編輯:關於Android編程
在Zygote的啟動過程中,我們有個handleSystemServerProcess沒有分析。handleSystemServerProcess就是用來啟動System進程的,下面我們來看一下。
/**
* Finish remaining work for the newly forked system server process.
*/
private static void handleSystemServerProcess(
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
/*
* First, set the capabilities if necessary
*/
if (parsedArgs.uid != 0) {
try {
setCapabilities(parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
} catch (IOException ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error setting capabilities", ex);
}
}
closeServerSocket();
/*
* Pass the remaining arguments to SystemServer.
* "--nice-name=system_server com.android.server.SystemServer"
*/
RuntimeInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.remainingArgs);
/* should never reach here */
}
注釋已經寫得很清楚了,主要作用就是為新fork的進程完成遺留的工作。由於System復制了Zygote的地址空間,因此獲得Zygote進程在啟動過程中所創建的一個socket,但是System不需要這個,就調用closeServerSocket關閉它,再跟蹤RuntimeInit.zygoteInit()方法,其代碼如下:
<code class=" hljs java"> /**
* The main function called when started through the zygote process. This
* could be unified with main(), if the native code in finishInit()
* were rationalized with Zygote startup.<p>
*
* Current recognized args:
* </p><ul>
* <li> --nice-name=<i>nice name to appear in ps</i>
* </li><li> <code> [--] <start class name> <args>
* </code></li></ul><code>
*
* @param argv arg strings
*/
public static final void zygoteInit(String[] argv)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
// TODO: Doing this here works, but it seems kind of arbitrary. Find
// a better place. The goal is to set it up for applications, but not
// tools like am.
System.setOut(new AndroidPrintStream(Log.INFO, "System.out"));
System.setErr(new AndroidPrintStream(Log.WARN, "System.err"));
commonInit();
zygoteInitNative();
int curArg = 0;
for ( /* curArg */ ; curArg < argv.length; curArg++) {
String arg = argv[curArg];
if (arg.equals("--")) {
curArg++;
break;
} else if (!arg.startsWith("--")) {
break;
} else if (arg.startsWith("--nice-name=")) {
String niceName = arg.substring(arg.indexOf('=') + 1);
Process.setArgV0(niceName);
}
}
if (curArg == argv.length) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Missing classname argument to RuntimeInit!");
// let the process exit
return;
}
// Remaining arguments are passed to the start class's static main
String startClass = argv[curArg++];
String[] startArgs = new String[argv.length - curArg];
System.arraycopy(argv, curArg, startArgs, 0, startArgs.length);
invokeStaticMain(startClass, startArgs);
}</code></code>
其中commonInit()和zygoteInitNative()都是完成一些zygote的初始化工作。zygoteInitNative()則是在System進程中啟動一個Binder線程池。注意最後一句代碼,是調用傳入的Java類的main()方法,而在這裡就是SystemServer類的main()方法,其代碼如下:
public static void main(String[]args){
//The system server has to run all of the time, so it needs to be
//as efficient as possible with its memory usage.
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.8f);
System.loadLibrary("android_servers");
init1(args);
}
顯然,main()方法中主要就是對於目標棧進行了優化,同時加載了android_servers這個native庫,加載它的目的是調用init1()這個native方法。
init1()方法的聲明如下:
/**
*This method is called from Zygote to initialize to the system. This will cause the native
*services (SurfaceFlinger, AudioFlinger, etc...) to be started. After that it will call back
*up into init2() to start the Android services.
*/
native public static void init1(String[]args);
注釋已經說得非常清楚了。為了尋找它對應的方法,我們找到了framework/base/service/jni/Android.mk,在它底部有一個libandroid_servers,說明這正是我們要找的,而它對應的源文件中顯然onload.cpp是含有JNI_OnLoad()函數的源文件,下面是onload.cpp的代碼:
extern "C" jint JNI_OnLoad(JavaVM* vm, void* reserved)
{
JNIEnv* env = NULL;
jint result = -1;
if (vm->GetEnv((void**) &env, JNI_VERSION_1_4) != JNI_OK) {
LOGE("GetEnv failed!");
return result;
}
LOG_ASSERT(env, "Could not retrieve the env!");
register_android_server_KeyInputQueue(env);
register_android_server_LightsService(env);
register_android_server_AlarmManagerService(env);
register_android_server_BatteryService(env);
register_android_server_SensorService(env);
register_android_server_VibratorService(env);
register_android_server_SystemServer(env);
return JNI_VERSION_1_4;
}
顯然,我們要找的是register_android_server_SystemServer(env);這個函數(其他幾個都是加載具體的本地服務方法映射),register_android_server_SystemServer()函數的代碼如下:
namespace android{
extern "C" int system_init();
static void android_server_SystemServer_init1(JNIEnv*env,jobject clazz)
{
system.init();
}
/*
*JNI registeration
*/
static JNINativeMethod gMethods[]={
/*name,signature,funcPtr*/
{"init1","([Ljava/lang/String;)V",(void*)android_server_SystemServer_init1},
}
int register_android_server_SystemServer(JNIEnv*env)
{
return jniRegisterNativeMethods(env,"com/android/server/SystemServer",
gMethods,NELEM(gMethods));
}
};
顯然,SystemServer中的init1()方法對應的native方法是android_server_SystemServer_init()方法,而該方法調用的是system_init()方法,而這個system_init()方法在frameworks/base/cmds/system_server/library/system_init.cpp中,其源碼如下:
extern "C" status_t system_init()
{
LOGI("Entered system_init()");
sp proc(ProcessState::self());
sp sm = defaultServiceManager();
LOGI("ServiceManager: %p\n", sm.get());
sp grim = new GrimReaper();
sm->asBinder()->linkToDeath(grim, grim.get(), 0);
char propBuf[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
property_get("system_init.startsurfaceflinger", propBuf, "1");
if (strcmp(propBuf, "1") == 0) {
// Start the SurfaceFlinger
//code_1
SurfaceFlinger::instantiate();
}
// On the simulator, audioflinger et al don't get started the
// same way as on the device, and we need to start them here
//code_2
if (!proc->supportsProcesses()) {
// Start the AudioFlinger
AudioFlinger::instantiate();
// Start the media playback service
MediaPlayerService::instantiate();
// Start the camera service
CameraService::instantiate();
// Start the audio policy service
AudioPolicyService::instantiate();
}
// And now start the Android runtime. We have to do this bit
// of nastiness because the Android runtime initialization requires
// some of the core system services to already be started.
// All other servers should just start the Android runtime at
// the beginning of their processes's main(), before calling
// the init function.
LOGI("System server: starting Android runtime.\n");
AndroidRuntime* runtime = AndroidRuntime::getRuntime();
LOGI("System server: starting Android services.\n");
//code_3
runtime->callStatic("com/android/server/SystemServer", "init2");
// If running in our own process, just go into the thread
// pool. Otherwise, call the initialization finished
// func to let this process continue its initilization.
if (proc->supportsProcesses()) {
LOGI("System server: entering thread pool.\n");
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
LOGI("System server: exiting thread pool.\n");
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
1)啟動了Surface Flinger服務,Surface Flinger是基於C++的服務,而System Server是Java進程,它不能直接調用Surface Flinger服務。因而System Server必須經由JNI通過調用system_init()函數來運行Surface Flinger服務。
2)要完全讀懂這段源碼,需要等學習完Binder IPC機制之後。 簡單地說就是如果是模擬器,則在這裡啟動並注冊AudioFlinger,MediaPlayerService,CameraService,AudioPolicyService(真機的話是在main_mediaserver.cpp中啟動這些服務);
3)那麼剩下的主要就是調用SystemServer的init2()方法了。其中callStatic()函數是JNI包裝函數,它允許在C++代碼中經由JNI調用Java類的靜態方法。
下面我們看一下init2()方法:
public static final void init2(){
Slog.i(TAG,"Entered the Android system server!");
Thread thr=new ServerThread();
thr.setName("android.server.ServerThread");
thr.start();
}
init2()的代碼非常簡單,就是新建並運行一個ServerThread,下面我們看一下ServerThread的run()方法:
@Override
public void run() {
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_SYSTEM_RUN,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
Looper.prepare();
android.os.Process.setThreadPriority(
android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND);
BinderInternal.disableBackgroundScheduling(true);
String factoryTestStr = SystemProperties.get("ro.factorytest");
int factoryTest = "".equals(factoryTestStr) ? SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_OFF
: Integer.parseInt(factoryTestStr);
LightsService lights = null;
PowerManagerService power = null;
BatteryService battery = null;
ConnectivityService connectivity = null;
IPackageManager pm = null;
Context context = null;
WindowManagerService wm = null;
BluetoothService bluetooth = null;
BluetoothA2dpService bluetoothA2dp = null;
HeadsetObserver headset = null;
DockObserver dock = null;
UiModeManagerService uiMode = null;
RecognitionManagerService recognition = null;
ThrottleService throttle = null;
// Critical services...
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Entropy Service");
ServiceManager.addService("entropy", new EntropyService());
Slog.i(TAG, "Power Manager");
power = new PowerManagerService();
ServiceManager.addService(Context.POWER_SERVICE, power);
Slog.i(TAG, "Activity Manager");
context = ActivityManagerService.main(factoryTest);
Slog.i(TAG, "Telephony Registry");
ServiceManager.addService("telephony.registry", new TelephonyRegistry(context));
AttributeCache.init(context);
Slog.i(TAG, "Package Manager");
pm = PackageManagerService.main(context,
factoryTest != SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_OFF);
ActivityManagerService.setSystemProcess();
mContentResolver = context.getContentResolver();
// The AccountManager must come before the ContentService
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Account Manager");
ServiceManager.addService(Context.ACCOUNT_SERVICE,
new AccountManagerService(context));
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting Account Manager", e);
}
Slog.i(TAG, "Content Manager");
ContentService.main(context,
factoryTest == SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL);
Slog.i(TAG, "System Content Providers");
ActivityManagerService.installSystemProviders();
Slog.i(TAG, "Battery Service");
battery = new BatteryService(context);
ServiceManager.addService("battery", battery);
Slog.i(TAG, "Lights Service");
lights = new LightsService(context);
Slog.i(TAG, "Vibrator Service");
ServiceManager.addService("vibrator", new VibratorService(context));
// only initialize the power service after we have started the
// lights service, content providers and the battery service.
power.init(context, lights, ActivityManagerService.getDefault(), battery);
Slog.i(TAG, "Alarm Manager");
AlarmManagerService alarm = new AlarmManagerService(context);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.ALARM_SERVICE, alarm);
Slog.i(TAG, "Init Watchdog");
Watchdog.getInstance().init(context, battery, power, alarm,
ActivityManagerService.self());
// Sensor Service is needed by Window Manager, so this goes first
Slog.i(TAG, "Sensor Service");
ServiceManager.addService(Context.SENSOR_SERVICE, new SensorService(context));
Slog.i(TAG, "Window Manager");
wm = WindowManagerService.main(context, power,
factoryTest != SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE, wm);
((ActivityManagerService)ServiceManager.getService("activity"))
.setWindowManager(wm);
// Skip Bluetooth if we have an emulator kernel
// TODO: Use a more reliable check to see if this product should
// support Bluetooth - see bug 988521
if (SystemProperties.get("ro.kernel.qemu").equals("1")) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Registering null Bluetooth Service (emulator)");
ServiceManager.addService(BluetoothAdapter.BLUETOOTH_SERVICE, null);
} else if (factoryTest == SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Registering null Bluetooth Service (factory test)");
ServiceManager.addService(BluetoothAdapter.BLUETOOTH_SERVICE, null);
} else {
Slog.i(TAG, "Bluetooth Service");
bluetooth = new BluetoothService(context);
ServiceManager.addService(BluetoothAdapter.BLUETOOTH_SERVICE, bluetooth);
bluetooth.initAfterRegistration();
bluetoothA2dp = new BluetoothA2dpService(context, bluetooth);
ServiceManager.addService(BluetoothA2dpService.BLUETOOTH_A2DP_SERVICE,
bluetoothA2dp);
int bluetoothOn = Settings.Secure.getInt(mContentResolver,
Settings.Secure.BLUETOOTH_ON, 0);
if (bluetoothOn > 0) {
bluetooth.enable();
}
}
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
Slog.e("System", "Failure starting core service", e);
}
DevicePolicyManagerService devicePolicy = null;
StatusBarService statusBar = null;
InputMethodManagerService imm = null;
AppWidgetService appWidget = null;
NotificationManagerService notification = null;
WallpaperManagerService wallpaper = null;
LocationManagerService location = null;
if (factoryTest != SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Device Policy");
devicePolicy = new DevicePolicyManagerService(context);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.DEVICE_POLICY_SERVICE, devicePolicy);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting DevicePolicyService", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Status Bar");
statusBar = new StatusBarService(context);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.STATUS_BAR_SERVICE, statusBar);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting StatusBarService", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Clipboard Service");
ServiceManager.addService(Context.CLIPBOARD_SERVICE,
new ClipboardService(context));
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting Clipboard Service", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Input Method Service");
imm = new InputMethodManagerService(context, statusBar);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE, imm);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting Input Manager Service", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "NetStat Service");
ServiceManager.addService("netstat", new NetStatService(context));
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting NetStat Service", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "NetworkManagement Service");
ServiceManager.addService(
Context.NETWORKMANAGEMENT_SERVICE, new NetworkManagementService(context));
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting NetworkManagement Service", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Connectivity Service");
connectivity = ConnectivityService.getInstance(context);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE, connectivity);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting Connectivity Service", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Throttle Service");
throttle = new ThrottleService(context);
ServiceManager.addService(
Context.THROTTLE_SERVICE, throttle);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting ThrottleService", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Accessibility Manager");
ServiceManager.addService(Context.ACCESSIBILITY_SERVICE,
new AccessibilityManagerService(context));
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting Accessibility Manager", e);
}
try {
/*
* NotificationManagerService is dependant on MountService,
* (for media / usb notifications) so we must start MountService first.
*/
Slog.i(TAG, "Mount Service");
ServiceManager.addService("mount", new MountService(context));
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting Mount Service", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Notification Manager");
notification = new NotificationManagerService(context, statusBar, lights);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE, notification);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting Notification Manager", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Device Storage Monitor");
ServiceManager.addService(DeviceStorageMonitorService.SERVICE,
new DeviceStorageMonitorService(context));
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting DeviceStorageMonitor service", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Location Manager");
location = new LocationManagerService(context);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.LOCATION_SERVICE, location);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting Location Manager", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Search Service");
ServiceManager.addService(Context.SEARCH_SERVICE,
new SearchManagerService(context));
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting Search Service", e);
}
if (INCLUDE_DEMO) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Installing demo data...");
(new DemoThread(context)).start();
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "DropBox Service");
ServiceManager.addService(Context.DROPBOX_SERVICE,
new DropBoxManagerService(context, new File("/data/system/dropbox")));
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting DropBoxManagerService", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Wallpaper Service");
wallpaper = new WallpaperManagerService(context);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.WALLPAPER_SERVICE, wallpaper);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting Wallpaper Service", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Audio Service");
ServiceManager.addService(Context.AUDIO_SERVICE, new AudioService(context));
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting Audio Service", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Headset Observer");
// Listen for wired headset changes
headset = new HeadsetObserver(context);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting HeadsetObserver", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Dock Observer");
// Listen for dock station changes
dock = new DockObserver(context, power);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting DockObserver", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "UI Mode Manager Service");
// Listen for dock station changes
uiMode = new UiModeManagerService(context);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting UiModeManagerService", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Backup Service");
ServiceManager.addService(Context.BACKUP_SERVICE,
new BackupManagerService(context));
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting Backup Service", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "AppWidget Service");
appWidget = new AppWidgetService(context);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.APPWIDGET_SERVICE, appWidget);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting AppWidget Service", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "Recognition Service");
recognition = new RecognitionManagerService(context);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting Recognition Service", e);
}
try {
com.android.server.status.StatusBarPolicy.installIcons(context, statusBar);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure installing status bar icons", e);
}
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "DiskStats Service");
ServiceManager.addService("diskstats", new DiskStatsService(context));
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting DiskStats Service", e);
}
}
// make sure the ADB_ENABLED setting value matches the secure property value
Settings.Secure.putInt(mContentResolver, Settings.Secure.ADB_ENABLED,
"1".equals(SystemProperties.get("persist.service.adb.enable")) ? 1 : 0);
// register observer to listen for settings changes
mContentResolver.registerContentObserver(Settings.Secure.getUriFor(Settings.Secure.ADB_ENABLED),
false, new AdbSettingsObserver());
// Before things start rolling, be sure we have decided whether
// we are in safe mode.
final boolean safeMode = wm.detectSafeMode();
if (safeMode) {
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().enterSafeMode();
// Post the safe mode state in the Zygote class
Zygote.systemInSafeMode = true;
// Disable the JIT for the system_server process
VMRuntime.getRuntime().disableJitCompilation();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
} else {
// Enable the JIT for the system_server process
VMRuntime.getRuntime().startJitCompilation();
}
// It is now time to start up the app processes...
if (devicePolicy != null) {
devicePolicy.systemReady();
}
if (notification != null) {
notification.systemReady();
}
if (statusBar != null) {
statusBar.systemReady();
}
wm.systemReady();
power.systemReady();
try {
pm.systemReady();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
// These are needed to propagate to the runnable below.
final BatteryService batteryF = battery;
final ConnectivityService connectivityF = connectivity;
final DockObserver dockF = dock;
final ThrottleService throttleF = throttle;
final UiModeManagerService uiModeF = uiMode;
final AppWidgetService appWidgetF = appWidget;
final WallpaperManagerService wallpaperF = wallpaper;
final InputMethodManagerService immF = imm;
final RecognitionManagerService recognitionF = recognition;
final LocationManagerService locationF = location;
// We now tell the activity manager it is okay to run third party
// code. It will call back into us once it has gotten to the state
// where third party code can really run (but before it has actually
// started launching the initial applications), for us to complete our
// initialization.
((ActivityManagerService)ActivityManagerNative.getDefault())
.systemReady(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
Slog.i(TAG, "Making services ready");
if (batteryF != null) batteryF.systemReady();
if (connectivityF != null) connectivityF.systemReady();
if (dockF != null) dockF.systemReady();
if (uiModeF != null) uiModeF.systemReady();
if (recognitionF != null) recognitionF.systemReady();
Watchdog.getInstance().start();
// It is now okay to let the various system services start their
// third party code...
if (appWidgetF != null) appWidgetF.systemReady(safeMode);
if (wallpaperF != null) wallpaperF.systemReady();
if (immF != null) immF.systemReady();
if (locationF != null) locationF.systemReady();
if (throttleF != null) throttleF.systemReady();
}
});
Looper.loop();
Slog.d(TAG, "System ServerThread is exiting!");
}
代碼雖然有點長,但是其實非常簡單,主要就是各Java服務的注冊。同本地系統服務一樣,Java系統服務必須先把相關服務注冊到Context Manager中,其他模塊才能使用這些服務。但是Java系統服務的注冊方式與基於C++的本地系統服務不同,它通過調用ServiceManager類的addService()靜態方法,將自身注冊到Context Manager中。
到這裡SystemServer的啟動過程也分析完了。
 Android學習筆記之四
Android學習筆記之四
基本視圖介紹1.文本 按鈕與輸入框文本 按鈕 輸入框的繼承關系TextView:android:text=”文本”android:textSize
 微信怎麼清理緩存?微信清理緩存辦法?
微信怎麼清理緩存?微信清理緩存辦法?
很多用戶不知道,其實在隨著用戶使用微信的時間推移,微信應用會產生大量的緩存文件,這樣久而久之會造成手機內存不足的問題,並且在手機運行速度方面也有所影響,故此
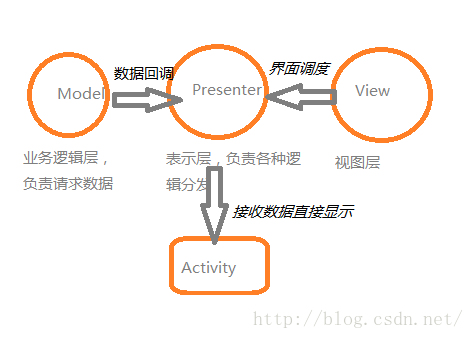 Android為什麼要使用MVP?使用RXJAVA完成簡單的MVP架構之旅
Android為什麼要使用MVP?使用RXJAVA完成簡單的MVP架構之旅
什麼是MVP?為什麼要使用MVP設計模式?因為要讓別人看得懂我們的代碼,使代碼更利於維護,簡單講就是模塊化,使各個包下的類各在其位,各司其職。比如怎樣請求數據和它被用來干
 Android 平台電容式觸摸屏的驅動原理
Android 平台電容式觸摸屏的驅動原理
硬件工作原理觸摸屏的工作原理概括來說就是上報坐標值,X軸、Y軸的值。所以在 Linux 中是采用 input 子系統來對其進行實現。本文主要歸納其驅動基本原理 與 And