編輯:關於Android編程
LinkedList類繼承了AbstractSequentialList< E >抽象類並實現了List接口。在AbstractSequentialList類中,其實主要是實現一些關於索引的方法。因此LinkedList中也支持“隨機訪問”。但這種隨機是偽隨機的,稍後我們可以看到。這裡我結合今天下午我參加的一場面試來簡要說一下關於LinkedList和ArrayList的一些問題。
ArrayList底層是動態數組實現的。隨機訪問的速度較快,即支持高效的隨機訪問,且在list末尾添加元素的開銷基本是固定的(如果不涉及到擴容的情況)。 LinkedList底層是鏈表實現。因此刪除和添加操作是比較占優勢的。 List接口下都是有序的集合。 實際使用中,ArrayList使用的較多,因為實際使用時一般會有內存大小的限制(這是那個公司面試我的那個技術人員說的)。(難道是LinkedList不好控制使用的內存???) 當插入較多,但是隨機查找較少的時候,用LinkedList可能性能會比較好。反之,用ArrayList。不過二者的使用均視實際情況而定。下面是源碼分析:
package java.util;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
public class LinkedList
extends AbstractSequentialList
implements List, Deque, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
transient int size = 0;//代表LinkedList中的節點個數
transient Node first;
transient Node last;//從這兩個成員變量可以看出來,LinkedList是雙向鏈表
public LinkedList() {
}
public LinkedList(Collection c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
//將e構成的節點作為首節點
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node f = first;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node l = last;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
//某個節點前添加節點
void linkBefore(E e, Node succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node pred = succ.prev;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
//刪除首節點並返回首節點中的數據
private E unlinkFirst(Node f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
//刪除尾節點並返回尾節點中的數據
private E unlinkLast(Node l) {
// assert l == last && l != null;
final E element = l.item;
final Node prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
//刪除指定的某個節點並返回該節點中的數據
E unlink(Node x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node next = x.next;
final Node prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
//得到首節點
public E getFirst() {
final Node f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
//得到尾節點
public E getLast() {
final Node l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
//刪除首節點(與前面相比只是增加了null控制邏輯)
public E removeFirst() {
final Node f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
//同上
public E removeLast() {
final Node l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
//增加節點為首節點
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
//增加節點為尾節點
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
//判斷是否包括某個對象
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) != -1;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
//刪除某個對象寄宿的節點
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean addAll(Collection c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
//將集合c中的數據添加進LinkedList,index為插入的位置,由此可見,添加方法總是從最後開始添加。
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
public void clear() {
// Clearing all of the links between nodes is "unnecessary", but:
// - helps a generational GC if the discarded nodes inhabit
// more than one generation
// - is sure to free memory even if there is a reachable Iterator
//全部置為null,help GC;
for (Node x = first; x != null; ) {
Node next = x.next;
x.item = null;
x.next = null;
x.prev = null;
x = next;
}
first = last = null;
size = 0;
modCount++;
}
// Positional Access Operations
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);//這裡是索引位置檢查
return node(index).item;
}
將某個節點的值替換並返回舊值
public E set(int index, E element) {
checkElementIndex(index);//索引合法性判斷
Node x = node(index);
E oldVal = x.item;
x.item = element;
return oldVal;
}
//將E節點加入鏈表,其索引為index
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);//注意:這裡是插入位置檢查,index可以取size,即尾節點的下一個位置也可以取的。
//跟上面進行的索引合法性判斷不同
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
//刪除指定的節點,並返回他
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
//索引位置的合法性檢查
private boolean isElementIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index < size;
}
//位置合法性的檢查,與上一個方法相比多出了一個尾節點後面那一個位置
private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index <= size;
}
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}
private void checkElementIndex(int index) {
if (!isElementIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {
if (!isPositionIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
//獲得指定位置處的node
Node node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)//無論尋找哪個節點,都是從首節點開始循環查找。且首節點的索引號為0.
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
//****************************** Search Operations*****************************
//從首節點開始查找並返回某個指定數據的索引,可以看出LinkedList中允許null屬性的存在
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = 0;
if (o == null) {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null)
return index;
index++;
}
} else {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
index++;
}
}
return -1;
}
//從尾節點開始查找
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
int index = size;
if (o == null) {
for (Node x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (x.item == null)
return index;
}
} else {
for (Node x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
}
}
return -1;
}
// ************************Queue operations************************.
//返回首節點中的數據(首節點可以為null)
public E peek() {
final Node f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
//返回首節點,但是前期是要保證首節點不能為null
public E element() {
return getFirst();
}
//返回首節點並且將其刪除,相當於出隊列。
public E poll() {
final Node f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
//簡單的刪除頭結點
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
//相當於入隊列
public boolean offer(E e) {
return add(e);
}
// ************Deque operations**************
//*************雙端操作,應用與雙向隊列******
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
public E peekFirst() {
final Node f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
public E peekLast() {
final Node l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : l.item;
}
public E pollFirst() {
final Node f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
public E pollLast() {
final Node l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l);
}
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
//出棧
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
//刪除第一個值為o的節點
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {
return remove(o);
}
//刪除最後一個值為o的節點
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//**************下面是迭代器*****************
public ListIterator listIterator(int index) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
//私有內部類
private class ListItr implements ListIterator {
private Node lastReturned;//上一個返回的節點
private Node next;//下一個節點
private int nextIndex;//下一個節點的索引
private int expectedModCount = modCount;//防止使用迭代器遍歷時LinkedList發生改變
ListItr(int index) {
// assert isPositionIndex(index);
next = (index == size) ? null : node(index);
nextIndex = index;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return nextIndex < size;
}
//迭代器實現返回下一個節點的值
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasNext())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next;
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
return lastReturned.item;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return nextIndex > 0;
}
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasPrevious())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next = (next == null) ? last : next.prev;
nextIndex--;
return lastReturned.item;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return nextIndex;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return nextIndex - 1;
}
public void remove() {
checkForComodification();
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
Node lastNext = lastReturned.next;
unlink(lastReturned);
if (next == lastReturned)
next = lastNext;
else
nextIndex--;
lastReturned = null;
expectedModCount++;
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
lastReturned.item = e;
}
//調用迭代器這個add方法也可能導致異常產生,而在ArrayList中調用該方法不會產生異常
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
lastReturned = null;
if (next == null)
linkLast(e);
else
linkBefore(e, next);
nextIndex++;
expectedModCount++;//在最後這個位置,ArrayList的處理是:expectedModCount = modCount;這裡區別很大
}
//consumer是一個功能函數接口
//這也是1.8新增加的特性
//Consumer接口中有2個方法,有且只有一個聲明為accept(T t)的方法,接收一個輸入參數並且沒有返回值。
//然後根據輸入參數對對象進行一些操作
//下面這個方法是通過Consumer接口對集合中的所有對象進行統一的操作
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
while (modCount == expectedModCount && nextIndex < size) {
action.accept(next.item);
lastReturned = next;
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
}
checkForComodification();
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
//私有內部節點類
private static class Node {
E item;
Node next;
Node prev;
Node(Node prev, E element, Node next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
public Iterator descendingIterator() {
return new DescendingIterator();
}
private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator {
private final ListItr itr = new ListItr(size());
public boolean hasNext() {
return itr.hasPrevious();
}
public E next() {
return itr.previous();
}
public void remove() {
itr.remove();
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private LinkedList superClone() {
try {
return (LinkedList) super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}
//執行的是淺克隆,即只是克隆了引用,而沒有克隆實例對象。
public Object clone() {
LinkedList clone = superClone();
// Put clone into "virgin" state
clone.first = clone.last = null;
clone.size = 0;
clone.modCount = 0;
// Initialize clone with our elements
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
clone.add(x.item);
return clone;
}
public Object[] toArray() {
Object[] result = new Object[size];
int i = 0;
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
result[i++] = x.item;
return result;
}
//這部分跟ArrayList基本一樣
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T[] toArray(T[] a) {
if (a.length < size)
a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance(
a.getClass().getComponentType(), size);
int i = 0;
Object[] result = a;
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
result[i++] = x.item;
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
//支持序列化傳輸
private static final long serialVersionUID = 876323262645176354L;
//序列化傳輸的寫操作
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// Write out any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out size
s.writeInt(size);
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
s.writeObject(x.item);
}
//序列化傳輸的讀操作
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in size
int size = s.readInt();
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
linkLast((E)s.readObject());
}
//1.8增加的新特性
@Override
public Spliterator spliterator() {
return new LLSpliterator(this, -1, 0);
}
/** A customized variant of Spliterators.IteratorSpliterator */
static final class LLSpliterator implements Spliterator {
static final int BATCH_UNIT = 1 << 10; // batch array size increment
static final int MAX_BATCH = 1 << 25; // max batch array size;
final LinkedList list; // null OK unless traversed
Node current; // current node; null until initialized
int est; // size estimate; -1 until first needed
int expectedModCount; // initialized when est set
int batch; // batch size for splits
LLSpliterator(LinkedList list, int est, int expectedModCount) {
this.list = list;
this.est = est;
this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;
}
final int getEst() {
int s; // force initialization
final LinkedList lst;
if ((s = est) < 0) {
if ((lst = list) == null)
s = est = 0;
else {
expectedModCount = lst.modCount;
current = lst.first;
s = est = lst.size;
}
}
return s;
}
public long estimateSize() { return (long) getEst(); }
public Spliterator trySplit() {
Node p;
int s = getEst();
if (s > 1 && (p = current) != null) {
int n = batch + BATCH_UNIT;
if (n > s)
n = s;
if (n > MAX_BATCH)
n = MAX_BATCH;
Object[] a = new Object[n];
int j = 0;
do { a[j++] = p.item; } while ((p = p.next) != null && j < n);
current = p;
batch = j;
est = s - j;
return Spliterators.spliterator(a, 0, j, Spliterator.ORDERED);
}
return null;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer action) {
Node p; int n;
if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException();
if ((n = getEst()) > 0 && (p = current) != null) {
current = null;
est = 0;
do {
E e = p.item;
p = p.next;
action.accept(e);
} while (p != null && --n > 0);
}
if (list.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer action) {
Node p;
if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException();
if (getEst() > 0 && (p = current) != null) {
--est;
E e = p.item;
current = p.next;
action.accept(e);
if (list.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
return false;
}
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED;
}
}
}
總結:
LinkedList是雙向鏈表。 size是鏈表節點的個數。 根據索引查找數據時,首節點的索引為0。 LinkedList中可以存儲null值節點。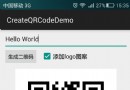 Android:使用ZXing生成二維碼(支持添加Logo圖案)
Android:使用ZXing生成二維碼(支持添加Logo圖案)
ZXing是谷歌的一個開源庫,可以用來生成二維碼、掃描二維碼。本文所介紹的是第一部分。首先上效果圖:ZXing相關各種文件官方下載地址:https://github.co
 Android知識梳理之自定義View
Android知識梳理之自定義View
雖然android本身給我們提供了形形色色的控件,基本能夠滿足日常開發的需求,但是面對日益同質化的app界面,和不同的業務需求.我們可能就需要自定義一些View來獲得比較
 Android Studio設置logcat顏色
Android Studio設置logcat顏色
在Android Studio裡面默認的logcat顯示顏色是灰色的,不同等級的log是沒有顏色分別的,如圖這一點遠不如Eclipse好看,但是Android Studi
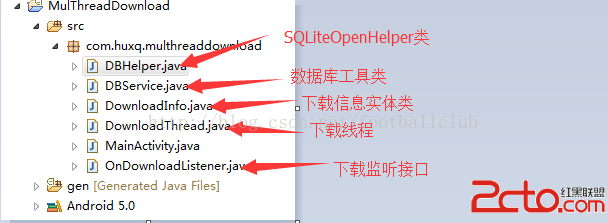 Android/java http多線程斷點下載(附源碼)
Android/java http多線程斷點下載(附源碼)
先看下項目結構: http多線程斷點下載涉及到 數據庫,多線程和http請求等幾個模塊,東西不是很多,想弄清楚也不是很困難,接下來我和大家分享下我的做法。 一、先看Ma