編輯:關於Android編程
市場人員反映公司的app使用系統設置俄語、西班牙語,double數據會把小數點變為逗號。調試一下,是自定義的語言時候(例如,俄語、西班牙語)轉換String.format("%.2f",67.876)。會出現的。
Android【設置】-【語言和輸入法】-【語言】列表中找到相應語言所對應的列表項
java.util.Locale類
在這個Locale類裡面,有些語言是沒有,例如俄語、西班牙語等。那麼這時候android開發時候需要這些語言,怎麼辦。只好後面自已新建,自定義。
/**
* Locale constant for en_CA.
*/
public static final Locale CANADA = new Locale(true, "en", "CA");
/**
* Locale constant for fr_CA.
*/
public static final Locale CANADA_FRENCH = new Locale(true, "fr", "CA");
/**
* Locale constant for zh_CN.
*/
public static final Locale CHINA = new Locale(true, "zh", "CN");
/**
* Locale constant for zh.
*/
public static final Locale CHINESE = new Locale(true, "zh", "");
/**
* Locale constant for en.
*/
public static final Locale ENGLISH = new Locale(true, "en", "");
/**
* There's a circular dependency between toLowerCase/toUpperCase and
* Locale.US. Work around this by avoiding these methods when constructing
* the built-in locales.
*
* @param unused required for this constructor to have a unique signature
*/
private Locale(boolean unused, String lowerCaseLanguageCode, String upperCaseCountryCode) {
this.languageCode = lowerCaseLanguageCode;
this.countryCode = upperCaseCountryCode;
this.variantCode = "";
}
/**
* Constructs a new {@code Locale} using the specified language, country,
* and variant codes.
*/
public Locale(String language, String country, String variant) {
if (language == null || country == null || variant == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (language.isEmpty() && country.isEmpty()) {
languageCode = "";
countryCode = "";
variantCode = variant;
return;
}
languageCode = language.toLowerCase(Locale.US);
// Map new language codes to the obsolete language
// codes so the correct resource bundles will be used.
if (languageCode.equals("he")) {
languageCode = "iw";
} else if (languageCode.equals("id")) {
languageCode = "in";
} else if (languageCode.equals("yi")) {
languageCode = "ji";
}
countryCode = country.toUpperCase(Locale.US);
// Work around for be compatible with RI
variantCode = variant;
}
@Override public Object clone() {
try {
return super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new AssertionError(e);
}
}
private static final Locale Locale_Russia = new Locale("RUS", "ru", "");
private static final Locale Locale_Spanish = new Locale("ES", "es", "");
public static void setApplicationLauguageType(Context context, int type) {
if (context == null) return;
Resources resources = context.getResources();//獲得res資源對象
Configuration config = resources.getConfiguration();//獲得設置對象
DisplayMetrics dm = resources .getDisplayMetrics();//獲得屏幕參數:主要是分辨率,像素等。
switch (type) {
case 0:
config.locale = Locale.getDefault();
break;
case 1:
config.locale = Locale.SIMPLIFIED_CHINESE;
break;
case 2:
config.locale = Locale.ENGLISH;
break;
case 3:
config.locale = Locale_Russia;
break;
case 4:
config.locale = Locale_Spanish;
break;
default:
config.locale = Locale.getDefault();
break;
}
resources.updateConfiguration(config, dm);
}
/**
* Returns a localized formatted string, using the supplied format and arguments,
* using the user's default locale.
*
*
If you're formatting a string other than for human * consumption, you should use the {@code format(Locale, String, Object...)} * overload and supply {@code Locale.US}. See * "Be wary of the default locale". * * @param format the format string (see {@link java.util.Formatter#format}) * @param args * the list of arguments passed to the formatter. If there are * more arguments than required by {@code format}, * additional arguments are ignored. * @return the formatted string. * @throws NullPointerException if {@code format == null} * @throws java.util.IllegalFormatException * if the format is invalid. * @since 1.5 */ public static String format(String format, Object... args) { return format(Locale.getDefault(), format, args); }
這上面是一般調用方法,String strResult = String.format("%0.2f",543.6356);
/**
* Returns a formatted string, using the supplied format and arguments,
* localized to the given locale.
*
* @param locale
* the locale to apply; {@code null} value means no localization.
* @param format the format string (see {@link java.util.Formatter#format})
* @param args
* the list of arguments passed to the formatter. If there are
* more arguments than required by {@code format},
* additional arguments are ignored.
* @return the formatted string.
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code format == null}
* @throws java.util.IllegalFormatException
* if the format is invalid.
* @since 1.5
*/
public static String format(Locale locale, String format, Object... args) {
if (format == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("format == null");
}
int bufferSize = format.length() + (args == null ? 0 : args.length * 10);
Formatter f = new Formatter(new StringBuilder(bufferSize), locale);
return f.format(format, args).toString();
}
double dValue = 360.672;
String strValue = String.format("%.2f",dValue);
結果360,672
double dValue = 360.672; String strValue = String.format(Locale.ENGLISH,"%.2f",dValue);
String strResult = String.format("%s:%.3f\r\n", getString(R.string.IteInfoCoorType, 654.76);
這個就要分開轉換再接起來,不然都是英文,轉換不了其他的語言的。
這個設計上缺陷是否是android sdk 或者jdk的存在bug。我使用都是jdk1.7和sdk 4.2版本。
歡迎大家發現與測試。
String.format("%.2f",dValue);
String.format(Locale.ENGLISH,"%.2f",dValue);
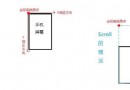 android坐標
android坐標
說來說去都不如 畫圖示意 簡單易懂啊!!!真是的! 來吧~~先上張圖~~! (一)首先明確一下Android中的坐標系統:屏幕的左上角是坐標系統原點(0,0)原
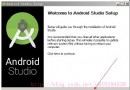 Android Studio安裝配置詳細步驟(圖文)
Android Studio安裝配置詳細步驟(圖文)
為什麼要使用Android StudioAndroid Studio是谷歌推出了新的Android開發環境,其重要性可想而知!1. 集成了Gradle 打包工具2. 所見
 Android仿IOS ViewPager滑動進度條
Android仿IOS ViewPager滑動進度條
最近做項目,碰到如下的需求:ViewPager分頁,如果是6頁(包括6頁)就用圓點,如果是6頁以上就用進度條來切換。前面一種交互方法最常見,用小圓點來表示當前選中的頁面,
 Android自動化測試--Espresso框架使用
Android自動化測試--Espresso框架使用
且說正文之前,還是先說說Android單元測試的意義或者說為什麼我們要進行Android的單元測試?為什麼要進行單元測試?單元測試可以幫助我們程序員將bug消滅在萌芽期,