編輯:關於Android編程
1 public class UpdataPeople extends Activity {
2
3 EditText updata_name;
4 EditText updata_phone;
5 EditText updata_address;
6 Button updata_quxiao;
7 Button updata_baocun;
8
9 String name;
10 String phone;
11
12 //創建一個子線程對象
13 UpdataThread updataThread ;
14
15 //定義一個全局變量,該Handler在主線程中重寫HandleMessage。
16 //若不定義成為全局變量,則在子線程中無發用到該Handler
17 private Handler mainHandler = null;
18
19 //創建一個非UI線程
20 class UpdataThread extends Thread {
21
22 public Handler mhandler;
23
24 public void run() {
25 Looper.prepare();
26 mhandler = new Handler() {
27
28 //定義處理消息的方法
29 @Override
30 public voidhandleMessage(Message msg) {
31 //---這裡面做一些耗時操作
32 if (msg.what == 0x123) {
33 //獲取msg所攜帶的數據
34 Bundle bundle =msg.getData();
35 if (bundle != null) {
36 String name =bundle.getString("name");
37 String phone =bundle.getString("phone");
38 Toast.makeText(getApplication(), "傳值成功" +name + phone, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
39 } else {
40 name = "";
41 phone = "";
42 }
43 //創建並連接數據庫,若該數據庫已經存在,則打開該數據庫
44 CreateDatabaseHelpercdh = new CreateDatabaseHelper(getApplication(), "myPeople.db3", 1);
45 //使用游標查詢數據庫,並返回結果集
46 Cursor cursor =cdh.getReadableDatabase().rawQuery("select * from people where name = ?and phone = ?", new String[]{name, phone});
47 //創建一個Bundle存儲查詢出來的結果
48 Bundle dataAll = newBundle();
49 //遍歷cursor,並將結果賦值給Bundle
50 while(cursor.moveToNext()) {
51 dataAll.putString("name", cursor.getString(1));
52 dataAll.putString("phone", cursor.getString(2));
53 dataAll.putString("address",cursor.getString(3));
54 }
55 //↓↓↓↓↓↓↓這一塊便是子線程將查詢的結果返回給主線程↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
56 //創建Message
57 Message msg_main = newMessage();
58 msg_main.what = 0x456;
59 //為Message添加數據
60 msg_main.setData(dataAll);
61 //向主線程發送消息
62 mainHandler.sendMessage(msg_main);
63
64 }
65 }
66 };
67 Looper.loop();
68 }
69 }
70
71 @Override
72 protected void onCreate(BundlesavedInstanceState) {
73 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
74 //實例化Thread
75 updataThread = new UpdataThread();
76 //啟動新線程
77 updataThread.start();
78 setContentView(R.layout.updatapeople);
79 //獲取布局文件裡的控件
80 updata_name = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.updata_name);
81 updata_phone = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.updata_phone);
82 updata_address = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.updata_address);
83 updata_quxiao = (Button)findViewById(R.id.updata_quxiao);
84 updata_baocun = (Button)findViewById(R.id.updata_baocun);
85
86 //獲取啟動該Activity的Intent
87 Intent intent = getIntent();
88 //取出Intent所攜帶的數據包
89 Bundle datas = intent.getExtras();
90 //取出包中所攜帶的各種數據
91 if (datas != null) {
92 name =datas.getString("name");
93 phone =datas.getString("phone");
94 } else {
95 name = "空";
96 phone = "空";
97 }
98 //↓↓↓↓↓↓↓這一塊便是主線程向子線程發送消息↓↓↓↓↓↓↓↓
99 //創建消息
100 Message msg = new Message();
101 //為msg標記一下(類似與--key--)
102 msg.what = 0x123;
103 //創建一個Bundle,並存放數據
104 Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
105 bundle.putString("name", name);
106 bundle.putString("phone", phone);
107 //將數據添加到msg
108 msg.setData(bundle);
109 //向新線程發送消息
110 updataThread.mhandler.sendMessage(msg);
111
112 //接受子線程返回的消息和子線程那邊的用法一樣
113 mainHandler = new Handler() {
114 @Override
115 public void handleMessage(Message msg_main) {
116 if (msg_main.what == 0x456){
117 //更新UI(因為在UI 線程中可以進行UI的更新。。。)
118 updata_name.setText(msg_main.getData().getString("name"));
119 }
120 }
121 };
 Android Content Provider詳解及示例代碼
Android Content Provider詳解及示例代碼
Android:Content Provider的使用。1、Content Provider 簡介2、使用現成的Content Provider3、定義自己的Conten
 Android 編程之入門開發文件夾管理器開發詳細講解-1
Android 編程之入門開發文件夾管理器開發詳細講解-1
在我們的手持設備中,一般都會自帶設備公司自己開發的文件管理系統、拍照系統之類的東東,今天我給大伙說說入門級開發的文件夾管理器,代碼贼少 總共就6個類吧,沒有
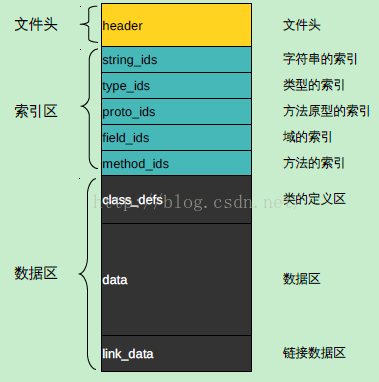 Android中dex文件的加載與優化流程
Android中dex文件的加載與優化流程
1、dex文件分析邏輯上,可以把dex文件分成3個區,頭文件、索引區和數據區。索引區的ids後綴為identifiers的縮寫。 headerdex文件裡的he
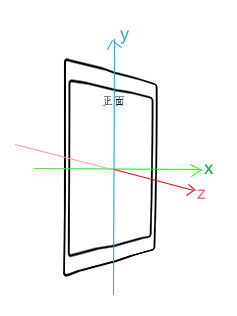 詳解Android 傳感器開發 完全解析
詳解Android 傳感器開發 完全解析
大家好,由於最近會有對智能硬件相關的開發需求,所以最近這些天分享的博文也就大致掛鉤智能硬件了,像上一篇的藍牙分享,相信很多讀者已經看過了,那麼今天我為大家帶來Androi