編輯:關於Android編程
1 /**
2 * Creates a thread pool that reuses a fixed number of threads
3 * operating off a shared unbounded queue. At any point, at most
4 * {@code nThreads} threads will be active processing tasks.
5 * If additional tasks are submitted when all threads are active,
6 * they will wait in the queue until a thread is available.
7 * If any thread terminates due to a failure during execution
8 * prior to shutdown, a new one will take its place if needed to
9 * execute subsequent tasks. The threads in the pool will exist
10 * until it is explicitly {@link ExecutorService#shutdown shutdown}.
11 *
12 * @param nThreads the number of threads in the pool
13 * @return the newly created thread pool
14 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code nThreads <= 0}
15 */
16 public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
17 return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
18 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
19 new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
20 }
這個線程池,就是有固定線程數的一個線程池,有共享的無界隊列來運行這些線程。
1 /**
2 * Creates a thread pool that creates new threads as needed, but
3 * will reuse previously constructed threads when they are
4 * available. These pools will typically improve the performance
5 * of programs that execute many short-lived asynchronous tasks.
6 * Calls to {@code execute} will reuse previously constructed
7 * threads if available. If no existing thread is available, a new
8 * thread will be created and added to the pool. Threads that have
9 * not been used for sixty seconds are terminated and removed from
10 * the cache. Thus, a pool that remains idle for long enough will
11 * not consume any resources. Note that pools with similar
12 * properties but different details (for example, timeout parameters)
13 * may be created using {@link ThreadPoolExecutor} constructors.
14 *
15 * @return the newly created thread pool
16 */
17 public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
18 return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
19 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
20 new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
21 }
這個線程池,是根據需要來創建這些線程的,但是以前構造過的線程 必要時可以重用他們,所以這個在很多android的開源項目裡都有用到,很頻繁,對於執行很多短期的異步任務來說,這個線程池可以極大的提高程序的性能。
1 /**
2 * Creates an Executor that uses a single worker thread operating
3 * off an unbounded queue. (Note however that if this single
4 * thread terminates due to a failure during execution prior to
5 * shutdown, a new one will take its place if needed to execute
6 * subsequent tasks.) Tasks are guaranteed to execute
7 * sequentially, and no more than one task will be active at any
8 * given time. Unlike the otherwise equivalent
9 * {@code newFixedThreadPool(1)} the returned executor is
10 * guaranteed not to be reconfigurable to use additional threads.
11 *
12 * @return the newly created single-threaded Executor
13 */
14 public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
15 return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
16 (new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
17 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
18 new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
19 }
而這個線程池就比較特殊一點,他只有一個worker線程在工作。 來看第一個程序:
1 public class Test1 {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 ExecutorService exectrorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
5 // execute異步的方法去執行這個runnable 但是這種方法無法取得運行之後的返回值
6 exectrorService.execute(new Runnable() {
7 @Override
8 public void run() {
9 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
10 int i = 0;
11 while (true) {
12 try {
13 Thread.sleep(2000);
14 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
15 // TODO Auto-generated catch block
16 e.printStackTrace();
17 }
18 System.out.println(i);
19 i++;
20 }
21 }
22
23 });
24
25 exectrorService.execute(new Runnable() {
26 @Override
27 public void run() {
28 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
29 int i = 100;
30 while (true) {
31 try {
32 Thread.sleep(2000);
33 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
34 // TODO Auto-generated catch block
35 e.printStackTrace();
36 }
37 System.out.println(i);
38 i++;
39 }
40 }
41
42 });
很簡單 沒有什麼好說的只是為了演示一下這個方法,繼續往下看:
1 public class Test1 {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 ExecutorService exectrorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
5 Future future = exectrorService.submit(new Runnable() {
6
7 @Override
8 public void run() {
9 System.out.println("thread start");
10 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
11 try {
12 Thread.sleep(13000);
13 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
14 // TODO Auto-generated catch block
15 e.printStackTrace();
16 }
17 System.out.println("task done");
18 }
19 });
20 System.out.println("ready to print status");
21 try {
22 // 執行完畢以後才會返回null,如果線程還沒有執行完畢 那這個地方會阻塞
23 System.out.println("future.get ==" + future.get());
24 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
25 // TODO Auto-generated catch block
26 e.printStackTrace();
27 } catch (ExecutionException e) {
28 // TODO Auto-generated catch block
29 e.printStackTrace();
30 }
31 System.out.println("finish ready");
 Android基礎——組件——TextView——帶滾動條
Android基礎——組件——TextView——帶滾動條
當內容超過了TextView的顯示范圍,這個時候就需要TextView裡面的內容滾動起來。 首先看下布局文件: 即便布局文件這樣設置了相關屬性,但是在
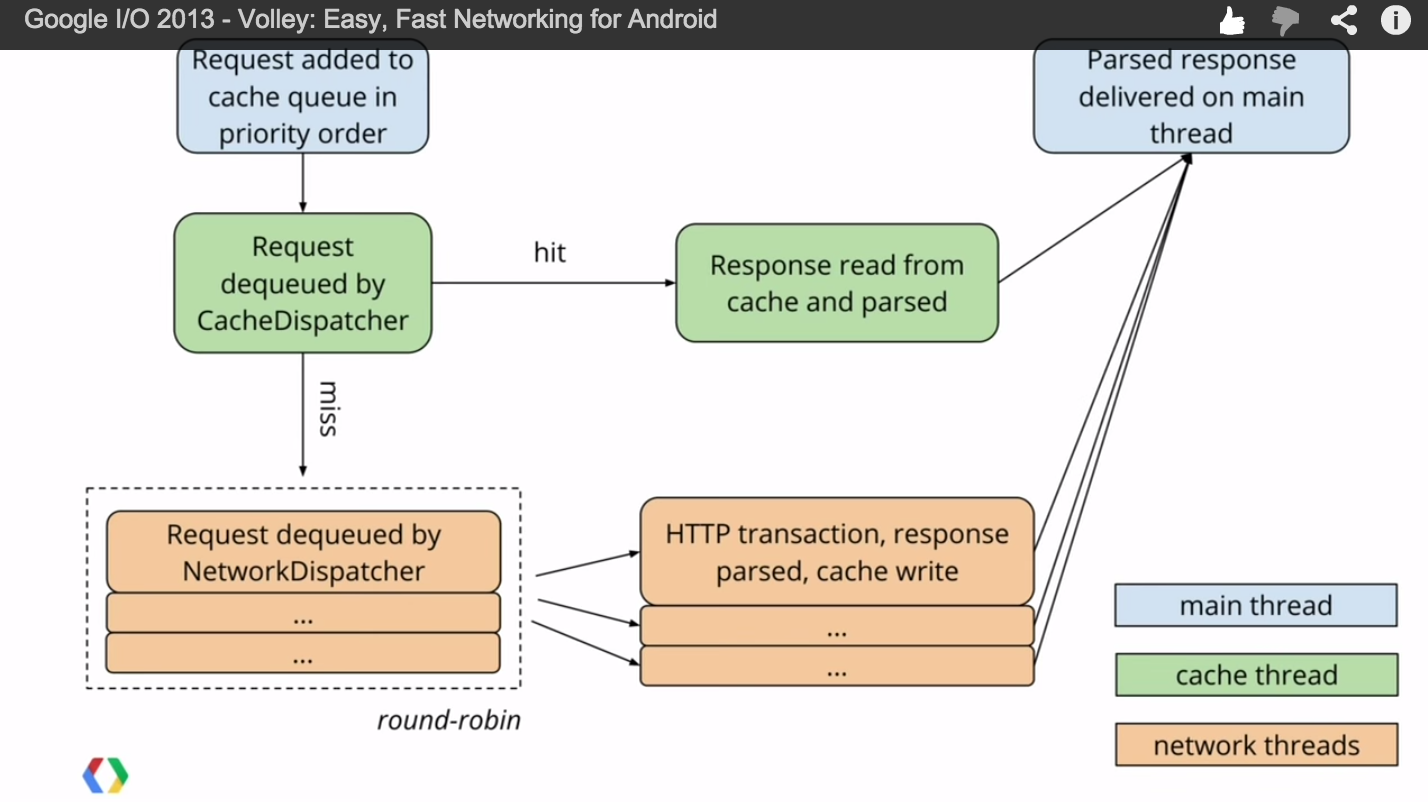 Volley 解析
Volley 解析
Request處理流程RequestQueue類中有三個主要的隊列。調用RequestQueue.add(request)加入的請求會先加入mCacheQueue(優先級
 【React Native開發】React Native For Android環境配置以及第一個實例
【React Native開發】React Native For Android環境配置以及第一個實例
(一)前言FaceBook早期開源發布了React Native For IOS,終於在2015年9月15日也發布了ReactNative for Android,雖然A
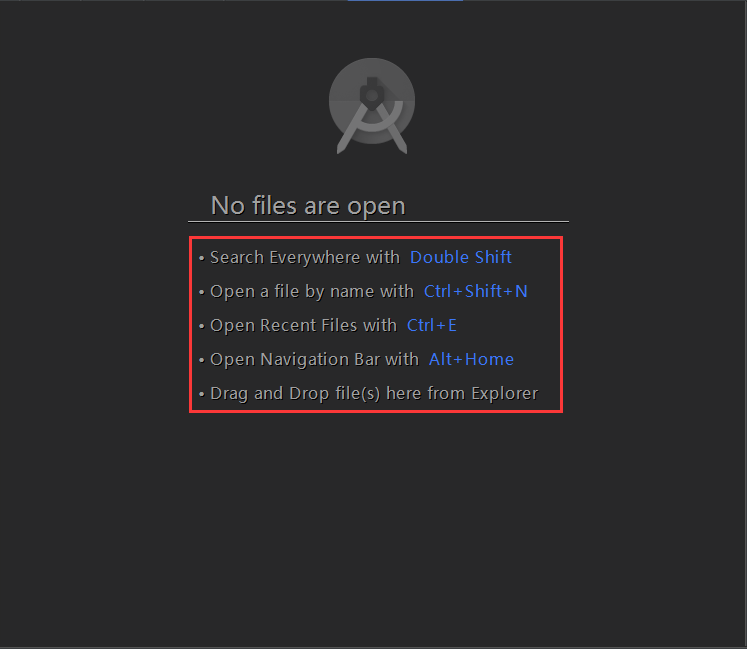 學習Android Studio開發工具之Activity2(&Fragment)
學習Android Studio開發工具之Activity2(&Fragment)
開篇先介紹幾個放在眼前卻經常忽視的快捷鍵如圖:展現出android Studio超強的搜索能力,提高大工程的開發維護效率。雙擊Shift按鍵效果Ctrl+Shift+N