 0 && !sourceRecord.finishing) {
resultRecord = sourceRecord;
}
}
}
final int launchFlags = intent.getFlags();
if ((launchFlags & Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_FORWARD_RESULT) != 0 && sourceRecord != null) {
// Transfer the result target from the source activity to the new
// one being started, including any failures.
if (requestCode >= 0) {
ActivityOptions.abort(options);
return ActivityManager.START_FORWARD_AND_REQUEST_CONFLICT;
..................................
}
}
if (err == ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS && intent.getComponent() == null) {
.................
}
if (err == ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS && aInfo == null) {
................
}
if (err == ActivityManager.START_SUCCESS
.................
}
...........................................
ActivityRecord r = new ActivityRecord(mService, callerApp, callingUid, callingPackage,
intent, resolvedType, aInfo, mService.mConfiguration, resultRecord, resultWho,
requestCode, componentSpecified, voiceSession != null, this, container, options);
....................................
err = startActivityUncheckedLocked(r, sourceRecord, voiceSession, voiceInteractor, startFlags, true, options, inTask);
從傳進來的參數caller得到調用者的進程信息,並保存在callerApp變量中,這裡就是Launcher應用程序的進程信息了。前面說過,參數resultTo是Launcher這個Activity裡面的一個Binder對象,通過它可以獲得Launcher這個Activity的相關信息,保存在sourceRecord變量中。
再接下來,創建即將要啟動的Activity的相關信息,並保存在r變量中:
ActivityRecord r = new ActivityRecord(mService, callerApp, callingUid, callingPackage,
intent, resolvedType, aInfo, mService.mConfiguration, resultRecord, resultWho,
requestCode, componentSpecified, voiceSession != null, this, container, options);
9.ActivityStackSupervisor.startActivityUncheckedLocked
這個方法主要用於
1、創建Acitivity棧,根據Activity的啟動模式,由於是點擊圖標進來的,一開始也設置了標志位Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK,所以會新創建一個Activity棧。如果之前已經有棧,且不是singleinstance,就不會再創建新的棧,會將待啟動的Activity添加到原來的棧中。
這個方法又會調用ActivityStack.resumeTopActivitiesLocked
10.ActivityStack.resumeTopActivitiesLocked
final boolean resumeTopActivityLocked(ActivityRecord prev, Bundle options) {
if (mStackSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity) {
// Don't even start recursing.
return false;
}
boolean result = false;
try {
// Protect against recursion.
mStackSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity = true;
if (mService.mLockScreenShown == ActivityManagerService.LOCK_SCREEN_LEAVING) {
mService.mLockScreenShown = ActivityManagerService.LOCK_SCREEN_HIDDEN;
mService.updateSleepIfNeededLocked();
}
result = resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(prev, options);
} finally {
mStackSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity = false;
}
return result;
}
11.ActivityStackSupervisor.resumeTopActivityInnerLocked
private boolean resumeTopActivityInnerLocked(ActivityRecord prev, Bundle options) {
.................................
if (mResumedActivity != null) {
if (DEBUG_STATES) Slog.d(TAG_STATES,
"resumeTopActivityLocked: Pausing " + mResumedActivity);
pausing |= startPausingLocked(userLeaving, false, true, dontWaitForPause);
}
...............................
mStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked(next, true, true);
........................
return true;
}
1)調用startPausingLocked方法,最終會通過ActivityManagerService通過Binder進程間通信機制通知Launcher進入Paused狀態;如果是通過其他Activity啟動的。會將其他Activity進入Paused狀態。由於這裡是Launcher發起的startActivity,所以Launcher進入Paused狀態。
2)調用了ActivityStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked方法。
12.ActivityStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked
void startSpecificActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r,
boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) {
// Is this activity's application already running?
ProcessRecord app = mService.getProcessRecordLocked(r.processName,
r.info.applicationInfo.uid, true);
r.task.stack.setLaunchTime(r);
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
if ((r.info.flags&ActivityInfo.FLAG_MULTIPROCESS) == 0
|| !"android".equals(r.info.packageName)) {
// Don't add this if it is a platform component that is marked
// to run in multiple processes, because this is actually
// part of the framework so doesn't make sense to track as a
// separate apk in the process.
app.addPackage(r.info.packageName, r.info.applicationInfo.versionCode,
mService.mProcessStats);
}
realStartActivityLocked(r, app, andResume, checkConfig);
return;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting activity "
+ r.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e);
}
// If a dead object exception was thrown -- fall through to
// restart the application.
}
mService.startProcessLocked(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo, true, 0,
"activity", r.intent.getComponent(), false, false, true);
}
在上述方法中有一句代碼:
ProcessRecord app = mService.getProcessRecordLocked(r.processName,
r.info.applicationInfo.uid, true);
注意,這裡由於是第一次啟動應用程序的Activity,取回來的app為null。在Activity應用程序中的AndroidManifest.xml配置文件中,我們沒有指定Application標簽的process屬性,系統就會默認使用package的名稱。每一個應用程序都有自己的uid,因此,這裡uid + process的組合就可以為每一個應用程序創建一個ProcessRecord。
所以下面if (app != null && app.thread != null)條件不成立,那麼條件裡面realStartActivityLocked 方法就不會執行,而是執行ActivityManagerService.startProcessLocked函數進行下一步操作。
13. ActivityManagerService.startProcessLocked
源碼大致如下
final ProcessRecord startProcessLocked(String processName, ApplicationInfo info,
boolean knownToBeDead, int intentFlags, String hostingType, ComponentName hostingName,
boolean allowWhileBooting, boolean isolated, int isolatedUid, boolean keepIfLarge,
String abiOverride, String entryPoint, String[] entryPointArgs, Runnable crashHandler) {
.............................
app = getProcessRecordLocked(processName, info.uid, keepIfLarge);
...................
String hostingNameStr = hostingName != null
? hostingName.flattenToShortString() : null;
if (app == null) {
checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: creating new process record");
// 創建一個新的ProcessRecord
app = newProcessRecordLocked(info, processName, isolated, isolatedUid);
if (app == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failed making new process record for "
+ processName + "/" + info.uid + " isolated=" + isolated);
return null;
}
app.crashHandler = crashHandler;
checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: done creating new process record");
} else {
............................
}
...............................
startProcessLocked(
app, hostingType, hostingNameStr, abiOverride, entryPoint, entryPointArgs);
........
return (app.pid != 0) ? app : null;
}
首先調用getProcessRecordLocked,但是返回的app為null,所以下面這一句就會執行。
app = newProcessRecordLocked(info, processName, isolated, isolatedUid);
mProcessNames.put(proc.processName, proc.uid, proc);
這時候mProcessNames這個全局變量就有數據了,再調用getProcessRecordLocked,返回的就不是null了。
接著,ActivityManagerService.startProcessLocked方法會執行另一個無返回值的startProcessLocked方法。
大致代碼如下
private final void startProcessLocked(ProcessRecord app, String hostingType,
String hostingNameStr, String abiOverride, String entryPoint, String[] entryPointArgs) {
.............................
try {
checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: getting gids from package manager");
final IPackageManager pm = AppGlobals.getPackageManager();
permGids = pm.getPackageGids(app.info.packageName, app.userId);
MountServiceInternal mountServiceInternal = LocalServices.getService(
MountServiceInternal.class);
mountExternal = mountServiceInternal.getExternalStorageMountMode(uid,
app.info.packageName);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowAsRuntimeException();
}
.....................................
entryPoint = "android.app.ActivityThread"
Process.ProcessStartResult startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, app.info.seinfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, entryPointArgs);
.......................
}
public static final ProcessStartResult start(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
int uid, int gid, int[] gids,
int debugFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
String seInfo,
String abi,
String instructionSet,
String appDataDir,
String[] zygoteArgs) {
try {
return startViaZygote(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
debugFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo,
abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, zygoteArgs);
} catch (ZygoteStartFailedEx ex) {
Log.e(LOG_TAG,
"Starting VM process through Zygote failed");
throw new RuntimeException(
"Starting VM process through Zygote failed", ex);
}
}
start方法又調用了startViaZygote方法,該方法的注釋為
Starts a new process via the zygote mechanism.會通過zygote機制開啟一個新的進程。由於我們導入的類名是android.app.ActivityThread,開啟一個ActivityThread進程,這也是為什麼一個應用程序只有一個ActivityThread,然後會執行他的main方法。
14.ActivityThread.main
這個方法就比較熟悉了,創建ActivityThread。構建消息循環系統。
public static void main(String[] args) {
.........................
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
......................
Looper.loop();
}
private void attach(boolean system) {
.........
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
try {
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
..................
}
其中mAppThread是ApplicationThread,是一個Binder對象,用於ActivityManagerService與ActivityThread通信。
15.ActivityManagerService.attachApplication
@Override
public final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread) {
synchronized (this) {
int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
可以看出邏輯轉向了attachApplicationLocked方法。
16.ActivityManagerService.attachApplicationLocked
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,
int pid) {
ProcessRecord app;
if (pid != MY_PID && pid >= 0) {
synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {
app = mPidsSelfLocked.get(pid);
}
} else {
app = null;
}
.................................
final String processName = app.processName;
try {
AppDeathRecipient adr = new AppDeathRecipient(
app, pid, thread);
thread.asBinder().linkToDeath(adr, 0);
app.deathRecipient = adr;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
app.resetPackageList(mProcessStats);
startProcessLocked(app, "link fail", processName);
return false;
}
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_PROC_BOUND, app.userId, app.pid, app.processName);
app.makeActive(thread, mProcessStats);
app.curAdj = app.setAdj = -100;
app.curSchedGroup = app.setSchedGroup = Process.THREAD_GROUP_DEFAULT;
app.forcingToForeground = null;
updateProcessForegroundLocked(app, false, false);
app.hasShownUi = false;
app.debugging = false;
app.cached = false;
app.killedByAm = false;
mHandler.removeMessages(PROC_START_TIMEOUT_MSG, app);
boolean normalMode = mProcessesReady || isAllowedWhileBooting(app.info);
..............
boolean badApp = false;
boolean didSomething = false;
// See if the top visible activity is waiting to run in this process...
if (normalMode) {
try {
if (mStackSupervisor.attachApplicationLocked(app)) {
didSomething = true;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown launching activities in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
}
..............................
return true;
}
boolean attachApplicationLocked(ProcessRecord app) throws RemoteException {
final String processName = app.processName;
boolean didSomething = false;
for (int displayNdx = mActivityDisplays.size() - 1; displayNdx >= 0; --displayNdx) {
ArrayList stacks = mActivityDisplays.valueAt(displayNdx).mStacks;
for (int stackNdx = stacks.size() - 1; stackNdx >= 0; --stackNdx) {
final ActivityStack stack = stacks.get(stackNdx);
if (!isFrontStack(stack)) {
continue;
}
ActivityRecord hr = stack.topRunningActivityLocked(null);
if (hr != null) {
if (hr.app == null && app.uid == hr.info.applicationInfo.uid
&& processName.equals(hr.processName)) {
try {
if (realStartActivityLocked(hr, app, true, true)) {
didSomething = true;
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception in new application when starting activity "
+ hr.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e);
throw e;
}
}
}
}
}
if (!didSomething) {
ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(null, 0);
}
return didSomething;
}
17.ActivityManagerService.realStartActivityLocked
該方法中有下面一句:
final boolean realStartActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig)
throws RemoteException {
.....................
app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity(new Intent(r.intent), r.appToken,
System.identityHashCode(r), r.info, new Configuration(mService.mConfiguration),
new Configuration(stack.mOverrideConfig), r.compat, r.launchedFromPackage,
task.voiceInteractor, app.repProcState, r.icicle, r.persistentState, results,
newIntents, !andResume, mService.isNextTransitionForward(), profilerInfo);
..........................
return true;
}
app.thread是是ApplicationThreadProxy對象,是一個代理對象,代理就是ApplicationThread,情況完全類似於ActivityManagerProxy代理類。所以邏輯轉向了ApplicationThread的scheduleLaunchActivity方法。
18.ApplicationThread.scheduleLaunchActivity
@Override public final void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident, ActivityInfo info, Configuration curConfig, Configuration overrideConfig, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor, int procState, Bundle state, PersistableBundle persistentState, ListpendingResults, List pendingNewIntents, boolean notResumed, boolean isForward, ProfilerInfo profilerInfo) { updateProcessState(procState, false); ActivityClientRecord r = new ActivityClientRecord(); r.token = token; r.ident = ident; r.intent = intent; r.referrer = referrer; r.voiceInteractor = voiceInteractor; r.activityInfo = info; r.compatInfo = compatInfo; r.state = state; r.persistentState = persistentState; r.pendingResults = pendingResults; r.pendingIntents = pendingNewIntents; r.startsNotResumed = notResumed; r.isForward = isForward; r.profilerInfo = profilerInfo; r.overrideConfig = overrideConfig; updatePendingConfiguration(curConfig); sendMessage(H.LAUNCH_ACTIVITY, r); }
函數首先創建一個ActivityClientRecord實例,並且初始化它的成員變量,然後發送一個啟動Activity的消息交給Handler處理,這個Handler有著一個很簡潔的名字:H,然後看一下H對消息的處理,H定義ActivityThrad類中。
19. H.handleMessage
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(TAG, ">>> handling: " + codeToString(msg.what));
switch (msg.what) {
case LAUNCH_ACTIVITY: {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityStart");
final ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord) msg.obj;
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
r.activityInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo);
handleLaunchActivity(r, null);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
} break;
...................................
}
20.ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity
private final void handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
......
Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);
if (a != null) {
r.createdConfig = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
Bundle oldState = r.state;
handleResumeActivity(r.token, false, r.isForward);
......
} else {
......
}
}
從上面的源碼可以看出,performLaunchActivity最終完成了Activity對象的創建和啟動過程,並且Activity通過handleResumeActivity方法來調用被啟動Activity的onResume這一生命周期方法。而onCreate這個這個生命周期方法在performLaunchActivity方法中被回調。
21.ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity
這個方法主要完成了如下幾件事
1)從ActivityClientRecord中獲取待啟動的Activity的組件信息。
ActivityInfo aInfo = r.activityInfo;
if (r.packageInfo == null) {
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfo(aInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo,
Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE);
}
ComponentName component = r.intent.getComponent();
if (component == null) {
component = r.intent.resolveActivity(
mInitialApplication.getPackageManager());
r.intent.setComponent(component);
}
if (r.activityInfo.targetActivity != null) {
component = new ComponentName(r.activityInfo.packageName,
r.activityInfo.targetActivity);
}
2)、通過Instrumenttation的newActivity方法使用類加載器創建Activity對象。
Activity activity = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = r.packageInfo.getClassLoader();
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
StrictMode.incrementExpectedActivityCount(activity.getClass());
r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
r.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
if (r.state != null) {
r.state.setClassLoader(cl);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
3)、通過LoadeApk的makeApplication方法來嘗試創建Application對象
Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
public Application makeApplication(boolean forceDefaultAppClass,
Instrumentation instrumentation) {
if (mApplication != null) {
return mApplication;
}
Application app = null;
String appClass = mApplicationInfo.className;
if (forceDefaultAppClass || (appClass == null)) {
appClass = "android.app.Application";
}
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader();
if (!mPackageName.equals("android")) {
initializeJavaContextClassLoader();
}
ContextImpl appContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(mActivityThread, this);
app = mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.newApplication(
cl, appClass, appContext);
appContext.setOuterContext(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate application " + appClass
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
mActivityThread.mAllApplications.add(app);
mApplication = app;
if (instrumentation != null) {
try {
instrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!instrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to create application " + app.getClass().getName()
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
// Rewrite the R 'constants' for all library apks.
SparseArray packageIdentifiers = getAssets(mActivityThread)
.getAssignedPackageIdentifiers();
final int N = packageIdentifiers.size();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
final int id = packageIdentifiers.keyAt(i);
if (id == 0x01 || id == 0x7f) {
continue;
}
rewriteRValues(getClassLoader(), packageIdentifiers.valueAt(i), id);
}
return app;
}
從makeApplication方法可以看出,通過mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.newApplication創建Application對象,然後通過callApplicationOnCreate方法間接回調onCreate方法。
4)、創建ContextImpl對象並通過Activity的attach方法來完成一些重要數據的初始化
Context appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r, activity);
CharSequence title = r.activityInfo.loadLabel(appContext.getPackageManager());
Configuration config = new Configuration(mCompatConfiguration);
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Launching activity "
+ r.activityInfo.name + " with config " + config);
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config,
r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor);
ContextImpl是一個很重要的數據結構,它是Context的具體實現,Context中的大部分邏輯都是由ContextImpl來完成的。ContextImpl是通過Activity的attach方法來和Activity建立鏈接的,處理之外,在attach方法中Activity還會完成Window的創建並建立自己和Window的關聯,這樣當Window接受到外部輸入事件後就可以將時間傳遞給Activity。
5)、調用Activity的onCreate
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState);
 Android - ToDoList(定制ArrayAdapter)
Android - ToDoList(定制ArrayAdapter)
ToDoList(定制ArrayAdapter) 本文地址: http://blog.csdn.net/caroline_wendy/article/details/
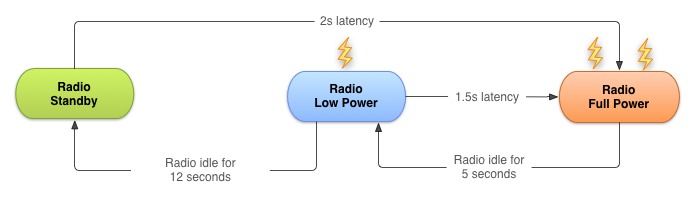 用android的GCM 網絡管理來優化電池使用時間
用android的GCM 網絡管理來優化電池使用時間
?GCM網絡管理器能讓app注冊能執行面向網絡的服務,每個任務只是完成一個工作。它的API能處理這些任務,允許Google Play Services通過系統集中處理這些
 nexus7一鍵刷安卓android L教程
nexus7一鍵刷安卓android L教程
nexus7一鍵刷安卓android L教程,谷歌之子,大家都知道他吧。現在小編給大家帶來了nexus7一鍵刷安卓android l的方法,目前的Andro
 android開發中遇到的問題匯總【九】
android開發中遇到的問題匯總【九】
244.http請求的url含有中字符時,需要Uri編碼。Uri.encoder()245.使用androidstudio時,不知道什麼原因svn不見了Android S