編輯:關於Android編程
之前第三章理論知識寫到過數據庫。數據庫是在程序內部自己訪問自己。而內容提供器是訪問別的程序數據的,即跨程序共享數據。對訪問的數據也無非就是CRUD。
自定義內容提供者,繼承ContentProvider類,重寫增刪改查方法,在方法中寫增刪改查數據庫的代碼,舉例增方法。自定義繼承使用ContentProvider
@Override
public Uri insert(Uri uri, ContentValues values) {
db.insert("person", null, values);
return uri;
}
在清單文件中定義內容提供者的標簽,注意必須要有authorities屬性,這是內容提供者的主機名,功能類似地址
創建一個其他應用,訪問自定義的內容提供者,實現對數據庫的插入操作
public void click(View v){
//得到內容分解器對象
ContentResolver cr = getContentResolver();//訪問使用ContentResolver
ContentValues cv = new ContentValues();
cv.put("name", "小方");
cv.put("phone", 138856);
cv.put("money", 3000);
//url:內容提供者的主機名,這裡的uri與上邊配置文件中的一樣
cr.insert(Uri.parse("content://com.it.person"), cv);
}
添加匹配規則
//指定多條uri
um.addURI("com.itheima.person", "person", PERSON_CODE);
um.addURI("com.itheima.person", "company", COMPANY_CODE);
//#號可以代表任意數字
um.addURI("com.itheima.person", "person/#", QUERY_ONE_PERSON_CODE);
通過Uri匹配器可以實現操作不同的表
@Override
public Uri insert(Uri uri, ContentValues values) {
if(um.match(uri) == PERSON_CODE){
db.insert("person", null, values);
}
else if(um.match(uri) == COMPANY_CODE){
db.insert("company", null, values);
}
else{
throw new IllegalArgumentException("不匹配");
}
return uri;
}
如果路徑中帶有數字,把路徑末尾的數字提取出來的api
int id = (int) ContentUris.parseId(uri);//返回的long類型,強制轉換int
讀取系統短信,首先查詢源碼獲得短信數據庫內容提供者的主機名和路徑,然後
ContentResolver cr = getContentResolver();
Cursor c = cr.query(Uri.parse("content://sms"), new String[]{"body", "date", "address", "type"}, null, null, null);
while(c.moveToNext()){
String body = c.getString(0);
String date = c.getString(1);
String address = c.getString(2);
String type = c.getString(3);
System.out.println(body+";" + date + ";" + address + ";" + type);
}
插入系統短信
ContentResolver cr = getContentResolver();
ContentValues cv = new ContentValues();
cv.put("body", "您尾號為XXXX的招行儲蓄卡收到轉賬1,000,000人民幣");
cv.put("address", 95555);
cv.put("type", 1);
cv.put("date", System.currentTimeMillis());
cr.insert(Uri.parse("content://sms"), cv);
先查詢raw_contacts表拿到聯系人id
Cursor cursor = cr.query(Uri.parse("content://com.android.contacts/raw_contacts"), new String[]{"contact_id"}, null, null, null);
然後拿著聯系人id去data表查詢屬於該聯系人的信息
Cursor c = cr.query(Uri.parse("content://com.android.contacts/data"), new String[]{"data1", "mimetype"}, "raw_contact_id = ?", new String[]{contactId}, null);
得到data1字段的值,就是聯系人的信息,通過mimetype判斷是什麼類型的信息
while(c.moveToNext()){
String data1 = c.getString(0);
String mimetype = c.getString(1);
if("vnd.android.cursor.item/email_v2".equals(mimetype)){
contact.setEmail(data1);
}
else if("vnd.android.cursor.item/name".equals(mimetype)){
contact.setName(data1);
}
else if("vnd.android.cursor.item/phone_v2".equals(mimetype)){
contact.setPhone(data1);
}
}
把確定的聯系人id插入raw_contacts表
cv.put("contact_id", _id);
cr.insert(Uri.parse("content://com.android.contacts/raw_contacts"), cv);
在data表插入數據
插3個字段:data1、mimetype、raw_contact_id
cv = new ContentValues();
cv.put("data1", "趙六");
cv.put("mimetype", "vnd.android.cursor.item/name");
cv.put("raw_contact_id", _id);
cr.insert(Uri.parse("content://com.android.contacts/data"), cv);
cv = new ContentValues();
cv.put("data1", "1596874");
cv.put("mimetype", "vnd.android.cursor.item/phone_v2");
cv.put("raw_contact_id", _id);
cr.insert(Uri.parse("content://com.android.contacts/data"), cv);
當數據庫數據改變時,內容提供者會發出通知,在內容提供者的uri上注冊一個內容觀察者,就可以收到數據改變的通知
cr.registerContentObserver(Uri.parse("content://sms"), true, new MyObserver(new Handler()));
class MyObserver extends ContentObserver{
public MyObserver(Handler handler) {
super(handler);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
//內容觀察者收到數據庫發生改變的通知時,會調用此方法
@Override
public void onChange(boolean selfChange) {
}
}
在內容提供者中發通知的代碼
ContentResolver cr = getContext().getContentResolver();
//發出通知,所有注冊在這個uri上的內容觀察者都可以收到通知
cr.notifyChange(uri, null); 手機SD卡損壞的修復方法
手機SD卡損壞的修復方法
經常會網友遇到手機使用時間較久後會遇到提示“SD卡已損壞,您可能必須將其重新格式化”故障,導致手機SD卡無法使用。最近身邊有朋友手機
 Android Mediaplayer本地音樂播放器(綁定服務)
Android Mediaplayer本地音樂播放器(綁定服務)
本文章介紹MediaPlayer本地音樂播放器,而當應用程序不再位於前台且沒有正在使用它的活動時,為了確保音頻繼續播放,我們需要建立一個服務Service。 Activi
 Android中圖案鎖的實現
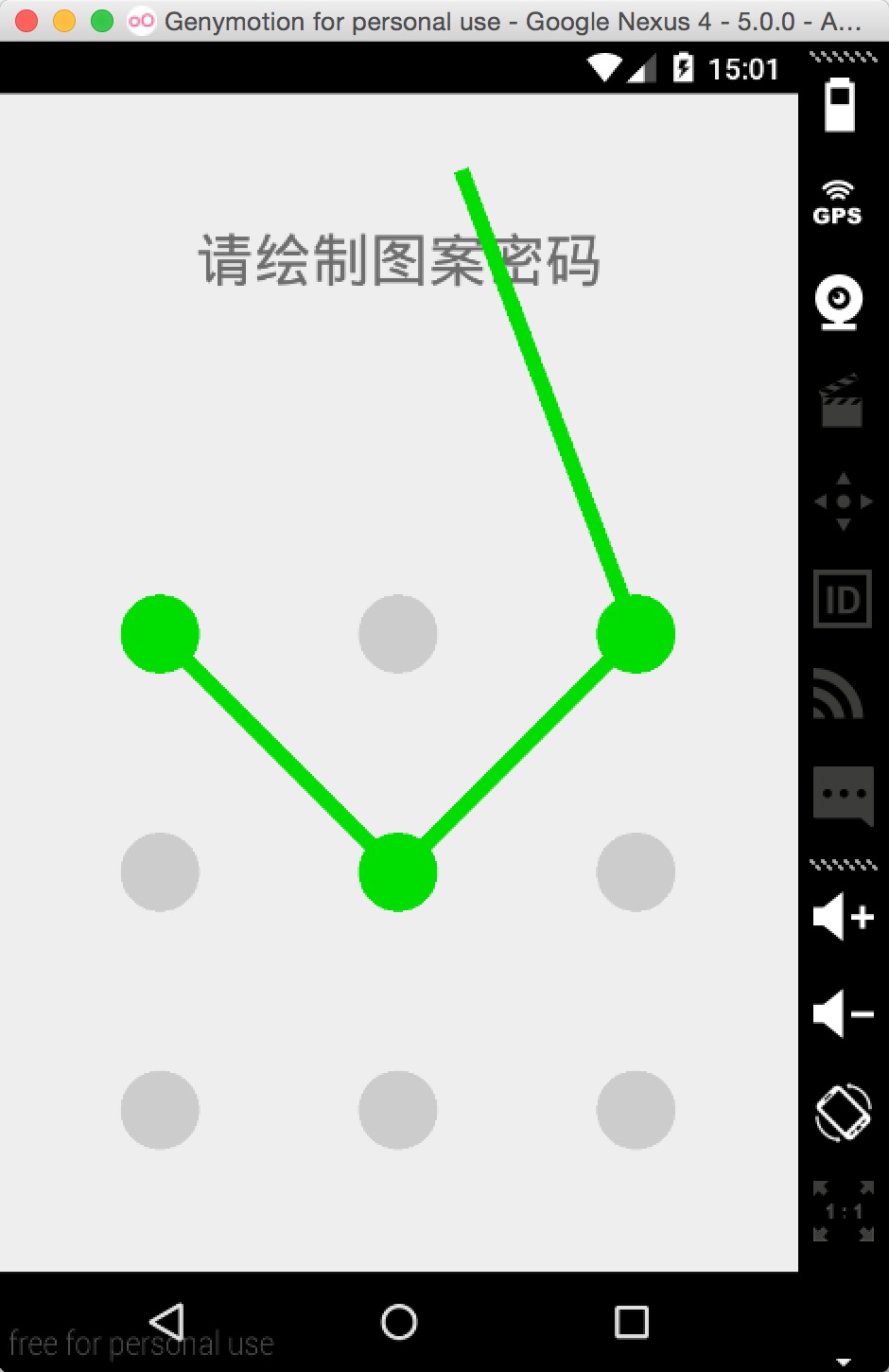
Android中圖案鎖的實現
很多品牌的Android手機都實現了圖案解鎖屏幕的功能,有些應用程序出於保護的目的也使用了圖案鎖(比如支付寶),本文將介紹一種圖案鎖的實現方式,這種實現的一個優勢在於方便
 Android編程中的四大基本組件與生命周期詳解
Android編程中的四大基本組件與生命周期詳解
本文實例講述了Android編程中的四大基本組件與生命周期。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:Android四大基本組件分別是Activity,Service服務,Cont