編輯:關於Android編程
Android中客戶端請求服務器端的兩種方式:Post方式和Get方式
在這裡不直接贅述了,直接上源碼如下:
(1).Post的方式:
/**
* Post的請求方式
*
* @param model
* 請求序號
* @param paramList
* 客戶端請求的數據參數列表
* @return
*/
public JSONObject doPost(int model, List paramList) {
try {
// 客戶端向服務器發送請求的數據
List params = new ArrayList();
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair(param1, 中國));
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair(param2, 美國));
// 1.定義請求的方式對象:
HttpPost post = new HttpPost(Base_URL);
// 2.定義請求的客戶端對象
HttpClient client = new DefaultHttpClient();
// 將請求的數據封裝在實體類中
HttpEntity entity = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(paramList, HTTP.UTF_8);
// 將實體類放置在URL中
post.setEntity(entity);
// 3.執行請求,返回響應的對象
HttpResponse response = client.execute(post);
if (response != null
&& response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == HttpStatus.SC_OK) {
// 獲得從服務器中返回的結果:從服務器中返回的結果是字符串的形式
String result = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(),
HTTP.UTF_8);
if (result.startsWith({)) {
try {
return new JSONObject(result);
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
(2).Get方式:
/**
*
* @param model
* 請求序號
* @param paramList
* 客戶端請求的數據參數列表
* @return
*/
public JSONObject doGet(int model, List paramList) {
// 客戶端向服務器發送請求的數據
// List params = new
// ArrayList();
// params.add(new BasicNameValuePair(param1, 中國));
// params.add(new BasicNameValuePair(param2, 美國));
// 對參數編碼
String param = URLEncodedUtils.format(paramList, HTTP.UTF_8);
// 將URL與參數拼接
// HttpGet get = new HttpGet(Base_URL + ? + param);
HttpGet get = new HttpGet(Base_URL + ? + param);
HttpClient httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient();
try {
// 發起GET請求
HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(get);
if (response != null
&& response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == HttpStatus.SC_OK) {
// 從服務器中獲得響應的數據
String result = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(),
HTTP.UTF_8);
try {
return new JSONObject(result);
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
整個工具類代碼如下:
package com.chengdong.su.downloaddemo.service;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.http.HttpEntity;
import org.apache.http.HttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.HttpStatus;
import org.apache.http.NameValuePair;
import org.apache.http.client.ClientProtocolException;
import org.apache.http.client.HttpClient;
import org.apache.http.client.entity.UrlEncodedFormEntity;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost;
import org.apache.http.client.utils.URLEncodedUtils;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.DefaultHttpClient;
import org.apache.http.message.BasicNameValuePair;
import org.apache.http.protocol.HTTP;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
import org.json.JSONException;
import org.json.JSONObject;
/**
* 客戶端向服務器端請求的工具
*
* @author scd
*
*/
public class HttpUtil {
/** 請求的URL */
private String Base_URL = http://www.baidu.com;
/** TAG */
private String TAG = getClass().getSimpleName();
/**
* Post的請求方式
*
* @param model
* 請求序號
* @param paramList
* 客戶端請求的數據參數列表
* @return
*/
public JSONObject doPost(int model, List paramList) {
try {
// 客戶端向服務器發送請求的數據
List params = new ArrayList();
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair(param1, 中國));
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair(param2, 美國));
// 1.定義請求的方式對象:
HttpPost post = new HttpPost(Base_URL);
// 2.定義請求的客戶端對象
HttpClient client = new DefaultHttpClient();
// 將請求的數據封裝在實體類中
HttpEntity entity = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(paramList, HTTP.UTF_8);
// 將實體類放置在URL中
post.setEntity(entity);
// 3.執行請求,返回響應的對象
HttpResponse response = client.execute(post);
if (response != null
&& response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == HttpStatus.SC_OK) {
// 獲得從服務器中返回的結果:從服務器中返回的結果是字符串的形式
String result = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(),
HTTP.UTF_8);
if (result.startsWith({)) {
try {
return new JSONObject(result);
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
*
* @param model
* 請求序號
* @param paramList
* 客戶端請求的數據參數列表
* @return
*/
public JSONObject doGet(int model, List paramList) {
// 客戶端向服務器發送請求的數據
// List params = new
// ArrayList();
// params.add(new BasicNameValuePair(param1, 中國));
// params.add(new BasicNameValuePair(param2, 美國));
// 對參數編碼
String param = URLEncodedUtils.format(paramList, HTTP.UTF_8);
// 將URL與參數拼接
// HttpGet get = new HttpGet(Base_URL + ? + param);
HttpGet get = new HttpGet(Base_URL + ? + param);
HttpClient httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient();
try {
// 發起GET請求
HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(get);
if (response != null
&& response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == HttpStatus.SC_OK) {
// 從服務器中獲得響應的數據
String result = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(),
HTTP.UTF_8);
try {
return new JSONObject(result);
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
 Android引用開源框架通過AsyncHttpClient實現文件上傳
Android引用開源框架通過AsyncHttpClient實現文件上傳
引用開源框架通過AsyncHttpClient進行文件上傳,具體內容如下一、步驟:1.添加權限(訪問網絡權限和讀寫權限)2.獲取上傳文件路徑並判斷是否為空3.若不為空,創
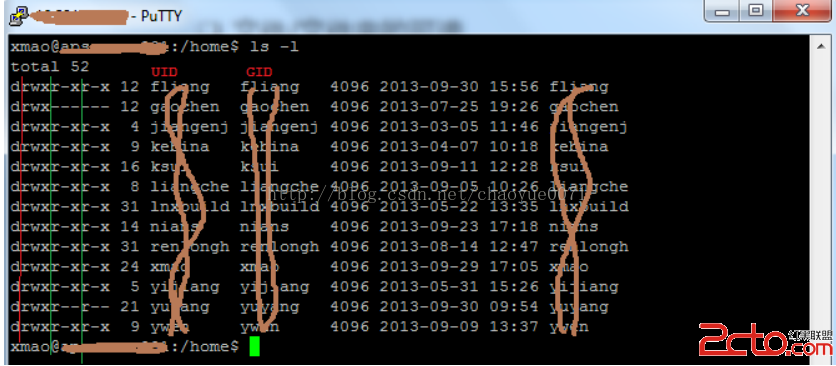 Android安全機制——操作系統安全機制-進程、用戶與文件安全
Android安全機制——操作系統安全機制-進程、用戶與文件安全
1.進程,線程2.多用戶,多用戶邊界(確定用戶可操作,訪問的資源,文件,可執行的操作)3.進程與文件都是用UID,GID來區分用戶,用rwx來區分操作,進程與文件通過ui
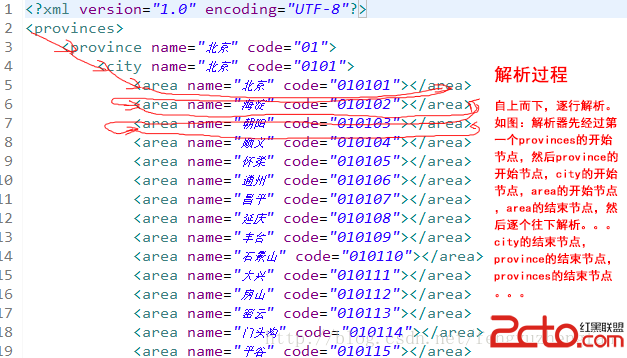 Android開發之使用PULL解析和生成XML
Android開發之使用PULL解析和生成XML
一、使用PULL解析XML 1.PULL簡介 我曾在《淺談XMl解析的幾種方式》一文中介紹了使用DOM方式,SAX方式,Jdom方式,以及dom4j的方式來
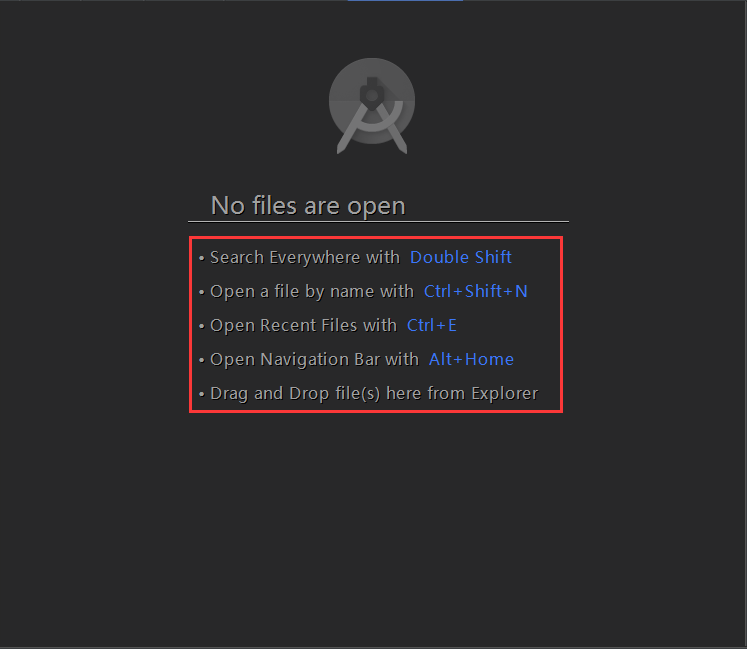 學習Android Studio開發工具之Activity2(&Fragment)
學習Android Studio開發工具之Activity2(&Fragment)
開篇先介紹幾個放在眼前卻經常忽視的快捷鍵如圖:展現出android Studio超強的搜索能力,提高大工程的開發維護效率。雙擊Shift按鍵效果Ctrl+Shift+N