編輯:關於Android編程
我們經常使用SharedPreferences保存一些簡單的數據,比如Settings的數據。如果我們只是簡單的使用,可能沒什麼問題,但是如果要用好它還是得明白它的實現方式,下面來從源碼上來分析下SharedPreferences的緩存,異步讀寫實現,多線程,多進程訪問。
SharedPreferences是Android提供的一種使用XML文件保存內容的機制。其內部就是通過xml寫入文件的。
SharedPreferences是一個接口類,這是使用它的一個基礎,我們可以通過Context的getSharedPreference來獲取SharedPreferences。如下所示:
SharedPreferences sp = context.getSharedPreferences("name",Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
第一個參數表示存儲的文件名,第二個表示創建文件時的模式。
它提供了getInt, getLong, getFloat,getChar, getString 來讀取int, long, float, char, String類型的數據,並且提供了一個Editor接口來用於寫入對應的數據類型。Android在API14時又提供了Set類型的數據寫入讀取。下面看一段簡單實用示例:
SharedPreferences sp = context.getSharedPreferences("name",Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
int val1 = sp.getInt("val1",0);
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = sp.edit();
editor.putInt("val1", val1+1);
editor.apply();
// editor.commit(); 跟apply方法是一樣的,但是apply是異步寫入。
下面就針對上面這段代碼流程,分析一下SharedPreferences的源碼。
我們通過context.getSharedPreferences方法獲取SharedPreferences,而Context得真正實現者是ContextImpl,所以看看ContextImpl裡面的getSharedPreferences方法:
@Override
public SharedPreferences getSharedPreferences(String name, int mode) {
SharedPreferencesImpl sp;
synchronized (ContextImpl.class) {
if (sSharedPrefs == null) {
sSharedPrefs = new ArrayMap>();
}
final String packageName = getPackageName();
ArrayMap packagePrefs = sSharedPrefs.get(packageName);
if (packagePrefs == null) {
packagePrefs = new ArrayMap();
sSharedPrefs.put(packageName, packagePrefs);
}
// At least one application in the world actually passes in a null
// name. This happened to work because when we generated the file name
// we would stringify it to "null.xml". Nice.
if (mPackageInfo.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion <
Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
if (name == null) {
name = "null";
}
}
sp = packagePrefs.get(name);
if (sp == null) {
File prefsFile = getSharedPrefsFile(name); //根據文件名,獲取存儲的文件
sp = new SharedPreferencesImpl(prefsFile, mode);
packagePrefs.put(name, sp);
return sp;
}
}
if ((mode & Context.MODE_MULTI_PROCESS) != 0 ||
getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion < android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB) {
// If somebody else (some other process) changed the prefs
// file behind our back, we reload it. This has been the
// historical (if undocumented) behavior.
sp.startReloadIfChangedUnexpectedly(); //在多進程模式或者目標sdk版本在HONEYCOMB以下版本每次讀取緩存了的sp,Android會檢查xml文件是否已經被重寫了。
}
return sp;
}
這段代碼首先判斷sSharedPrefs是否為空,如果為空則給他初始化。sSharedPrefs是一個用來緩存SharedPreferences的ArrayMap,它的key為包名,它的value為ArrayMap,這個ArrayMap保存的鍵值對是SharedPreferences文件名和對應的SharedPreferencesImpl(是SharedPreferences的實現類)。如果SharedPreferencesImpl已經存在,它會直接返回已經存在的SharedPreferencesImpl。如果是在多進程模式下,或者目標版本低於HONEYCOMB的時候,會檢查是否需要重新從磁盤中加載文件。但是需要說的是MODE_MULTI_PROCESS模式已經被deprecated了,官方建議使用ContentProvider來處理多進程訪問,其實我們項目中就遇到這麼一個問題導致了一個BUG。
在重新創建SharedPreferencesImpl的時候,getSharedPreferences會調用getSharedPrefsFile來獲取存儲的xml文件,這個函數對xml文件名進行了組裝:
@Override
public File getSharedPrefsFile(String name) {
return makeFilename(getPreferencesDir(), name + ".xml");
}
通過getPreferencesDir()來獲取shared_prefs目錄,然後根據文件名加上xml後綴。Android沒有提供直接訪問shared_prefs目錄的API,getPreferencesDir是一個私有類,我們如果想要直接訪問這個目錄,可以通過下面這段代碼訪問:
String sharedPrefsDir = context.getCacheDir().getParent().getAbsolutePath()+"/shared_prefs";
從上面的代碼已經知道SharedPreferences具體的實現者是SharedPreferencesImpl。我們都知道Android的SharedPreferences對XML操作是使用DOM方式解析的(一開始就把整個XML給讀取出來)。在SharedpreferencesImpl源碼中,它的構造函數裡面它就把XML文件給讀取出來了:
SharedPreferencesImpl(File file, int mode) {
mFile = file;
mBackupFile = makeBackupFile(file);
mMode = mode;
mLoaded = false;
mMap = null;
startLoadFromDisk();
}
它的構造函數中startLoadFromDisk就是將xml給讀取出來的。下面看看startLoadFromDisk:
private void startLoadFromDisk() {
synchronized (this) {
mLoaded = false;
}
new Thread("SharedPreferencesImpl-load") {
public void run() {
synchronized (SharedPreferencesImpl.this) {
loadFromDiskLocked();
}
}
}.start();
}
它使用了一個異步線程來讀取xml,最終實現的函數是loadFromDiskLocked(),在讀取的時候它必須獲取SharedPreferencesImpl.this的鎖:
private void loadFromDiskLocked() {
...
Map map = null;
StructStat stat = null;
try {
stat = Os.stat(mFile.getPath());
if (mFile.canRead()) {
BufferedInputStream str = null;
try {
str = new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream(mFile), 16*1024);
map = XmlUtils.readMapXml(str);
...
mLoaded = true;
if (map != null) {
mMap = map;
mStatTimestamp = stat.st_mtime;
mStatSize = stat.st_size;
} else {
mMap = new HashMap();
}
這個函數裡面省略了一些代碼,想看全部的,可以直接去SharedPreferencesImpl文件看。這個函數最終調用了XmlUtils.readMapXml來調用,讀取整個xml的內容,放到mMap當中。
SharedPreferencesImpl的讀取是非常簡單的,因為在構造函數當中就已經讀取整個xml文件的內容到mMap當中了,所以再次讀取的時候直接從mMap當中讀取就好了,但是得注意同步的問題:
public int getInt(String key, int defValue) {
synchronized (this) {
awaitLoadedLocked();
Integer v = (Integer)mMap.get(key);
return v != null ? v : defValue;
}
}
函數awaitLoadedLocked就是等待讀取文件完成。因為如果讀取具體元素的時候,讀取文件線程卻沒有完成,那麼必須等待文件讀取完成,不然結果肯定會亂。
SharedPreferences的寫入是通過Editor來實現的,Editor接口在SharedPreferencesImpl具體實現是EditorImpl,在這看看它的源碼:
public final class EditorImpl implements Editor {
private final Map mModified = Maps.newHashMap();
private boolean mClear = false;
public Editor putInt(String key, int value) {
synchronized (this) {
mModified.put(key, value);
return this;
}
}
//... 省略了其他類型的value操作,和clear,remove函數。
public void apply() {
final MemoryCommitResult mcr = commitToMemory();
final Runnable awaitCommit = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
mcr.writtenToDiskLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
}
};
QueuedWork.add(awaitCommit);
Runnable postWriteRunnable = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
awaitCommit.run();
QueuedWork.remove(awaitCommit);
}
};
SharedPreferencesImpl.this.enqueueDiskWrite(mcr, postWriteRunnable); // enqueueDiskWrite會調用異步線程執行postWriteRunnable。
// Okay to notify the listeners before it's hit disk
// because the listeners should always get the same
// SharedPreferences instance back, which has the
// changes reflected in memory.
notifyListeners(mcr);
}
....省略了commitToMemory
public boolean commit() {
MemoryCommitResult mcr = commitToMemory();
SharedPreferencesImpl.this.enqueueDiskWrite(
mcr, null /* sync write on this thread okay */); //第二個參數為null,enqueueDiskWrite會直接寫入。
try {
mcr.writtenToDiskLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
return false;
}
notifyListeners(mcr);
return mcr.writeToDiskResult;
}
... 省略了notifyListeners
}
從源碼上面可以看出,首先使用put寫入的時候,只是寫入到一個mModified裡面,但是實際上還沒寫入SharedPreferencesImpl的mMap當中,更沒有寫入磁盤,只有當調用commit或者apply函數的時候才會開始寫入。而apply是異步寫入,而commit是在當前線程直接寫入。commit在enqueueDiskWrite的第二個參數傳入null,看看enqueueDiskWrite的實現:
private void enqueueDiskWrite(final MemoryCommitResult mcr,
final Runnable postWriteRunnable) {
final Runnable writeToDiskRunnable = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
synchronized (mWritingToDiskLock) {
writeToFile(mcr);
}
synchronized (SharedPreferencesImpl.this) {
mDiskWritesInFlight--;
}
if (postWriteRunnable != null) {
postWriteRunnable.run();
}
}
};
final boolean isFromSyncCommit = (postWriteRunnable == null); //如果postWriteRunnable就同步寫入
// Typical #commit() path with fewer allocations, doing a write on
// the current thread.
if (isFromSyncCommit) {
boolean wasEmpty = false;
synchronized (SharedPreferencesImpl.this) {
wasEmpty = mDiskWritesInFlight == 1;
}
if (wasEmpty) {
writeToDiskRunnable.run();
return;
}
}
QueuedWork.singleThreadExecutor().execute(writeToDiskRunnable);
}
但是需要指出的是,兩種方式首先都會先使用commitTomemory函數將修改的內容寫入到SharedPreferencesImpl當中。看看commitToMemory的實現:
private MemoryCommitResult commitToMemory() {
MemoryCommitResult mcr = new MemoryCommitResult();
synchronized (SharedPreferencesImpl.this) {
// We optimistically don't make a deep copy until
// a memory commit comes in when we're already
// writing to disk.
if (mDiskWritesInFlight > 0) {
// We can't modify our mMap as a currently
// in-flight write owns it. Clone it before
// modifying it.
// noinspection unchecked
mMap = new HashMap(mMap);
}
mcr.mapToWriteToDisk = mMap;
mDiskWritesInFlight++;
boolean hasListeners = mListeners.size() > 0;
if (hasListeners) {
mcr.keysModified = new ArrayList();
mcr.listeners =
new HashSet(mListeners.keySet());
}
synchronized (this) {
if (mClear) {
if (!mMap.isEmpty()) {
mcr.changesMade = true;
mMap.clear();
}
mClear = false;
}
for (Map.Entry e : mModified.entrySet()) { // 在這開始將修改的內容寫入到mMap當中。
String k = e.getKey();
Object v = e.getValue();
// "this" is the magic value for a removal mutation. In addition,
// setting a value to "null" for a given key is specified to be
// equivalent to calling remove on that key.
if (v == this || v == null) {
if (!mMap.containsKey(k)) {
continue;
}
mMap.remove(k);
} else {
if (mMap.containsKey(k)) {
Object existingValue = mMap.get(k);
if (existingValue != null && existingValue.equals(v)) {
continue;
}
}
mMap.put(k, v);
}
mcr.changesMade = true;
if (hasListeners) {
mcr.keysModified.add(k);
}
}
mModified.clear();
}
}
return mcr;
}
我們可以通過下面兩個函數注冊監視xml文件變化的通知,在這裡我直接把函數源碼給順便貼出來了,因為比較簡短:
public void registerOnSharedPreferenceChangeListener(OnSharedPreferenceChangeListener listener) {
synchronized(this) {
mListeners.put(listener, mContent);
}
}
public void unregisterOnSharedPreferenceChangeListener(OnSharedPreferenceChangeListener listener) {
synchronized(this) {
mListeners.remove(listener);
}
}
在前面分析了的函數commitToMemory中會返回修改的內容保存在MemoryCommitResult當中,然後使用使用notifyListener函數通知監聽者。
SharedPreferences從功能上面來講就是三個部分讀取(一開始異步全部讀取出來,get的時候,如果沒有讀取完,會等待),寫入,監聽SharedPreferences的變化。另外Android會使用ArrayMap對SharedPreferences進行緩存,以SharedPreferences的name作為key。需要進一步理解的是關於多線程,多進程時的使用。
首先從線程方面來看,從源碼上看apply是使用異步線程寫入磁盤,commit是同步寫入磁盤。所以我們在主線程使用的commit的時候,需要考慮是否會出現ANR問題。我們不用擔心apply異步寫入會出現先寫入的內容,在該線程之後讀取會讀取不到,因為它寫入內存的時候沒有使用異步線程,所以在主線程最好使用apply。所有的線程讀取的時候都會加SharedPreferencesImpl.this鎖,editor寫入內存的時候(寫入SharedPreferencesImpl.this.mMap)也會加SharedPreferencesImpl.this鎖,另外editor調用put,clear, remove方法的時候都會加上EditorImpl.this鎖,這些是線程安全的保證,只有在commit/apply後才會寫入內存(mMap, xml內容緩存的map變量)和磁盤。
另外從多進程方面來看,SharedPreferences本身提供了MODE_MULTI_PROCESS的模式,但是現在已經deprecated了,不建議使用。MODE_MULTI_PROCESS也僅僅是每次讀取緩存的SharedPreferencesImpl時重寫讀取一次磁盤(其實效率很低,而且從源碼看,並不能很好地保持同步)。所以Android建議使用ContentProvider來保持多進程的訪問。有人已經實現了,可以通過google搜索multi process sharedpreferences找到,因為我沒看過那些,所以自己搜吧,我是直接看的公司的。
 解決android3.0版本以上應用接收不到開機廣播問題
解決android3.0版本以上應用接收不到開機廣播問題
現在是2014-07-16 下午15:27. 好久沒寫過東西,突然間靈感噴發想寫點東西(其實是剛剛弄好了一個棘手的問題,自豪中。。呵呵呵呵 我牛掰)。廢話不多說,進入正題
 A07_TimePicker & DatePicker & AnalogClock & DigitalClock 的設置小結
A07_TimePicker & DatePicker & AnalogClock & DigitalClock 的設置小結
目標:學習時間日期和時鐘的設置 picker的計算機專業解釋是“選擇器”。 簡單翻譯一下: TimePicker 時間選擇器 DatePicker 日期選擇器 Analo
 自定義控件進階,如何用簡單的寫缤紛復雜的自定義控件
自定義控件進階,如何用簡單的寫缤紛復雜的自定義控件
一個安卓開發的朋友發我一個視頻並向詢問我視頻中效果怎麼實現,我當即給他說 ,這個簡單,用幀動畫就可以實現。然後就被他pass掉了,於是我只好祭出plan B。但是我當時沒
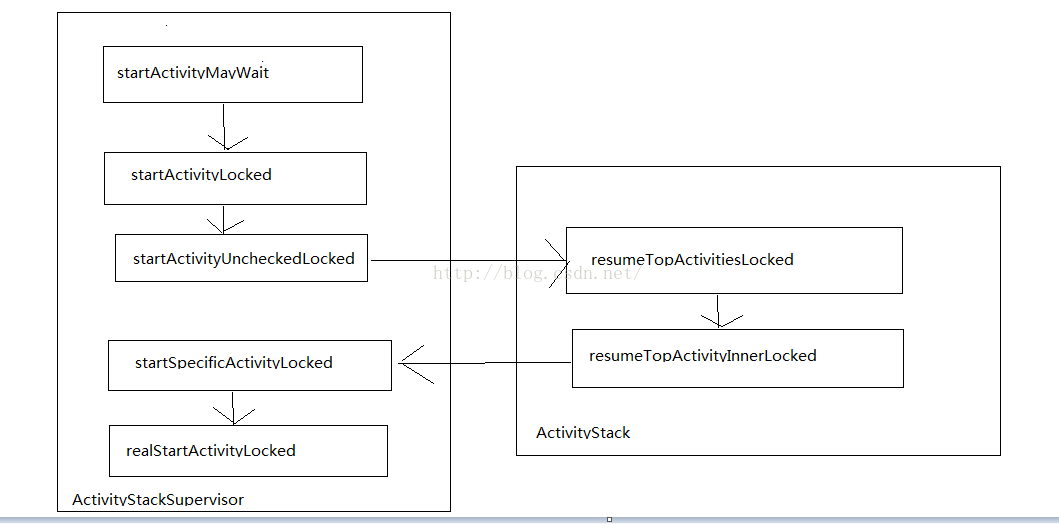 四大組件的工作過程探索(一)
四大組件的工作過程探索(一)
四大組件的運行狀態: Android中的四大組件中除了BroadcastReceiver以外,其他三種組件都必須在Android Mainfrst中注冊。對於,Bro