編輯:關於Android編程
相關概念:
ViewRoot:ViewRoot對應於ViewRootImpl類,它是連接WindowManager和DecorView的紐帶,View的三大流程都是在viewroot中完成。
View的繪制流程:
View的繪制流程是從ViewRoot的performTraversals方法開始的,它經過measure,layout,draw三個過程才最終將一個View繪制出來,performTraversals會一次調用performMeasure,performLayout和performDraw三個方法,這三個方法分別會完成view的measure,layout,draw的流程,在measure方法中,又會調用onMeasure方法,在onMeasure方法中會對所有的子元素進行measure過程,這個時候measure流程就從父容器傳遞給子容器,這樣就完成了一次測量接著子元素會重復父容器的measure的測量過程,如此反復的完成整個View樹的過程,同理performLayout的執行原理和performDraw的執行原理和performMeasure的原理類似。
measure過程中決定了View的寬和高,Measure完成後,可以通過getMeasureWidth和getMeasureHeight方法來獲取到View測量後的寬和高,在幾乎所有情況下,它都等於最終的寬/高,但有一些特殊的情況。Layout過程中決定了View四個頂點的坐標,和實際View的寬和高。完成後可以通過getTop,getBottom,getLeft,getRight來拿到四個頂點的位置,並且可以通過getWidth,和getHeight完成最終的寬和高。Draw過程決定View的顯示,只有Draw以後View才會顯示在屏幕上。
DecorView作為頂級View,一般情況它內部包含一個豎直方向的Linearlayout,在這個LinearLayout裡面有上下兩個部分,上面是標題欄,下面是內容欄,在Activity中我們設置的setContentView所設置的View,實際上是被加載到了內容欄上了,而內容欄的id叫content,我們的布局確實又加載到了content上,因此叫做setContentView。,實際上DecorView是一個FrameLayout,View事件都是經過DecorView才傳到我們的View。
理解MeasureSpec
MeasureSpec可以翻譯為測量規格,在測量中,系統會將View的LayoutParams根據父容器所施加的規則轉換成相應的MeasureSpec,然後再根據MeasureSpec測量出View的寬和高。MeasureSpec代表一個32位的int值,高2位代表SpecMode,低30位代表SpecSize,SpecMode是指測量模式,而SpecSize是指某種測量模式下的測量出來的大小,
MeasureSpec有三種模式:
UNSPECIFIED
父容器不對View有任何限制,要多大就多大,這種情況一般用於系統內部,表示一種測量狀態。
EXACTLY
父容器已經測量出來View的精確大小,這個時候View的最終大小就是MeasureSpec測量的值,它對應於LayoutParams中的Match_parent和具體數值的兩種情況。
AT_MOST
父容器指定了一個可用大小即SpecSize,View的大小不能大於這個值,具體多少,要看View的具體情況,它對應於LayoutParams的wrap_content這種情況。
View的寬高受View自身的LayoutParams和父容器的約束所決定,轉換成相應的MeasureSpec,一旦MeasureSpec確定,onMeasure中就可以View測量的寬和高。
對於普通的View來說,這裡是指我們布局中的View,View的measure過程是由ViewGroup傳遞過來的,先看一下ViewGroup的measureChiled
View的工作流程:
View的工作流程是指measure,layout,draw這三大流程,即測量,布局和繪制,其中measure是測量view的寬和高,layout是確定View控件四個頂點的位置,而draw則將View繪制在屏幕上。
View的measure過程:
View的measure過程由其measure方法來完成,measure方法是一個final類型,這意味著子類不能去重新這個方法,而measure方法中會調用onMeasure這個方法,因此我們去重寫onMeasure這個方法。
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(),widthMeasureSpec), getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(),widthMeasureSpec));
}
setMeasureDimension會設置View寬和高的測量值,下面看一下getDefaultSize()這個方法:
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
如果測量模式是MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED 則默認值為size,是其它兩種模式的話,就用測量的值,測量的值為specSize.
下面看一下,getSuggestedMinimumWidth這個方法:
protected int getSuggestedMinimumWidth() {
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinWidth : max(mMinWidth, mBackground.getMinimumWidth());
}
返回值得大小取決於控件view有沒有設置背景,有設置背景,那麼view的寬或者高的大小為mMinWidth和背景的最小寬或者高,如果沒有背景,那麼view的寬/高的測量返回這就是mMinWidth這個值,這個值為0。
下面我們實際書寫寫關於onMeasure方法的代碼:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int mWidth = 0;//這是我們想要設置的寬度
int mHeight = 0;//這是我們想要設置的高度
int widthMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if(widthMeasureSpec==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightMeasureSpec==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, mHeight);
}else if(widthMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, heightSize);
}else if(heightMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, mHeight);
}
}
ViewGroup的測量過程:
對於ViewGroup來說,除了完成自己的measure過程外,還要遍歷去測量子View的measure方法,各個子元素在遞歸去執行這個過程,和View不同的是,ViewGroup是一個抽象類,因此它沒有重寫View的onMeasure方法,但它提供了一個叫measureChildren的方法
protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
final int size = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
final View child = children[i];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != GONE) {
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
從代碼中可以看出來,在measureChildren方法中,會遍歷所有子View,然後通過measureChild這個方法去測量每一個子View。
measureChild方法如下:
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
最後一行表明,去調用view的measure方法,在最後調用onMeasure方法,這又回到了View的measure過程。
實際情況可以這麼寫:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
{
/**
* 顯示的設置一個寬度
*/
if (!once)
{
LinearLayout wrapper = (LinearLayout) getChildAt(0);
menu = (ViewGroup) wrapper.getChildAt(0);
ViewGroup content = (ViewGroup) wrapper.getChildAt(1);
mMenuWidth = mScreenWidth - mMenuRightPadding;
mHalfMenuWidth = mMenuWidth / 2;
menu.getLayoutParams().width = mMenuWidth;
content.getLayoutParams().width = mScreenWidth;
}
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
在onMeasure完後可以通過getMeasureWidth和getMeasureHeight來得到測量view的寬和高,在某些極端情況下,系統可能需要多次測量,在這種情況下,我們通過getMeasureWidth和getMeasureHeight拿到的寬和高是不准確的,一個較好的習慣是在onLayout方法中獲取View的測量寬或者高。
可能遇到的問題:
View的onMeasure和Acitivity的生命周期是不同步的,在onCreat,onStart,onResume中getMeasureWidth/getMeasureHeight獲得寬和高,很可能是0,這裡給出了4中解決方法。
1.Activity中的onWindowFocesChanged方法,通過上面的方法可以獲得測量後的寬高。單這個方法會被調用多次。
@Override
public void onWindowFocusChanged(boolean hasFocus) {
super.onWindowFocusChanged(hasFocus);
if(hasFocus){
int mWidth=view.getMeasuredWidth();
int height=view.getMeasuredHeight();
}
}
2.view.post(runnable)方法: 通過post可以將一個runnable投遞到消息隊列的尾部,然後等待Looper調用此runnable的時候,View也初始化好了。
view.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
int mWidth=view.getMeasuredWidth();
int mHeight=view.getMeasuredHeight();
}
});
3.ViewTreeObserver 使用OnGlobalLayoutListener這個接口,當View樹的狀態發生改變或者View樹內部View的可見性發生改變的時候,onGlobalLayout方法會被回調,需要注意的是隨著View樹的改變,這個方法會被調用多次:
ViewTreeObserver observer=view.getViewTreeObserver();
observer.addOnGlobalLayoutListener(new OnGlobalLayoutListener() {
@Override
public void onGlobalLayout() {
view.getViewTreeObserver().removeOnGlobalLayoutListener(this);
int mWidth=view.getMeasuredWidth();
int mHeight=view.getMeasuredHeight();
}
});
4.view.measure(int widthMeasureSpec,int heightMeasureSpec ) 比較復雜,這裡不做解釋了。
Layout過程:
Layout的作用是ViewGroup用來確定子元素的位置,當ViewGroup的位置被確定後,它在onLayout方法中會遍歷所有子元素,並調用layout方法。而layout方法中onLayout方法會被調用,所以我們重寫這個方法。Layout方法和Measure相比要簡單許多,layout是確定View本身的位置,而onLayout方法會確定所有子元素的位置,先看View的layout方法:
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
if ((mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT) != 0) {
onMeasure(mOldWidthMeasureSpec, mOldHeightMeasureSpec);
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
int oldL = mLeft;
int oldT = mTop;
int oldB = mBottom;
int oldR = mRight;
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners != null) {
ArrayList listenersCopy =
(ArrayList)li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners.clone();
int numListeners = listenersCopy.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; ++i) {
listenersCopy.get(i).onLayoutChange(this, l, t, r, b, oldL, oldT, oldR, oldB);
}
}
}
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_IS_LAID_OUT;
}
在第16行走onLayout方法,layout方法的流程是:首先通過setFrame方法來設定View四個頂點的位置,即初始化了,l,t,r,b這四個值,View的這四個頂點一確定,那麼View在父容器中的位置也就確定了,接著會被調用onLayout方法,這個方法的用途是為了確定子View在父控件中的位置,和onMeasure類似,onLayout的實現和具體的布局有關,view和viewGroup軍沒有實現onLayout方法,因此我們隨便找一個父控件看onLayout方法,例如LinearLayout中的onLayout方法:
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
layoutVertical(l, t, r, b);
} else {
layoutHorizontal(l, t, r, b);
}
}
Draw過程:
draw過程的原裡就簡單了,它的作用是將View繪制到屏幕上,View的繪制過程遵循如下幾步:
1.繪制背景 2.繪制自己 3.繪制children 4.繪制裝飾。
draw方法的代碼如下:
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
if (mClipBounds != null) {
canvas.clipRect(mClipBounds);
}
final int privateFlags = mPrivateFlags;
final boolean dirtyOpaque = (privateFlags & PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) == PFLAG_DIRTY_OPAQUE &&
(mAttachInfo == null || !mAttachInfo.mIgnoreDirtyState);
mPrivateFlags = (privateFlags & ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) | PFLAG_DRAWN;
/*
* Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed
* in the appropriate order:
*
* 1. Draw the background
* 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading
* 3. Draw view's content
* 4. Draw children
* 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers
* 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance)
*/
// Step 1, draw the background, if needed
int saveCount;
if (!dirtyOpaque) {
final Drawable background = mBackground;
if (background != null) {
final int scrollX = mScrollX;
final int scrollY = mScrollY;
if (mBackgroundSizeChanged) {
background.setBounds(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop);
mBackgroundSizeChanged = false;
}
if ((scrollX | scrollY) == 0) {
background.draw(canvas);
} else {
canvas.translate(scrollX, scrollY);
background.draw(canvas);
canvas.translate(-scrollX, -scrollY);
}
}
}
// skip step 2 & 5 if possible (common case)
final int viewFlags = mViewFlags;
boolean horizontalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_HORIZONTAL) != 0;
boolean verticalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_VERTICAL) != 0;
if (!verticalEdges && !horizontalEdges) {
// Step 3, draw the content
if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas);
// Step 4, draw the children
dispatchDraw(canvas);
// Step 6, draw decorations (scrollbars)
onDrawScrollBars(canvas);
if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas);
}
// we're done...
return;
}
/*
* Here we do the full fledged routine...
* (this is an uncommon case where speed matters less,
* this is why we repeat some of the tests that have been
* done above)
*/
boolean drawTop = false;
boolean drawBottom = false;
boolean drawLeft = false;
boolean drawRight = false;
float topFadeStrength = 0.0f;
float bottomFadeStrength = 0.0f;
float leftFadeStrength = 0.0f;
float rightFadeStrength = 0.0f;
// Step 2, save the canvas' layers
int paddingLeft = mPaddingLeft;
final boolean offsetRequired = isPaddingOffsetRequired();
if (offsetRequired) {
paddingLeft += getLeftPaddingOffset();
}
int left = mScrollX + paddingLeft;
int right = left + mRight - mLeft - mPaddingRight - paddingLeft;
int top = mScrollY + getFadeTop(offsetRequired);
int bottom = top + getFadeHeight(offsetRequired);
if (offsetRequired) {
right += getRightPaddingOffset();
bottom += getBottomPaddingOffset();
}
final ScrollabilityCache scrollabilityCache = mScrollCache;
final float fadeHeight = scrollabilityCache.fadingEdgeLength;
int length = (int) fadeHeight;
// clip the fade length if top and bottom fades overlap
// overlapping fades produce odd-looking artifacts
if (verticalEdges && (top + length > bottom - length)) {
length = (bottom - top) / 2;
}
// also clip horizontal fades if necessary
if (horizontalEdges && (left + length > right - length)) {
length = (right - left) / 2;
}
if (verticalEdges) {
topFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getTopFadingEdgeStrength()));
drawTop = topFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f;
bottomFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getBottomFadingEdgeStrength()));
drawBottom = bottomFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f;
}
if (horizontalEdges) {
leftFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getLeftFadingEdgeStrength()));
drawLeft = leftFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f;
rightFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getRightFadingEdgeStrength()));
drawRight = rightFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f;
}
saveCount = canvas.getSaveCount();
int solidColor = getSolidColor();
if (solidColor == 0) {
final int flags = Canvas.HAS_ALPHA_LAYER_SAVE_FLAG;
if (drawTop) {
canvas.saveLayer(left, top, right, top + length, null, flags);
}
if (drawBottom) {
canvas.saveLayer(left, bottom - length, right, bottom, null, flags);
}
if (drawLeft) {
canvas.saveLayer(left, top, left + length, bottom, null, flags);
}
if (drawRight) {
canvas.saveLayer(right - length, top, right, bottom, null, flags);
}
} else {
scrollabilityCache.setFadeColor(solidColor);
}
// Step 3, draw the content
if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas);
// Step 4, draw the children
dispatchDraw(canvas);
// Step 5, draw the fade effect and restore layers
final Paint p = scrollabilityCache.paint;
final Matrix matrix = scrollabilityCache.matrix;
final Shader fade = scrollabilityCache.shader;
if (drawTop) {
matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * topFadeStrength);
matrix.postTranslate(left, top);
fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix);
canvas.drawRect(left, top, right, top + length, p);
}
if (drawBottom) {
matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * bottomFadeStrength);
matrix.postRotate(180);
matrix.postTranslate(left, bottom);
fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix);
canvas.drawRect(left, bottom - length, right, bottom, p);
}
if (drawLeft) {
matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * leftFadeStrength);
matrix.postRotate(-90);
matrix.postTranslate(left, top);
fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix);
canvas.drawRect(left, top, left + length, bottom, p);
}
if (drawRight) {
matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * rightFadeStrength);
matrix.postRotate(90);
matrix.postTranslate(right, top);
fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix);
canvas.drawRect(right - length, top, right, bottom, p);
}
canvas.restoreToCount(saveCount);
// Step 6, draw decorations (scrollbars)
onDrawScrollBars(canvas);
if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas);
}
}
View繪制過程的傳遞是通過dispatchDraw來實現的,dispatchDraw會遍歷所有子元素的draw方法,如此draw事件就一層層的傳遞下去。
自定義View所涉及到的一些有關問題:
1.如果有必要讓你的View支持padding
這是因為直接繼承View的控件,如果不在draw方法中處理paddding,那麼padding屬性無法起作用,另外直接繼承自ViewGroup的控件需要在onMeasure和onLayout中考慮padding和子元素的margin對其造成的影響,不然將導致padding和子元素的margin失效。
在onDraw中考慮padding的代碼:
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
int paddingLeft=getPaddingLeft();
int paddingRight=getPaddingRight();
int paddingTop=getPaddingTop();
int paddingBottom=getPaddingBottom();
int mWidth=getWidth()-paddingLeft-getPaddingRight();
int mHeight=getHeight()-paddingTop-paddingBottom;
canvas.drawCircle(mWidth/2, mHeight/2,50,paint);
}
為了使用自定義屬性,必須在布局文件中添加schemas聲明:xmlns:app=”http:android.com/apl/res-auto”,在這個聲明中,app是自定義的,可以換成任意名字,但是自定義屬性xml使用的時候必須和這個一致,也有另外一種聲明方式,如:schemas:xmlns:app=”http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.ryg.chapter_4”,這種方式是apk/res後面附加應用的包名,但是這種方式並沒有本質的區別。
繼承ViewGroop的onMeasure和onLayout方法:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int mWidth=0;
int mHeight=0;
int mChildCount=getChildCount();
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSpec=MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpec=MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int HeightMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
if(mChildCount==0){
setMeasuredDimension(0, 0);
}else{
if(MeasureSpec.AT_MOST==widthMode && MeasureSpec.AT_MOST==HeightMode){
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, mHeight);
}else if(MeasureSpec.AT_MOST==widthMode){
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, heightSpec);
}else if(MeasureSpec.AT_MOST==HeightMode){
setMeasuredDimension(widthMode, mHeight);
}
}
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
super.onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
int childLeft=0;
int childCount=getChildCount();
for(int i=0;i
 AsyncTask陷阱之:Handler,Looper與MessageQueue的詳解
AsyncTask陷阱之:Handler,Looper與MessageQueue的詳解
AsyncTask的隱蔽陷阱先來看一個實例這個例子很簡單,展示了AsyncTask的一種極端用法,挺怪的。復制代碼 代碼如下:public class AsyncTask
 SEAndroid 介紹及其基本實現原理
SEAndroid 介紹及其基本實現原理
1. 什麼是SEAndroid SEAndroid(Security-Enhanced Android)是有美國國家安全局(NSA)開發的開源安全項目,是在
 小米5尊享版和標准版有什麼區別
小米5尊享版和標准版有什麼區別
小米5尊享版和標准版有什麼區別?備受期待的小米手機5於2月24日發布,推出了三個版本,分別是標准版、高配版和尊享版,標准版和高配版僅在內存上有不同,而尊享版
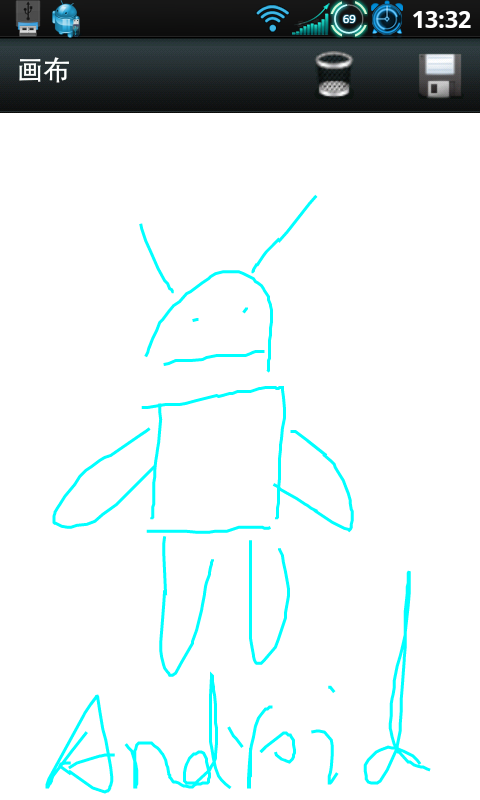 Android編程實現手繪及保存為圖片的方法(附demo源碼下載)
Android編程實現手繪及保存為圖片的方法(附demo源碼下載)
本文實例講述了Android編程實現手繪及保存為圖片的方法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:運行效果圖預覽:應 yzuo_08 要求做了此Demo,跟以前那個手寫板Dem