編輯:關於Android編程
原文地址:http://android.xsoftlab.net/training/basics/network-ops/index.html
這節課將會學習最基本的網絡連接,監視網絡連接狀況及網絡控制等內容。除此之外還會附帶描述如何解析、使用XML數據。
這節課所包含的示例代碼演示了最基本的網絡操作過程。開發者可以將這部分的代碼作為應用程序最基本的網絡操作代碼。
通過這節課的學習,將會學到最基本的網絡下載及數據解析的相關知識。
Note: 可以查看課程Transmitting Network Data Using Volley學習Volley的相關知識。這個HTTP庫可以使網絡操作更方便更快捷。Volley是一個開源框架庫,可以使應用的網絡操作順序更加合理並善於管理,還會改善應用的相關性能。
這節課將會學習如何實現一個含有網絡連接的簡單程序。課程中所描述的步驟是網絡連接的最佳實現過程。
如果應用要使用網絡操作,那麼清單文件中應該包含以下權限:
大多數的Android應用使用HTTP來發送、接收數據。Android中包含了兩個HTPP客戶端:HttpURLConnection及Apache的HTTP客戶端。兩者都支持HTTPS,上傳,下載,超時時間配置,IPv6,連接池。我們推薦在Gingerbread及以上的版本中使用HttpURLConnection。有關這個話題的更多討論信息,請參見博客Android’s HTTP Clients.
在嘗試連接到網絡之前,應當通過getActiveNetworkInfo()方法及isConnected()方法檢查網絡連接是否可用。要記得,設備可能處於不在網絡范圍的情況中,也可能用戶並沒有開啟WIFI或者移動數據。該話題的更多信息請參見 Managing Network Usage.
public void myClickHandler(View view) {
...
ConnectivityManager connMgr = (ConnectivityManager)
getSystemService(Context.CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE);
NetworkInfo networkInfo = connMgr.getActiveNetworkInfo();
if (networkInfo != null && networkInfo.isConnected()) {
// fetch data
} else {
// display error
}
...
}
網絡操作所用的時間通常是不確定的。為了防止由於網絡操作而引起的糟糕的用戶體驗,應該將這個過程放入獨立的線程中執行。AsyncTask類為這種實現提供了幫助。更多該話題的討論請參見Multithreading For Performance。
在下面的代碼段中,myClickHandler()方法調用了new DownloadWebpageTask().execute(stringUrl)。類DownloadWebpageTask是AsyncTask的子類。DownloadWebpageTask實現了AsyncTask的以下方法:
doInBackground()中執行了downloadUrl()方法。它將Web頁的URL地址作為參數傳給了該方法。downloadUrl()方法會獲得並處理Web頁面的內容。當處理結束時,這個方法會將處理後的結果返回。 onPostExecute()獲得返回後的結果將其顯示在UI上。
public class HttpExampleActivity extends Activity {
private static final String DEBUG_TAG = "HttpExample";
private EditText urlText;
private TextView textView;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
urlText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.myUrl);
textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.myText);
}
// When user clicks button, calls AsyncTask.
// Before attempting to fetch the URL, makes sure that there is a network connection.
public void myClickHandler(View view) {
// Gets the URL from the UI's text field.
String stringUrl = urlText.getText().toString();
ConnectivityManager connMgr = (ConnectivityManager)
getSystemService(Context.CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE);
NetworkInfo networkInfo = connMgr.getActiveNetworkInfo();
if (networkInfo != null && networkInfo.isConnected()) {
new DownloadWebpageTask().execute(stringUrl);
} else {
textView.setText("No network connection available.");
}
}
// Uses AsyncTask to create a task away from the main UI thread. This task takes a
// URL string and uses it to create an HttpUrlConnection. Once the connection
// has been established, the AsyncTask downloads the contents of the webpage as
// an InputStream. Finally, the InputStream is converted into a string, which is
// displayed in the UI by the AsyncTask's onPostExecute method.
private class DownloadWebpageTask extends AsyncTask {
@Override
protected String doInBackground(String... urls) {
// params comes from the execute() call: params[0] is the url.
try {
return downloadUrl(urls[0]);
} catch (IOException e) {
return "Unable to retrieve web page. URL may be invalid.";
}
}
// onPostExecute displays the results of the AsyncTask.
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(String result) {
textView.setText(result);
}
}
...
}
上面的代碼執行了以下操作:
1.當用戶按下按鈕時會調用myClickHandler()方法,應用會將指定的URL地址傳遞給DownloadWebpageTask。 2.DownloadWebpageTask的doInBackground()方法調用了downloadUrl()方法。在執行網絡傳輸的線程中可以使用HttpURLConnection來執行GET請求並下載輸入。在調用了connect()方法之後,可以通過getInputStream()方法獲得輸入流形式的數據。
在doInBackground()方法中調用了downloadUrl()方法。downloadUrl()方法將URL作為參數通過HttpURLConnection與網絡建立連接。一旦連接建立,應用通過getInputStream()方法來接收字節流形式的數據。
// Given a URL, establishes an HttpUrlConnection and retrieves
// the web page content as a InputStream, which it returns as
// a string.
private String downloadUrl(String myurl) throws IOException {
InputStream is = null;
// Only display the first 500 characters of the retrieved
// web page content.
int len = 500;
try {
URL url = new URL(myurl);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setReadTimeout(10000 /* milliseconds */);
conn.setConnectTimeout(15000 /* milliseconds */);
conn.setRequestMethod("GET");
conn.setDoInput(true);
// Starts the query
conn.connect();
int response = conn.getResponseCode();
Log.d(DEBUG_TAG, "The response is: " + response);
is = conn.getInputStream();
// Convert the InputStream into a string
String contentAsString = readIt(is, len);
return contentAsString;
// Makes sure that the InputStream is closed after the app is
// finished using it.
} finally {
if (is != null) {
is.close();
}
}
}
注意getResponseCode()方法返回的是連接的狀態碼。該狀態碼可以用來獲取連接的其它信息。狀態碼為200則表明連接成功。
InputStream所讀取的是字節數據。一旦獲得InputStream對象,通常需要將其解碼或者轉化為其它類型的數據。比如,如果下載了一張圖片,則應該將字節流轉碼為圖片:
InputStream is = null;
...
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(is);
ImageView imageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image_view);
imageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap);
在上的示例中,InputStream代表了Web頁面的文本內容。下面的代碼展示了如何將字節流轉換為字符串:
// Reads an InputStream and converts it to a String.
public String readIt(InputStream stream, int len) throws IOException, UnsupportedEncodingException {
Reader reader = null;
reader = new InputStreamReader(stream, "UTF-8");
char[] buffer = new char[len];
reader.read(buffer);
return new String(buffer);
}
 Android性能優化之布局優化篇
Android性能優化之布局優化篇
怎樣才能寫出優秀的Android App,是每一個程序員追求的目標。那麼怎麼才能寫出一個優秀的App呢?相信很多初學者也會有這種迷茫。一句話來回答這個問題:細節很重要。今
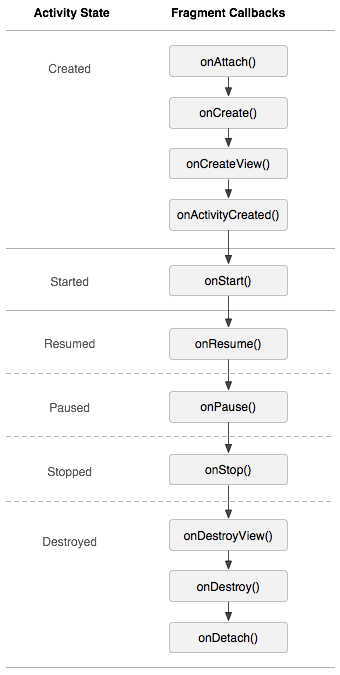 Android中Fragment的解析和使用詳解
Android中Fragment的解析和使用詳解
前言Android Fragment的生命周期和Activity類似,實際可能會涉及到數據傳遞,onSaveInstanceState的狀態保存,FragmentMana
 [Android&Java]設計模式代碼篇:觀察者模式
[Android&Java]設計模式代碼篇:觀察者模式
觀察者,就如同一個人,對很多東西都感興趣,就好像音樂、電子產品、Game、股票等,這些東西的變化都能引起愛好者們的注意並時刻關注他們。在代碼中,我們也有這樣的一種方式來設
 詳解Android中的MVP架構分解和實現
詳解Android中的MVP架構分解和實現
1、概述傳統的Android開發架構一般是MVC模式, Model:業務邏輯和實體模型 View:對應於布局文件 Controllor:對應於Activity 單