編輯:關於Android編程
package org.cocos2d.tests;
import java.util.Iterator;
import org.cocos2d.actions.UpdateCallback;
import org.cocos2d.config.ccMacros;
import org.cocos2d.events.CCTouchDispatcher;
import org.cocos2d.layers.CCLayer;
import org.cocos2d.layers.CCScene;
import org.cocos2d.nodes.CCDirector;
import org.cocos2d.nodes.CCLabel;
import org.cocos2d.nodes.CCSprite;
import org.cocos2d.nodes.CCSpriteSheet;
import org.cocos2d.opengl.CCGLSurfaceView;
import org.cocos2d.types.CGPoint;
import org.cocos2d.types.CGRect;
import org.cocos2d.types.CGSize;
import org.cocos2d.types.ccColor3B;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.Window;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.Vector2;
import com.badlogic.gdx.physics.box2d.Body;
import com.badlogic.gdx.physics.box2d.BodyDef;
import com.badlogic.gdx.physics.box2d.BodyDef.BodyType;
import com.badlogic.gdx.physics.box2d.EdgeShape;
import com.badlogic.gdx.physics.box2d.FixtureDef;
import com.badlogic.gdx.physics.box2d.PolygonShape;
import com.badlogic.gdx.physics.box2d.World;
/**
* A test that demonstrates basic JBox2D integration by using AtlasSprites connected to physics bodies.
* <br/>
* <br/>
* This implementation is based on the original Box2DTest (from cocos2d-iphone) but using the JBox2D
* library and adjusting for differences with the new API as well as some differences in sensitivity
* (and such) that were observed when testing on the Android platform.
*
* @author Ray Cardillo
*/
// Box2dTest, there is a downloadable demo here:
// http://code.google.com/p/cocos2d-android-1/downloads/detail?name=cocos2d%20%20and%20jbox2d.3gp&can=2&q=#makechanges
//
public class Box2dTest extends Activity {//物理盒子系統
// private static final String LOG_TAG = JBox2DTest.class.getSimpleName();
static {
System.loadLibrary("gdx");//加載一個gdx庫
}
private CCGLSurfaceView mGLSurfaceView;//創建一個view
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);//無標題
getWindow().setFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN,
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN);//全屏
getWindow().setFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_KEEP_SCREEN_ON,
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_KEEP_SCREEN_ON);//不黑屏
mGLSurfaceView = new CCGLSurfaceView(this);//生成view,並關聯上下文到導演
CCDirector director = CCDirector.sharedDirector();//生成得到導演(唯一)
director.attachInView(mGLSurfaceView);//把view交給導演的list
director.setDeviceOrientation(CCDirector.kCCDeviceOrientationLandscapeLeft);//橫屏
setContentView(mGLSurfaceView);//把view映射刀屏幕
// show FPS
CCDirector.sharedDirector().setDisplayFPS(true);//顯示幀頻率
// frames per second
CCDirector.sharedDirector().setAnimationInterval(1.0f / 60.0f);//幀速
CCScene scene = CCScene.node();//得到一個場景
scene.addChild(new Box2DTestLayer());//把一個box的圖層添加到場景裡
// Make the Scene active
CCDirector.sharedDirector().runWithScene(scene);//讓導演運行這個場景,運行到剛才的view中
}
@Override
public void onStart() {//開始方法
super.onStart();
}
@Override
public void onPause() {//暫停方法
super.onPause();
CCDirector.sharedDirector().onPause();
}
@Override
public void onResume() {
super.onResume();
CCDirector.sharedDirector().onResume();
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {//銷毀方法
super.onDestroy();
CCDirector.sharedDirector().end();
//CCTextureCache.sharedTextureCache().removeAllTextures();
}
//
// Demo of calling integrating Box2D physics engine with cocos2d sprites
// a cocos2d example
// http://code.google.com/p/cocos2d-iphone
//
// by Steve Oldmeadow
//
static class Box2DTestLayer extends CCLayer {//以下是這個方法生成的方法
public static final int kTagTileMap = 1;
public static final int kTagSpriteManager = 1;
public static final int kTagAnimation1 = 1;
// Pixel to meters ratio. Box2D uses meters as the unit for measurement.
// This ratio defines how many pixels correspond to 1 Box2D "meter"
// Box2D is optimized for objects of 1x1 meter therefore it makes sense
// to define the ratio so that your most common object type is 1x1 meter.
protected static final float PTM_RATIO = 32.0f;
// Simulation space should be larger than window per Box2D recommendation.
protected static final float BUFFER = 1.0f;
//FPS for the PhysicsWorld to sync to
protected static final float FPS = (float)CCDirector.sharedDirector().getAnimationInterval();//得到整個動畫的幀頻率
private static float rdelta = 0;
protected final World bxWorld;//生成一個世界的引用..
public Box2DTestLayer() {//構造方法
super();
this.setIsTouchEnabled(true);//可以點擊
this.setIsAccelerometerEnabled(true);//啟用設置加速,加速控制器可以啟動
CGSize s = CCDirector.sharedDirector().winSize();//得到屏幕的大小引用
// Define the gravity vector.
Vector2 gravity = new Vector2(9.8f, -9.8f);//定義一個二維向量
float scaledWidth = s.width/PTM_RATIO;//縮放寬
float scaledHeight = s.height/PTM_RATIO;//縮放高
// Vector2 lower = new Vector2(-BUFFER, -BUFFER);//更小
// Vector2 upper = new Vector2(scaledWidth+BUFFER, scaledHeight+BUFFER);//更大
bxWorld = new World(gravity, true);//新建並設置這個世界的重力向量
bxWorld.setContinuousPhysics(true);//連續物理可用
// Define the ground body.
BodyDef bxGroundBodyDef = new BodyDef();//定義地面身體
bxGroundBodyDef.position.set(0.0f, 0.0f);//身體的位置
// Call the body factory which allocates memory for the ground body
// from a pool and creates the ground box shape (also from a pool).
// The body is also added to the world.
Body groundBody = bxWorld.createBody(bxGroundBodyDef);//將身體添加到世界
// Define the ground box shape.
EdgeShape groundBox = new EdgeShape();//定義一個形狀
Vector2 bottomLeft = new Vector2(0f,0f);//定義4個2維向量
Vector2 topLeft = new Vector2(0f,scaledHeight);
Vector2 topRight = new Vector2(scaledWidth,scaledHeight);
Vector2 bottomRight = new Vector2(scaledWidth,0f);
// bottom
groundBox.set( bottomLeft, bottomRight );//設置一條線
groundBody.createFixture(groundBox,0);//把這條線作為物理盒子的邊界
// top
groundBox.set( topLeft, topRight );//同理
groundBody.createFixture(groundBox,0);
// left
groundBox.set( topLeft, bottomLeft );
groundBody.createFixture(groundBox,0);
// right
groundBox.set( topRight, bottomRight );
groundBody.createFixture(groundBox,0);
//Set up sprite
CCSpriteSheet mgr = CCSpriteSheet.spriteSheet("blocks.png", 150);
//建立一個圖像表單,用來拆分出小塊
addChild(mgr, 0, kTagSpriteManager);//表單添加進去,順序0,把標簽號定為1
addNewSpriteWithCoords(CGPoint.ccp(s.width / 2.0f, s.height / 2.0f));
//上面是一個方法下面解釋
CCLabel label = CCLabel.makeLabel("Tap screen", "DroidSans", 32);//創建一個標記
label.setPosition(CGPoint.make(s.width / 2f, s.height - 50f));//設置坐標
label.setColor(new ccColor3B(0, 0, 255));//設置顏色
addChild(label);
}
private UpdateCallback tickCallback = new UpdateCallback() {//創建一個時間返回
@Override
public void update(float d) {//時間更新
tick(d);
}
};
@Override
public void onEnter() {
super.onEnter();
// start ticking (for physics simulation)
schedule(tickCallback);
}
@Override
public void onExit() {
super.onExit();
// stop ticking (for physics simulation)
unschedule(tickCallback);
}
private void addNewSpriteWithCoords(CGPoint pos) {
CCSpriteSheet sheet = (CCSpriteSheet) getChildByTag(kTagSpriteManager);//得到一個表格
//We have a 64x64 sprite sheet with 4 different 32x32 images. The following code is
//just randomly picking one of the images
int idx = (ccMacros.CCRANDOM_0_1() > .5 ? 0:1);//定義一個隨機數。得到1/0
int idy = (ccMacros.CCRANDOM_0_1() > .5 ? 0:1);
// CCSprite sprite = CCSprite.sprite("blocks.png", CGRect.make(32 * idx,32 * idy,32,32));//生成一個精靈。用那個圖片,截取公式位置的圖像
// this.addChild(sprite);//添加精靈
CCSprite sprite = CCSprite.sprite(sheet, CGRect.make(32 * idx,32 * idy,32,32));//生成精靈,用剛才的那個圖集,截取某塊
sheet.addChild(sprite);//添加子類
sprite.setPosition(pos); //設置點
// Define the dynamic body.
//Set up a 1m squared box in the physics world
BodyDef bodyDef = new BodyDef();//新建一個剛體
bodyDef.type = BodyType.DynamicBody;//設置為類型3動態剛體
bodyDef.position.set(pos.x/PTM_RATIO, pos.y/PTM_RATIO);//設置身體位置
// Define another box shape for our dynamic body.
PolygonShape dynamicBox = new PolygonShape();//新建多邊形
dynamicBox.setAsBox(.5f, .5f);//These are mid points for our 1m box
//作為一個盒子時的頂點0.5,0.5
// dynamicBox.density = 1.0f;
// dynamicBox.friction = 0.3f;
synchronized (bxWorld) {//線程鎖
// Define the dynamic body fixture and set mass so it's dynamic.
Body body = bxWorld.createBody(bodyDef);//在世界內創建這個剛體
body.setUserData(sprite);//使用這個數據精靈
FixtureDef fixtureDef = new FixtureDef();//固定的東西
fixtureDef.shape = dynamicBox;
fixtureDef.density = 1.0f;//密度
fixtureDef.friction = 0.3f;//摩擦系數
body.createFixture(fixtureDef);//把這些固定參數給這個物體
}
}
public synchronized void tick(float delta) {//時間類
if ((rdelta += delta) < FPS) return;//計算得不用快過幀..
// It is recommended that a fixed time step is used with Box2D for stability
// of the simulation, however, we are using a variable time step here.
// You need to make an informed choice, the following URL is useful
// http://gafferongames.com/game-physics/fix-your-timestep/
// Instruct the world to perform a simulation step. It is
// generally best to keep the time step and iterations fixed.
synchronized (bxWorld) {
bxWorld.step(FPS, 8, 1);//計算的速度
}
rdelta = 0;//累計時間
// Iterate over the bodies in the physics world
Iterator<Body> it = bxWorld.getBodies();//新建迭代器得到世界的剛體集合
while(it.hasNext()) {
Body b = it.next();//得到剛體
Object userData = b.getUserData();//剛體的數據
if (userData != null && userData instanceof CCSprite) {
//如果數據不為空,且是個精靈的實例而
//Synchronize the Sprites position and rotation with the corresponding body
final CCSprite sprite = (CCSprite)userData;//得到這個圖像
final Vector2 pos = b.getPosition();//得到這個剛體的點
sprite.setPosition(pos.x * PTM_RATIO, pos.y * PTM_RATIO);
//設置點
sprite.setRotation(-1.0f * ccMacros.CC_RADIANS_TO_DEGREES(b.getAngle()));//設置弧度
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean ccTouchesBegan(MotionEvent event) {//觸屏事件
CGPoint location = CCDirector.sharedDirector()
.convertToGL(CGPoint.make(event.getX(), event.getY()));//得到點
addNewSpriteWithCoords(location);//添加一個物品在那個點
return CCTouchDispatcher.kEventHandled;//返回數據
}
static float prevX=0, prevY=0;
Vector2 gravity = new Vector2();//定義2維數組
@Override
public void ccAccelerometerChanged(float accelX, float accelY, float accelZ) {//當加速傳感器有感覺了
//#define kFilterFactor 0.05f
float kFilterFactor = 1.0f; // don't use filter. the code is here just as an example
float accX = (float) accelX * kFilterFactor + (1- kFilterFactor)* prevX;//x方向
float accY = (float) accelY * kFilterFactor + (1- kFilterFactor)* prevY;//y方向
prevX = accX;
prevY = accY;
// no filtering being done in this demo (just magnify the gravity a bit)
gravity.set( accY * 9.8f, accX * -9.8f );//得到重力的向量
bxWorld.setGravity( gravity ); //給世界設置重力向量
}
}
}
 Android自定義View實現字母導航欄的代碼
Android自定義View實現字母導航欄的代碼
思路分析:1、自定義View實現字母導航欄2、ListView實現聯系人列表3、字母導航欄滑動事件處理4、字母導航欄與中間字母的聯動5、字母導航欄與ListView的聯動
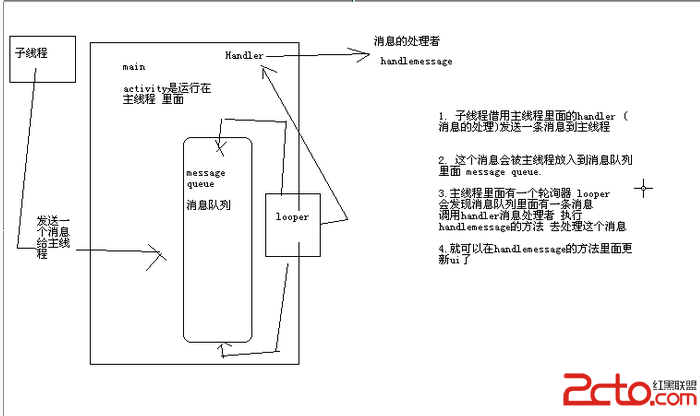 android中子線程更新UI的方式淺析
android中子線程更新UI的方式淺析
一、為何寫作此文??你是不是經常看到很多書籍中說:不能在子線程中操作ui,不然會報錯。你是不是也遇到了如下的疑惑(見下面的代碼):@Override prote
 Android從零單排之獲取ImageView的寬高為0?
Android從零單排之獲取ImageView的寬高為0?
問題描述 說起來我也夠菜的!⊙﹏⊙b汗。 今天搞了一個關於圖片的demo,想動態的改變一張圖片的大小和margin值。但是在activity
 Android自定義控件之仿美團下拉刷新
Android自定義控件之仿美團下拉刷新
美團的下拉刷新分為三個狀態:第一個狀態為下拉刷新狀態(pull to refresh),在這個狀態下是一個綠色的橢圓隨著下拉的距離動態改變其大小。第二個部分為放開刷新狀態