編輯:關於Android編程
從源碼可以看出ViewRoot是ViewParent的實現類
public final class ViewRoot extends Handler implements ViewParent,
ViewRoot對應於的ViewRootImp也是ViewParent的實現類
public final class ViewRootImpl implements ViewParent,View.AttachInfo.Callbacks, HardwareRenderer.HardwareDrawCallbacks
我們知道View有三大流程(measure->layout->draw),都是通過ViewRoot完成的。內部通過performalTraversals()方法依次向下傳遞的。
measure決定了View的寬高,當measure完成後,我們可以通過以下代碼獲取view的測量寬度、測量高度,
t.getMeasuredHeight();
t.getMeasuredWidth();
注意:我們不可以在Activity的onCreate方法中對一個view使用上述代碼獲取寬度,因為在執行Activity的onCreate()方法時measure還沒測量好,需要在前面調用以下代碼來
t.measure(0, 0);
這裡的0是MeasureSpec,下面後介紹到。還有種獲取寬度、高度的方式,如下:
t.getViewTreeObserver().addOnGlobalLayoutListener(new OnGlobalLayoutListener() {
@Override
public void onGlobalLayout() {
width = t.getMeasuredWidth();
height = t.getMeasuredHeight();
t.getViewTreeObserver().removeGlobalOnLayoutListener(this);
}
}) ;
其實方法有很多種,我們也可以通過view.post()將獲取寬度、高度的代碼放到一個任務隊列的末尾、重寫onWindowFocusChanged()方法等。
繼續分析,View的measure是又measure()方法完成的。查看源碼
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) {
Insets insets = getOpticalInsets();
int oWidth = insets.left + insets.right;
int oHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom;
widthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.adjust(widthMeasureSpec, optical ? -oWidth : oWidth);
heightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.adjust(heightMeasureSpec, optical ? -oHeight : oHeight);
}
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT) == PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT ||
widthMeasureSpec != mOldWidthMeasureSpec ||
heightMeasureSpec != mOldHeightMeasureSpec) {
// first clears the measured dimension flag
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
resolveRtlPropertiesIfNeeded();
// measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// flag not set, setMeasuredDimension() was not invoked, we raise
// an exception to warn the developer
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) != PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) {
throw new IllegalStateException("onMeasure() did not set the"
+ " measured dimension by calling"
+ " setMeasuredDimension()");
}
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
}
mOldWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec;
mOldHeightMeasureSpec = heightMeasureSpec;
}
這是一個final方法,因此子類不可以重寫,但是我們從源碼中可以看到有如下代碼
// measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
再看onMeasure()
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
由此可以看出最後是通過setMeasuredDimension()方法進行設置寬度、高度的。再看看getDefaultSize()方法
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
這個方法比較簡單,其中specSize是測量後的大小,然後通過swich根據specMode來設置不同的值,當specMode為AT_MOST、EXACTLY時,返回specSize。而當specMode是UNSPECIFIED時,返回的就直接是getSuggestedMinimumHeight()的值。
protected int getSuggestedMinimumHeight() {
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinHeight : max(mMinHeight, mBackground.getMinimumHeight());
}
根據背景是否為null,如果為null,則返回mMinHeight,mMinHeight默認為0。寫到這,突然想到PoupuWindow的使用,不知道有沒有童鞋遇到過明明代碼沒錯但是就是不出現效果,非得設置個背景才有效,即使背景什麼都沒有,不知道是不是也是上面的原因,回頭研究下。。。
layout決定了View的四個點的坐標和位置信息,此時獲取的寬度高度是真正寬度高度,並且我們可以獲取left、right、top、bottom值,直接通過getWidth()、getHeight()獲取寬度、高度。
源碼如下:
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int oldL = mLeft;
int oldT = mTop;
int oldB = mBottom;
int oldR = mRight;
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners != null) {
ArrayList listenersCopy =
(ArrayList)li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners.clone();
int numListeners = listenersCopy.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; ++i) {
listenersCopy.get(i).onLayoutChange(this, l, t, r, b, oldL, oldT, oldR, oldB);
}
}
}
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
}
由上面代碼可以看出上述代碼先是調用了下面這行代碼用來確定四個頂點的位置
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
然後調用了onLayout()方法,而在onLayout()方法中,我們發現只是一個空實現,因此需要我們子類去重寫
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
}
這裡我們查看一下RelativeLayout的onLayout方法,看其具體實現
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
// The layout has actually already been performed and the positions
// cached. Apply the cached values to the children.
final int count = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams st =
(RelativeLayout.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
child.layout(st.mLeft, st.mTop, st.mRight, st.mBottom);
}
}
}
相對布局的onLayout()方法的代碼比較簡單,首先是獲取布局子view的個數,然後for遍歷,只要不是gone的都是依次獲取布局參數,然後調用子view的layout()方法,子view又調用setFrame(l, t, r, b),因此相對布局的每一個子view都是重疊的。
draw完成了View的顯示過程,只有在draw完成之後才會才屏幕上東西。
在View的draw()方法的實現我們可以看到如下:
/*
* Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed
* in the appropriate order:
*
* 1. Draw the background
* 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading
* 3. Draw view's content
* 4. Draw children
* 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers
* 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance)
*/
翻譯過來就是:
畫背景 有需要的話畫layers 畫內容 畫字view 有需要的話畫edges和報存layers 畫裝飾DecorView是頂級View,一般包括一個豎直方向的LineayLayout,主要包括標題欄和內容。標題欄一般是主題設置的,內容部分是在代碼中體現的
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
DecorView其實就是一個FrameLayout,View的事件都會經過它,然後再傳遞給子view
MeasureSpec是一個32位的二進制數,高2位代表測量模式specMode,低30位代表測量大小specMode
整個類比較簡單,源碼如下
public static class MeasureSpec {
private static final int MODE_SHIFT = 30;
private static final int MODE_MASK = 0x3 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Measure specification mode: The parent has not imposed any constraint
* on the child. It can be whatever size it wants.
*/
public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Measure specification mode: The parent has determined an exact size
* for the child. The child is going to be given those bounds regardless
* of how big it wants to be.
*/
public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Measure specification mode: The child can be as large as it wants up
* to the specified size.
*/
public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Creates a measure specification based on the supplied size and mode.
*
* The mode must always be one of the following:
*
*
{@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#UNSPECIFIED}
*
{@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#EXACTLY}
*
{@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#AT_MOST}
*
* *
Note: On API level 17 and lower, makeMeasureSpec's * implementation was such that the order of arguments did not matter * and overflow in either value could impact the resulting MeasureSpec. * {@link android.widget.RelativeLayout} was affected by this bug. * Apps targeting API levels greater than 17 will get the fixed, more strict * behavior.
* * @param size the size of the measure specification * @param mode the mode of the measure specification * @return the measure specification based on size and mode */ public static int makeMeasureSpec(int size, int mode) { if (sUseBrokenMakeMeasureSpec) { return size + mode; } else { return (size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK); } } /** * Extracts the mode from the supplied measure specification. * * @param measureSpec the measure specification to extract the mode from * @return {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#UNSPECIFIED}, * {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#AT_MOST} or * {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#EXACTLY} */ public static int getMode(int measureSpec) { return (measureSpec & MODE_MASK); } /** * Extracts the size from the supplied measure specification. * * @param measureSpec the measure specification to extract the size from * @return the size in pixels defined in the supplied measure specification */ public static int getSize(int measureSpec) { return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK); } static int adjust(int measureSpec, int delta) { return makeMeasureSpec(getSize(measureSpec + delta), getMode(measureSpec)); } /** * Returns a String representation of the specified measure * specification. * * @param measureSpec the measure specification to convert to a String * @return a String with the following format: "MeasureSpec: MODE SIZE" */ public static String toString(int measureSpec) { int mode = getMode(measureSpec); int size = getSize(measureSpec); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("MeasureSpec: "); if (mode == UNSPECIFIED) sb.append("UNSPECIFIED "); else if (mode == EXACTLY) sb.append("EXACTLY "); else if (mode == AT_MOST) sb.append("AT_MOST "); else sb.append(mode).append(" "); sb.append(size); return sb.toString(); } }
其中比較重要的是specMode。
specMode有三個值分別是:
AT_MOST:這個值表示父容器指定了可用大小,view的大小不可以大於該指定大小,這個對應於LayoutParams的wrap_content。這個模式處理起來稍麻煩點,因為需要我們自行測量。 EXACTLY:父容器已經知道子view 的精確大小,這時候的view 的大小就是specSize。 UNSPECIFIED:父容器不對view有任何限制,這個模式用的比較少。上面提到到AT_MOST的時候該模式對應於LayoutParams的wrap_content,那麼說明LayoutParams也會影響view的測量的。在對View進行測量的時候,系統會將LayoutParams在父容器的約束下轉換成MeasureSpec.
總的來說:對於普通View的MeasureSpec由父容器的MeasureSpec和LayoutParams決定,而對應頂級View來說,因為沒有父容器,故由窗口的大小和自身LayoutParams決定。而一旦MeasureSpec確定,就可以對其測量了。這裡提到MesureSpec是又父容器的MeasureSpec和LayoutParams決定的,就從源碼看看。
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
這是ViewGroup的measureChild方法,該方法調用了getChildMeasureSpec()方法,並且將父容器的MeasureSpec傳遞過去然後再返回子view的MeasureSpec。
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
// be
resultSize = 0;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = 0;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
從源碼可以看出,首先通過父容器的MeasureSpec來switch判斷,例如,如果父容器的MeasureSpec是EXACTLY,而自view的LayoutParams是WRAP_CONTENT,那麼
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
理論說的比較多,上代碼,
注意:這裡的父布局的寬度、高度我使用的是wrap_content,而MyView的寬度、高度使用的都是是match_parent。
public class CircleView extends View {
private int mColor = Color.BLUE ;
private Paint mPaint = new Paint(Paint.DEV_KERN_TEXT_FLAG) ;
public CircleView(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public CircleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
private void init() {
mPaint.setColor(mColor);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST
&& heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(200, 200);
} else if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(200, heightSpecSize);
} else if (heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize, 200);
}
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft();
int paddingRight = getPaddingRight();
int paddingBottom = getPaddingBottom();
int paddingTop = getPaddingTop();
int width = getWidth();
width = width - paddingLeft - paddingRight ;
int height = getHeight() ;
height = height - paddingTop - paddingBottom;
int radius = Math.min(width/2, height/2);
canvas.drawCircle(paddingLeft + width / 2 , paddingTop + height / 2 , radius, mPaint);
}
}
在onMeasure()方法中判斷子view的測量模式,如果模式為AT_MOST的話,我們需要自己手動為其指定高度和寬度,而根據前面我們分析getChildMeasureSpec()方法中可以知道,我們這裡對應的是滴一個else if語句塊。因此此時onDraw()畫出來的是200dp。其實從源碼可以看出,子父容器為AT_MOST的條件下,子view是WRAP_CONTENT和是MATCH_PARENT沒什麼區別。當然,若是父容器是EXACTLY的話,兩者是有區別的。然後就是setMeasuredDimension()方法調用,這個方法之前在分析源碼的時候看到過了,默認會調用這個方法的,作用就是設置寬度高度。
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
由於代碼比較簡單,就不上傳了,需要的留言。。。
OK,這篇簡單的分析了自定義view的基本知識和一個小demo,下篇將會繼續學習自定義View。
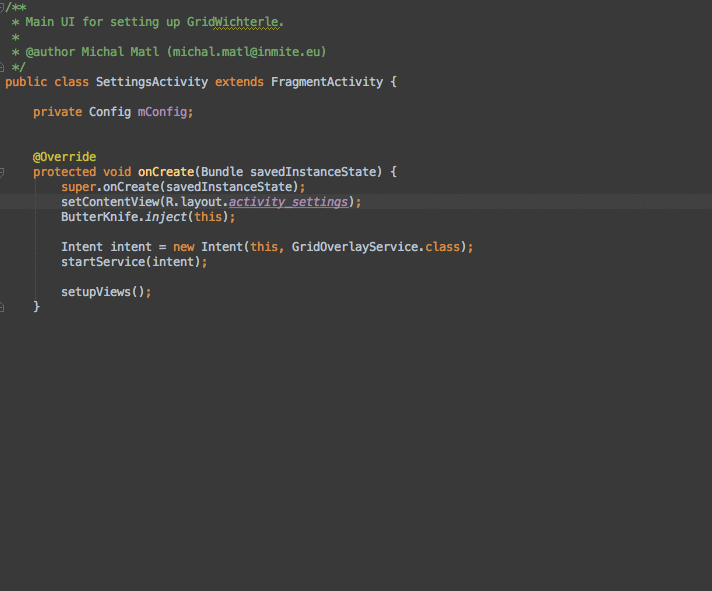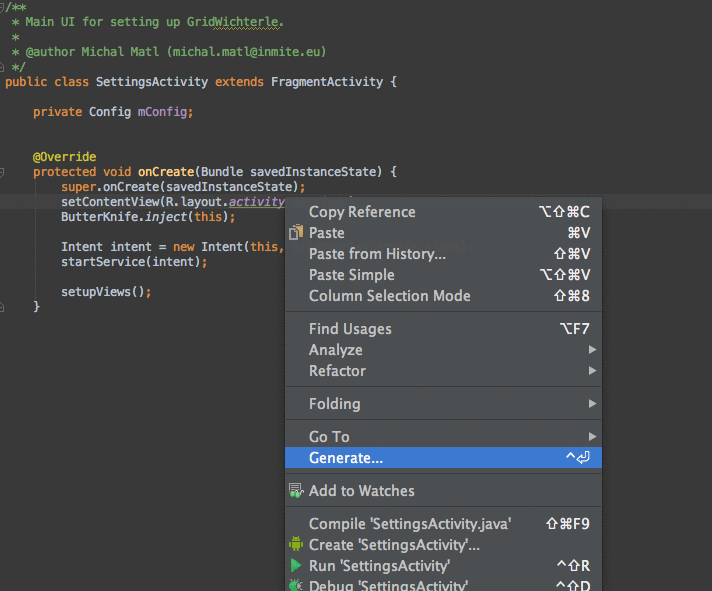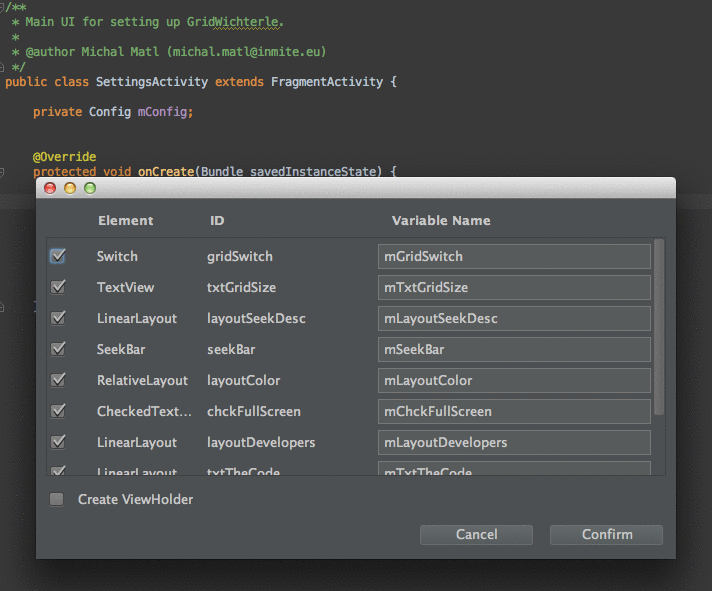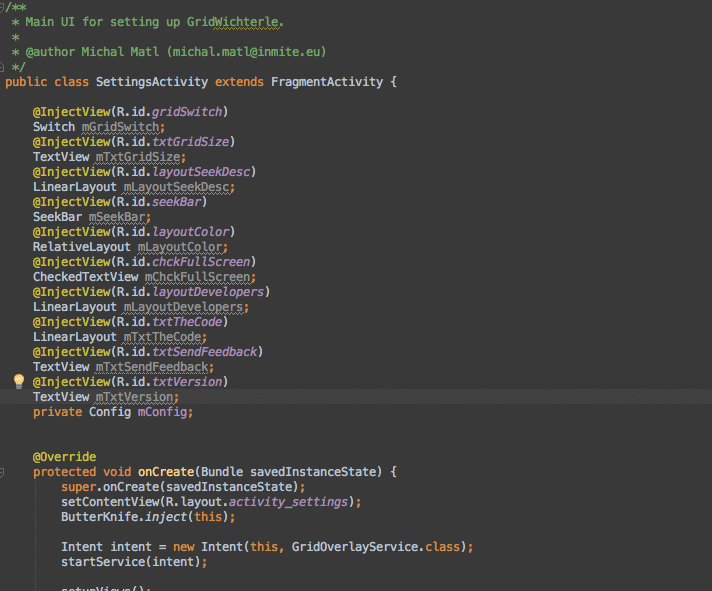 AndroidStudio上面最好用的插件
AndroidStudio上面最好用的插件
AndroidStudio上面最好用的插件Android ButterKnife Zelezny在Activity,Fragment,Adapter中選中布局xml自動生
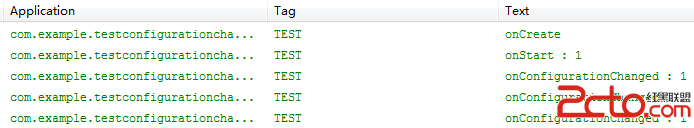 Android的onConfigurationChanged
Android的onConfigurationChanged
在Android開發中,如果某些事件觸發(例如:旋屏事件),則Activity會重新調用onCreate方法,對Activity重新初始化,這樣不僅效率低,而且會造成數據
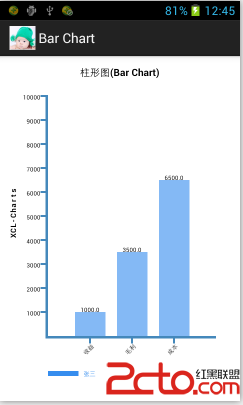 自己寫的Android圖表庫XCL-Charts例子展示
自己寫的Android圖表庫XCL-Charts例子展示
話說有了靈感就要抓住,來了興趣就要去研究它。 所以雖然最近很忙,但我還是沒有丟下Android圖表實現的研究,終於現在我的圖表庫基類 基本上已經有點模樣了,不在是小打小鬧
 Android控件系列之相冊Gallery&Adapter適配器入門&控件縮放動畫入門
Android控件系列之相冊Gallery&Adapter適配器入門&控件縮放動畫入門
學習目的: 1、掌握在Android中如何建立Gallery 2、初步理解Android適配器的原理 3、實現簡單的控件縮放動畫 簡介: 1、Gallery是Androi