編輯:關於Android編程
在Android系統啟動的過程中,系統會通過PackageManagerService來掃描特定的目錄,以便可以對保存在裡面的apk進行安裝。PackageManagerService主要做兩件事情:
- 解析這個apk的配置文件AndroidManifest.xml以便獲得它的安裝信息
- 為這個apk分配Linux用戶ID和用戶組ID以便apk在系統中可以獲取到合適的運行權限
下面我們來開始分析PackageManagerService是如何安裝apk並執行上面兩件事情的
在前面分析Zygote的時候,有分析到PackageManagerService是由PackageManagerService.main來啟動的,因此我們一開始就來分析PackageManagerService.main
public static PackageManagerService main(Context context, Installer installer,
boolean factoryTest, boolean onlyCore) {
PackageManagerService m = new PackageManagerService(context, installer,
factoryTest, onlyCore);
ServiceManager.addService("package", m);
return m;
}
這裡一開始先把PackageManagerService服務new一個出來,在啟動的時候會調用他的構造函數,構造函數裡面會對系統中特定的目錄以便對保存在裡面的apk進行安裝。之後將它注冊到ServiceManager中,這樣就其他組件就可以通過ServiceManager來獲得他的訪問接口了。
來看看PackageManagerService的構造函數
public PackageManagerService(Context context, Installer installer,
boolean factoryTest, boolean onlyCore) {
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_PMS_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
if (mSdkVersion <= 0) {
Slog.w(TAG, "**** ro.build.version.sdk not set!");
}
mContext = context;
mFactoryTest = factoryTest;
mOnlyCore = onlyCore;
mLazyDexOpt = "eng".equals(SystemProperties.get("ro.build.type"));
mMetrics = new DisplayMetrics();
mSettings = new Settings(mPackages);
mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.system", Process.SYSTEM_UID,
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM, ApplicationInfo.PRIVATE_FLAG_PRIVILEGED);
mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.phone", RADIO_UID,
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM, ApplicationInfo.PRIVATE_FLAG_PRIVILEGED);
mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.log", LOG_UID,
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM, ApplicationInfo.PRIVATE_FLAG_PRIVILEGED);
mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.nfc", NFC_UID,
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM, ApplicationInfo.PRIVATE_FLAG_PRIVILEGED);
mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.bluetooth", BLUETOOTH_UID,
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM, ApplicationInfo.PRIVATE_FLAG_PRIVILEGED);
mSettings.addSharedUserLPw("android.uid.shell", SHELL_UID,
ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM, ApplicationInfo.PRIVATE_FLAG_PRIVILEGED);
// TODO: add a property to control this?
long dexOptLRUThresholdInMinutes;
if (mLazyDexOpt) {
dexOptLRUThresholdInMinutes = 30; // only last 30 minutes of apps for eng builds.
} else {
dexOptLRUThresholdInMinutes = 7 * 24 * 60; // apps used in the 7 days for users.
}
mDexOptLRUThresholdInMills = dexOptLRUThresholdInMinutes * 60 * 1000;
String separateProcesses = SystemProperties.get("debug.separate_processes");
if (separateProcesses != null && separateProcesses.length() > 0) {
if ("*".equals(separateProcesses)) {
mDefParseFlags = PackageParser.PARSE_IGNORE_PROCESSES;
mSeparateProcesses = null;
Slog.w(TAG, "Running with debug.separate_processes: * (ALL)");
} else {
mDefParseFlags = 0;
mSeparateProcesses = separateProcesses.split(",");
Slog.w(TAG, "Running with debug.separate_processes: "
+ separateProcesses);
}
} else {
mDefParseFlags = 0;
mSeparateProcesses = null;
}
mInstaller = installer;
mPackageDexOptimizer = new PackageDexOptimizer(this);
mMoveCallbacks = new MoveCallbacks(FgThread.get().getLooper());
mOnPermissionChangeListeners = new OnPermissionChangeListeners(
FgThread.get().getLooper());
getDefaultDisplayMetrics(context, mMetrics);
SystemConfig systemConfig = SystemConfig.getInstance();
mGlobalGids = systemConfig.getGlobalGids();
mSystemPermissions = systemConfig.getSystemPermissions();
mAvailableFeatures = systemConfig.getAvailableFeatures();
synchronized (mInstallLock) {
// writer
synchronized (mPackages) {
mHandlerThread = new ServiceThread(TAG,
Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND, true /*allowIo*/);
mHandlerThread.start();
mHandler = new PackageHandler(mHandlerThread.getLooper());
Watchdog.getInstance().addThread(mHandler, WATCHDOG_TIMEOUT);
File dataDir = Environment.getDataDirectory();
mAppDataDir = new File(dataDir, "data");
mAppInstallDir = new File(dataDir, "app");
mAppLib32InstallDir = new File(dataDir, "app-lib");
mAsecInternalPath = new File(dataDir, "app-asec").getPath();
mUserAppDataDir = new File(dataDir, "user");
mDrmAppPrivateInstallDir = new File(dataDir, "app-private");
sUserManager = new UserManagerService(context, this,
mInstallLock, mPackages);
// Propagate permission configuration in to package manager.
ArrayMap permConfig
= systemConfig.getPermissions();
for (int i=0; i libConfig = systemConfig.getSharedLibraries();
for (int i=0; i alreadyDexOpted = new ArraySet();
/**
* Add everything in the in the boot class path to the
* list of process files because dexopt will have been run
* if necessary during zygote startup.
*/
final String bootClassPath = System.getenv("BOOTCLASSPATH");
final String systemServerClassPath = System.getenv("SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH");
if (bootClassPath != null) {
String[] bootClassPathElements = splitString(bootClassPath, ':');
for (String element : bootClassPathElements) {
alreadyDexOpted.add(element);
}
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "No BOOTCLASSPATH found!");
}
if (systemServerClassPath != null) {
String[] systemServerClassPathElements = splitString(systemServerClassPath, ':');
for (String element : systemServerClassPathElements) {
alreadyDexOpted.add(element);
}
} else {
Slog.w(TAG, "No SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH found!");
}
final List allInstructionSets = InstructionSets.getAllInstructionSets();
final String[] dexCodeInstructionSets =
getDexCodeInstructionSets(
allInstructionSets.toArray(new String[allInstructionSets.size()]));
/**
* Ensure all external libraries have had dexopt run on them.
*/
if (mSharedLibraries.size() > 0) {
// NOTE: For now, we're compiling these system "shared libraries"
// (and framework jars) into all available architectures. It's possible
// to compile them only when we come across an app that uses them (there's
// already logic for that in scanPackageLI) but that adds some complexity.
for (String dexCodeInstructionSet : dexCodeInstructionSets) {
for (SharedLibraryEntry libEntry : mSharedLibraries.values()) {
final String lib = libEntry.path;
if (lib == null) {
continue;
}
try {
int dexoptNeeded = DexFile.getDexOptNeeded(lib, null, dexCodeInstructionSet, false);
if (dexoptNeeded != DexFile.NO_DEXOPT_NEEDED) {
alreadyDexOpted.add(lib);
mInstaller.dexopt(lib, Process.SYSTEM_UID, true, dexCodeInstructionSet, dexoptNeeded, false);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Library not found: " + lib);
} catch (IOException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Cannot dexopt " + lib + "; is it an APK or JAR? "
+ e.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
File frameworkDir = new File(Environment.getRootDirectory(), "framework");
// Gross hack for now: we know this file doesn't contain any
// code, so don't dexopt it to avoid the resulting log spew.
alreadyDexOpted.add(frameworkDir.getPath() + "/framework-res.apk");
// Gross hack for now: we know this file is only part of
// the boot class path for art, so don't dexopt it to
// avoid the resulting log spew.
alreadyDexOpted.add(frameworkDir.getPath() + "/core-libart.jar");
/**
* There are a number of commands implemented in Java, which
* we currently need to do the dexopt on so that they can be
* run from a non-root shell.
*/
String[] frameworkFiles = frameworkDir.list();
if (frameworkFiles != null) {
// TODO: We could compile these only for the most preferred ABI. We should
// first double check that the dex files for these commands are not referenced
// by other system apps.
for (String dexCodeInstructionSet : dexCodeInstructionSets) {
for (int i=0; i<frameworkfiles.length; i++)="" {="" file="" libpath="new" file(frameworkdir,="" frameworkfiles[i]);="" string="" path="libPath.getPath();" skip="" the="" if="" we="" already="" did="" it.="" (alreadydexopted.contains(path))="" continue;="" }="" it="" is="" not="" a="" type="" want="" to="" dexopt.="" (!path.endswith(".apk")="" &&="" !path.endswith(".jar"))="" try="" int="" dexoptneeded="DexFile.getDexOptNeeded(path," null,="" dexcodeinstructionset,="" false);="" (dexoptneeded="" !="DexFile.NO_DEXOPT_NEEDED)" minstaller.dexopt(path,="" process.system_uid,="" true,="" dexoptneeded,="" catch="" (filenotfoundexception="" e)="" slog.w(tag,="" "jar="" found:="" "="" +="" path);="" (ioexception="" "exception="" reading="" jar:="" path,="" e);="" final="" versioninfo="" ver="mSettings.getInternalVersion();" misupgrade="!Build.FINGERPRINT.equals(ver.fingerprint);" when="" upgrading="" from="" pre-m,="" promote="" system="" app="" permissions="" install="" runtime="" mpromotesystemapps="mIsUpgrade" ver.sdkversion=""
這段代碼很長,不過其實其邏輯也很是很簡單的。其中有個類型為Settings的成員變量mSettings,這是用來管理apk安裝信息的,假如Apk安裝了,那麼Settings就會記錄下他的信息,下次再碰到要安裝這個apk的時候直接調用之前保存的信息就可以了。這個操作是由Settings.readLPw操作來完成的。
接著使用scanDirLI來安裝保存在/system/framework、/system/app、/vendor/app、/data/app、/data/app-private中的apk。
安裝完之後就調用updatePermissionsLPw來申請為了特定的資源訪問權限的apk分配相應的linux用戶組ID。
最後調用Settings.readLPw將之前獲得的權限和apk安裝信息保存到本地的一個配置文件中,以便下次在安裝這些apk的時候,就可以將需要的apk信息很快速的恢復回來。
接著我們來一一分析這幾個函數
boolean readLPw(PackageManagerService service, List users, int sdkVersion,
boolean onlyCore) {
FileInputStream str = null;
if (mBackupSettingsFilename.exists()) {
try {
str = new FileInputStream(mBackupSettingsFilename);
}
} catch (java.io.IOException e) {
// We'll try for the normal settings file.
}
}
mPendingPackages.clear();
mPastSignatures.clear();
mKeySetRefs.clear();
try {
if (str == null) {
if (!mSettingsFilename.exists()) {
return false;
}
str = new FileInputStream(mSettingsFilename);
}
XmlPullParser parser = Xml.newPullParser();
parser.setInput(str, StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name());
int type;
int outerDepth = parser.getDepth();
while ((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT
&& (type != XmlPullParser.END_TAG || parser.getDepth() > outerDepth)) {
String tagName = parser.getName();
if (tagName.equals("package")) {
readPackageLPw(parser);
}
...
} else if (tagName.equals("shared-user")) {
readSharedUserLPw(parser);
}
}
str.close();
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
...
} catch (java.io.IOException e) {
...
}
return true;
}
這裡是主要是針對packages.xml和packages-backup.xml,第一個是保存的上一次的apk安裝信息,第二個是備份前一個的文件。通過XmlPullParser將安裝信息寫入這個兩個xml文件,具體什麼信息就不關心了,主要看看用戶ID相關的信息就好了。通過調用readPackageLPw來獲取用戶ID。接著調用readSharedUserLPw來獲取上一次安裝這個apk時分配過來的用戶ID。
private void scanDirLI(File dir, int parseFlags, int scanFlags, long currentTime) {
final File[] files = dir.listFiles();
if (ArrayUtils.isEmpty(files)) {
Log.d(TAG, "No files in app dir " + dir);
return;
}
if (DEBUG_PACKAGE_SCANNING) {
Log.d(TAG, "Scanning app dir " + dir + " scanFlags=" + scanFlags
+ " flags=0x" + Integer.toHexString(parseFlags));
}
for (File file : files) {
final boolean isPackage = (isApkFile(file) || file.isDirectory())
&& !PackageInstallerService.isStageName(file.getName());
if (!isPackage) {
// Ignore entries which are not packages
continue;
}
try {
scanPackageLI(file, parseFlags | PackageParser.PARSE_MUST_BE_APK,
scanFlags, currentTime, null);
} catch (PackageManagerException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failed to parse " + file + ": " + e.getMessage());
// Delete invalid userdata apps
if ((parseFlags & PackageParser.PARSE_IS_SYSTEM) == 0 &&
e.error == PackageManager.INSTALL_FAILED_INVALID_APK) {
logCriticalInfo(Log.WARN, "Deleting invalid package at " + file);
if (file.isDirectory()) {
mInstaller.rmPackageDir(file.getAbsolutePath());
} else {
file.delete();
}
}
}
}
}
先循環檢測參數dir所描述的一個目錄中的每一個文件。檢測到以”.apk”結尾的文件後,就調用scanPackageLI來對他們進行解析,解析完後就會返回一個Package對象pkg。
如果scanPackageLI發現他檢測的apk不是一個真正的apk的話,就會刪除它。
private void updatePermissionsLPw(String changingPkg, PackageParser.Package pkgInfo,
int flags) {
final String volumeUuid = (pkgInfo != null) ? getVolumeUuidForPackage(pkgInfo) : null;
updatePermissionsLPw(changingPkg, pkgInfo, volumeUuid, flags);
}
private void updatePermissionsLPw(String changingPkg,
PackageParser.Package pkgInfo, String replaceVolumeUuid, int flags) {
// Make sure there are no dangling permission trees.
Iterator it = mSettings.mPermissionTrees.values().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
final BasePermission bp = it.next();
if (bp.packageSetting == null) {
// We may not yet have parsed the package, so just see if
// we still know about its settings.
bp.packageSetting = mSettings.mPackages.get(bp.sourcePackage);
}
if (bp.packageSetting == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Removing dangling permission tree: " + bp.name
+ " from package " + bp.sourcePackage);
it.remove();
} else if (changingPkg != null && changingPkg.equals(bp.sourcePackage)) {
if (pkgInfo == null || !hasPermission(pkgInfo, bp.name)) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Removing old permission tree: " + bp.name
+ " from package " + bp.sourcePackage);
flags |= UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_ALL;
it.remove();
}
}
}
// Make sure all dynamic permissions have been assigned to a package,
// and make sure there are no dangling permissions.
it = mSettings.mPermissions.values().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
final BasePermission bp = it.next();
if (bp.type == BasePermission.TYPE_DYNAMIC) {
if (DEBUG_SETTINGS) Log.v(TAG, "Dynamic permission: name="
+ bp.name + " pkg=" + bp.sourcePackage
+ " info=" + bp.pendingInfo);
if (bp.packageSetting == null && bp.pendingInfo != null) {
final BasePermission tree = findPermissionTreeLP(bp.name);
if (tree != null && tree.perm != null) {
bp.packageSetting = tree.packageSetting;
bp.perm = new PackageParser.Permission(tree.perm.owner,
new PermissionInfo(bp.pendingInfo));
bp.perm.info.packageName = tree.perm.info.packageName;
bp.perm.info.name = bp.name;
bp.uid = tree.uid;
}
}
}
if (bp.packageSetting == null) {
// We may not yet have parsed the package, so just see if
// we still know about its settings.
bp.packageSetting = mSettings.mPackages.get(bp.sourcePackage);
}
if (bp.packageSetting == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Removing dangling permission: " + bp.name
+ " from package " + bp.sourcePackage);
it.remove();
} else if (changingPkg != null && changingPkg.equals(bp.sourcePackage)) {
if (pkgInfo == null || !hasPermission(pkgInfo, bp.name)) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Removing old permission: " + bp.name
+ " from package " + bp.sourcePackage);
flags |= UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_ALL;
it.remove();
}
}
}
// Now update the permissions for all packages, in particular
// replace the granted permissions of the system packages.
if ((flags&UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_ALL) != 0) {
for (PackageParser.Package pkg : mPackages.values()) {
if (pkg != pkgInfo) {
// Only replace for packages on requested volume
final String volumeUuid = getVolumeUuidForPackage(pkg);
final boolean replace = ((flags & UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_REPLACE_ALL) != 0)
&& Objects.equals(replaceVolumeUuid, volumeUuid);
grantPermissionsLPw(pkg, replace, changingPkg);
}
}
}
if (pkgInfo != null) {
// Only replace for packages on requested volume
final String volumeUuid = getVolumeUuidForPackage(pkgInfo);
final boolean replace = ((flags & UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_REPLACE_PKG) != 0)
&& Objects.equals(replaceVolumeUuid, volumeUuid);
grantPermissionsLPw(pkgInfo, replace, changingPkg);
}
}
mPackages裡面保存了所有安裝的apk,接著調用grantPermissionsLPw來分配他們的Linux用戶組ID,以便他們可以獲得所申請的資源訪問權限。
至此系統啟動時的apk安裝過程分析就結束了,至於啟動後再安裝的過程也是類似的,只是換了一個安裝入口。
 仿微信的滑動和改變字體圖標顏色
仿微信的滑動和改變字體圖標顏色
今天在慕課上學了仿微信的滑動,於是就重新敲了代碼在原有的圖形上又增加了改變字體的顏色。這裡將代碼放在這裡便於以後學習。整個過程用了ViewPager與PagerAdapt
 Android熱補丁動態修復技術(三)—— 使用Javassist注入字節碼,完成熱補丁框架雛形(可使用)
Android熱補丁動態修復技術(三)—— 使用Javassist注入字節碼,完成熱補丁框架雛形(可使用)
一、關於CSDN mardown編輯器的坑 Android熱補丁動態修復技術(三)這篇博文其實在4月8日的晚上已經發布了,然後緊接著寫第四篇,但是我將(四)保存到草稿箱
 android ExpandableListView詳解
android ExpandableListView詳解
點擊顯示展開項,先看效果:開始,1.先搞個XML顯示主界面:main_activity.xml: 2.進入main_activity開始搞顯示工作:
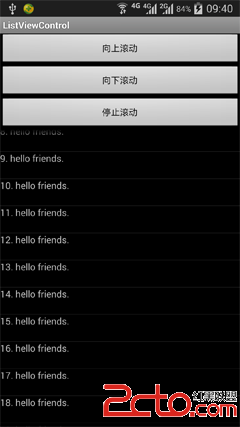 android通過代碼控制ListView上下滾動
android通過代碼控制ListView上下滾動
本文將介紹一種通過代碼控制ListView上下滾動的方法。 先上圖: 按下按鈕會觸發ListView滾動或停止。 實現該功能並不難,下面給出主要代碼MainAct