編輯:關於Android編程
提到Netroid或許很多人不知道這個框架,但我如果說Volley想必沒有人不知道吧。Netroid是一個基於Volley實現的Android Http庫。提供執行網絡請求、緩存返回結果、批量圖片加載、大文件斷點下載的常見Http交互功能,關於網絡請求,圖片加載沒什麼好說的,Volley已經有很多人解析過了,這裡來說一下大文件斷點下載。
關於大文件斷點下載,網上也有很多實現的demo,為什麼要單單說Netroid呢?因為Netroid斷點續傳不依賴數據庫,我在網上看到過很多的斷點續傳的例子,無一例外都是依賴於數據庫,包括DownloadManager,大名鼎鼎的xutils,但是這兩個都有一定的問題。
1.DownloadManager在三星手機上必須打開下載管理才能應用,而打開這個管理必須需要手動打開,一般情況下無傷大雅,視情況而定
2.xutils這個框架別的不知道,文件下載這塊慎用
好了,進入正題,Netroid的地址:www.2cto.com下面簡單的說一下這個框架文件下載的實現和原理,
// 1
RequestQueue queue = Netroid.newRequestQueue(getApplicationContext(), null);
// 2
mDownloder = new FileDownloader(queue, 1) {
@Override
public FileDownloadRequest buildRequest(String storeFilePath, String url) {
return new FileDownloadRequest(storeFilePath, url) {
@Override
public void prepare() {
addHeader("Accept-Encoding", "identity");
super.prepare();
}
};
}
};
// 3
task.controller = mDownloder.add(mSaveDirPath + task.storeFileName, task.url, new Listener() {
@Override
public void onPreExecute() {
task.invalidate();
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(Void response) {
showToast(task.storeFileName + " Success!");
}
@Override
public void onError(NetroidError error) {
NetroidLog.e(error.getMessage());
}
@Override
public void onFinish() {
NetroidLog.e("onFinish size : " + Formatter.formatFileSize(
FileDownloadActivity.this, new File(mSaveDirPath + task.storeFileName).length()));
task.invalidate();
}
@Override
public void onProgressChange(long fileSize, long downloadedSize) {
task.onProgressChange(fileSize, downloadedSize);
// NetroidLog.e("---- fileSize : " + fileSize + " downloadedSize : " + downloadedSize);
}
});
實現的話很簡單,主要分為三步就可以了
1.創建一個請求隊列
2.構建一個文件下載管理器
3.將下載任務添加到隊列
現在根據上面的三步來看一下它的實現原理:
第一步:創建一個請求隊列:RequestQueue queue = Netroid.newRequestQueue(getApplicationContext(), null);
/**
* Creates a default instance of the worker pool and calls {@link RequestQueue#start()} on it.
* @param context A {@link Context} to use for creating the cache dir.
* @return A started {@link RequestQueue} instance.
*/
public static RequestQueue newRequestQueue(Context context, DiskCache cache) {
int poolSize = RequestQueue.DEFAULT_NETWORK_THREAD_POOL_SIZE;
HttpStack stack;
String userAgent = "netroid/0";
try {
String packageName = context.getPackageName();
PackageInfo info = context.getPackageManager().getPackageInfo(packageName, 0);
userAgent = packageName + "/" + info.versionCode;
} catch (NameNotFoundException e) {
}
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.GINGERBREAD) {
stack = new HurlStack(userAgent, null);
} else {
// Prior to Gingerbread, HttpUrlConnection was unreliable.
// See: http://android-developers.blogspot.com/2011/09/androids-http-clients.html
stack = new HttpClientStack(userAgent);
}
//實例化BasicNetwork,主要用於執行下載請求
Network network = new BasicNetwork(stack, HTTP.UTF_8);
//創建請求隊列
RequestQueue queue = new RequestQueue(network, poolSize, cache);
//很重要的一步
queue.start();
return queue;
}
/**
* Starts the dispatchers in this queue.
*/
public void start() {
stop(); // Make sure any currently running dispatchers are stopped.
// Create the cache dispatcher and start it.
mCacheDispatcher = new CacheDispatcher(mCacheQueue, mNetworkQueue, mCache, mDelivery);
mCacheDispatcher.start();
// Create network dispatchers (and corresponding threads) up to the pool size.
for (int i = 0; i < mDispatchers.length; i++) {
//一個線程,從請求隊列中獲取任務並執行
NetworkDispatcher networkDispatcher =
new NetworkDispatcher(mNetworkQueue, mNetwork, mCache, mDelivery);
mDispatchers[i] = networkDispatcher;
//Thread run()
networkDispatcher.start();
}
}
/**
* Stops the cache and network dispatchers.
*/
public void stop() {
if (mCacheDispatcher != null) {
mCacheDispatcher.quit();
}
for (NetworkDispatcher mDispatcher : mDispatchers) {
//Thread interrupt()線程中斷
if (mDispatcher != null) mDispatcher.quit();
}
}
框架中對於文件是沒有緩存機制的,所以mCacheDispatcher可以不用理它,看一下NetworkDispatcher這個線程做了什麼:com.duowan.mobile.netroid.NetworkDispatcher
public class NetworkDispatcher extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
//設置線程優先級
Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
Request request;
while (true) {
try {
// Take a request from the queue.如果隊列為空,則阻塞
request = mQueue.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// We may have been interrupted because it was time to quit.唯有線程中斷的時候mQuit才為true,InterruptedException為中斷異常
//mQueue.take()如果隊列為null,只會阻塞,不會跑出異常
if (mQuit) return;
continue;
}
try {
request.addMarker("network-queue-take");
//准備執行
mDelivery.postPreExecute(request);
// If the request was cancelled already,
// do not perform the network request.
if (request.isCanceled()) {
request.finish("network-discard-cancelled");
mDelivery.postCancel(request);
mDelivery.postFinish(request);
continue;
}
// Perform the network request.最重要一步!Netroid實例化的BasicNetwork在這裡執行網絡請求
NetworkResponse networkResponse = mNetwork.performRequest(request);
request.addMarker("network-http-complete");
// Parse the response here on the worker thread.重命名一下,沒做什麼
Response response = request.parseNetworkResponse(networkResponse);
request.addMarker("network-parse-complete");
// Write to cache if applicable.
if (mCache != null && request.shouldCache() && response.cacheEntry != null) {
response.cacheEntry.expireTime = request.getCacheExpireTime();
mCache.putEntry(request.getCacheKey(), response.cacheEntry);
request.addMarker("network-cache-written");
}
// Post the response back.
request.markDelivered();
mDelivery.postResponse(request, response);
} catch (NetroidError netroidError) {
mDelivery.postError(request, request.parseNetworkError(netroidError));
} catch (Exception e) {
NetroidLog.e(e, "Unhandled exception %s", e.toString());
mDelivery.postError(request, new NetroidError(e));
}
}
}
}
這裡最重要的一步就是NetworkResponse networkResponse = mNetwork.performRequest(request);執行網絡請求,但是我們不要忘記我們的mQueue還是空的,mQueue.take()正在阻塞著呢,所以,現在還沒有辦法進行網絡請求,因此我們需要在mQueue中填充任務,才能進行我們的網絡請求。不要忘記這裡哦,因為我們還會回到這裡!
第二步:創建一個文件下載管理器:new FileDownloader(queue, 1)
mDownloder = new FileDownloader(queue, 1) {
@Override
public FileDownloadRequest buildRequest(String storeFilePath, String url) {
return new FileDownloadRequest(storeFilePath, url) {
@Override
public void prepare() {
addHeader("Accept-Encoding", "identity");
super.prepare();
}
};
}
};
這裡有沒有看著很嚇人,我起初看的時候也嚇了一跳,其實就是實例化的時候,順手override了一下
/** The parallel task count, recommend less than 3. */ private final int mParallelTaskCount; /** The linked Task Queue. */ private final LinkedList這裡是需要注意的一點,mParallelTaskCount並發的數量最好<3.mTaskQueue; /** * Construct Downloader and init the Task Queue. * @param queue The RequestQueue for dispatching Download task. * @param parallelTaskCount * Allows parallel task count, * don't forget the value must less than ThreadPoolSize of the RequestQueue. */ public FileDownloader(RequestQueue queue, int parallelTaskCount) { if (parallelTaskCount >= queue.getThreadPoolSize()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("parallelTaskCount[" + parallelTaskCount + "] must less than threadPoolSize[" + queue.getThreadPoolSize() + "] of the RequestQueue."); } mTaskQueue = new LinkedList (); mParallelTaskCount = parallelTaskCount; mRequestQueue = queue; }
第三步:將下載任務添加到隊列,task.controller = mDownloder.add(mSaveDirPath + task.storeFileName, task.url, new Listener
/**
* Create a new download request, this request might not run immediately because the parallel task limitation,
* you can check the status by the {@link DownloadController} which you got after invoke this method.
*
* Note: don't perform this method twice or more with same parameters, because we didn't check for
* duplicate tasks, it rely on developer done.
*
* Note: this method should invoke in the main thread.
*
* @param storeFilePath Once download successed, we'll find it by the store file path.
* @param url The download url.
* @param listener The event callback by status;
* @return The task controller allows pause or resume or discard operation.
*/
public DownloadController add(String storeFilePath, String url, Listener listener) {
// only fulfill requests that were initiated from the main thread.(reason for the Delivery?)
//看名字就知道
throwIfNotOnMainThread();
//創建一個下載控制器
DownloadController controller = new DownloadController(storeFilePath, url, listener);
synchronized (mTaskQueue) {
//這可不是mQueue,這裡只是一個DownloadController的LinkedList集合
mTaskQueue.add(controller);
}
//重點來了
schedule();
return controller;
}
/**
* Traverse the Task Queue, count the running task then deploy more if it can be.
*/
private void schedule() {
// make sure only one thread can manipulate the Task Queue.
synchronized (mTaskQueue) {
// counting ran task.
int parallelTaskCount = 0;
for (DownloadController controller : mTaskQueue) {
//累計隊列中正在下載的的任務數
if (controller.isDownloading()) parallelTaskCount++;
}
//當正在下載的個數大於並行任務數的時候,不在執行下載任務
/*
* 這裡舉個例子說明一下:我們默認mParallelTaskCount=1
* 當我們添加第一個任務的時候,這個的controller.isDownloading()肯定是false
* 所以parallelTaskCount >= mParallelTaskCount是不成立的,當我們再添加一個任務的時候,現在mTaskQueue.size是2了
* 且第一個isDownloading,為了保證並發數量為1,會return,說的有點亂,不知道說明白了沒有
*/
if (parallelTaskCount >= mParallelTaskCount) return;
// try to deploy all Task if they're await.
for (DownloadController controller : mTaskQueue) {
//deploy(),將任務添加到隊列中
if (controller.deploy() && ++parallelTaskCount == mParallelTaskCount) return;
}
}
}
/**
* For the parallel reason, only the {@link FileDownloader#schedule()} can call this method.
* @return true if deploy is successed.
*/
private boolean deploy() {
if (mStatus != STATUS_WAITING) return false;
//第二步我說很嚇人那個地方
mRequest = buildRequest(mStoreFilePath, mUrl);
// we create a Listener to wrapping that Listener which developer specified,
// for the onFinish(), onSuccess(), onError() won't call when request was cancel reason.
mRequest.setListener(new Listener() {
boolean isCanceled;
@Override
public void onPreExecute() {
mListener.onPreExecute();
}
@Override
public void onFinish() {
// we don't inform FINISH when it was cancel.
if (!isCanceled) {
mStatus = STATUS_PAUSE;
mListener.onFinish();
// when request was FINISH, remove the task and re-schedule Task Queue.
// remove(DownloadController.this);
}
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(Void response) {
// we don't inform SUCCESS when it was cancel.
if (!isCanceled) {
mListener.onSuccess(response);
mStatus = STATUS_SUCCESS;
remove(DownloadController.this);
}
}
@Override
public void onError(NetroidError error) {
// we don't inform ERROR when it was cancel.
if (!isCanceled) mListener.onError(error);
}
@Override
public void onCancel() {
mListener.onCancel();
isCanceled = true;
}
@Override
public void onProgressChange(long fileSize, long downloadedSize) {
mListener.onProgressChange(fileSize, downloadedSize);
}
});
mStatus = STATUS_DOWNLOADING;
//我擦,終於把任務加到隊列中了
mRequestQueue.add(mRequest);
return true;
}
mRequestQueue.add(mRequest);任務加到隊列中了,都到了這裡了看一下怎麼加的吧
public Request add(Request request) {
// Tag the request as belonging to this queue and add it to the set of current requests.
request.setRequestQueue(this);
synchronized (mCurrentRequests) {
mCurrentRequests.add(request);
}
// Process requests in the order they are added.
request.setSequence(getSequenceNumber());
request.addMarker("add-to-queue");
// If the request is uncacheable or forceUpdate, skip the cache queue and go straight to the network.
if (request.isForceUpdate() || !request.shouldCache()) {
mDelivery.postNetworking(request);
mNetworkQueue.add(request);
return request;
}
}
request.shouldCache()有興趣的可以自己去看一下,這裡說明了文件下載沒有緩存機制,這裡就不多說了,因為如果你還沒有忘記的話,mQueue.take()還在阻塞著呢,好了讓我們回到第一步,執行網絡請求
NetworkResponse networkResponse = mNetwork.performRequest(request);
@Override
public NetworkResponse performRequest(Request request) throws NetroidError {
// Determine if request had non-http perform.
NetworkResponse networkResponse = request.perform();
if (networkResponse != null) return networkResponse;
long requestStart = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
while (true) {
// If the request was cancelled already,
// do not perform the network request.
if (request.isCanceled()) {
request.finish("perform-discard-cancelled");
mDelivery.postCancel(request);
throw new NetworkError(networkResponse);
}
HttpResponse httpResponse = null;
byte[] responseContents = null;
try {
// prepare to perform this request, normally is reset the request headers.
request.prepare();
httpResponse = mHttpStack.performRequest(request);
StatusLine statusLine = httpResponse.getStatusLine();
int statusCode = statusLine.getStatusCode();
responseContents = request.handleResponse(httpResponse, mDelivery);
if (statusCode < 200 || statusCode > 299) throw new IOException();
// if the request is slow, log it.
long requestLifetime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart;
logSlowRequests(requestLifetime, request, responseContents, statusLine);
return new NetworkResponse(statusCode, responseContents, parseCharset(httpResponse));
} catch (SocketTimeoutException e) {
attemptRetryOnException("socket", request, new TimeoutError());
} catch (ConnectTimeoutException e) {
attemptRetryOnException("connection", request, new TimeoutError());
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Bad URL " + request.getUrl(), e);
} catch (IOException e) {
if (httpResponse == null) throw new NoConnectionError(e);
int statusCode = httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode();
NetroidLog.e("Unexpected response code %d for %s", statusCode, request.getUrl());
if (responseContents != null) {
networkResponse = new NetworkResponse(statusCode, responseContents, parseCharset(httpResponse));
if (statusCode == HttpStatus.SC_UNAUTHORIZED || statusCode == HttpStatus.SC_FORBIDDEN) {
attemptRetryOnException("auth", request, new AuthFailureError(networkResponse));
} else {
// TODO: Only throw ServerError for 5xx status codes.
throw new ServerError(networkResponse);
}
} else {
throw new NetworkError(networkResponse);
}
}
}
}
responseContents = request.handleResponse(httpResponse, mDelivery);,寫文件,斷點續傳的原理
/**
* In this method, we got the Content-Length, with the TemporaryFile length,
* we can calculate the actually size of the whole file, if TemporaryFile not exists,
* we'll take the store file length then compare to actually size, and if equals,
* we consider this download was already done.
* We used {@link RandomAccessFile} to continue download, when download success,
* the TemporaryFile will be rename to StoreFile.
*/
@Override
public byte[] handleResponse(HttpResponse response, Delivery delivery) throws IOException, ServerError {
// Content-Length might be negative when use HttpURLConnection because it default header Accept-Encoding is gzip,
// we can force set the Accept-Encoding as identity in prepare() method to slove this problem but also disable gzip response.
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
//獲取文件的總大小
long fileSize = entity.getContentLength();
if (fileSize <= 0) {
NetroidLog.d("Response doesn't present Content-Length!");
}
long downloadedSize = mTemporaryFile.length();
/*
* 是否支持斷點續傳
*
* 客戶端每次提交下載請求時,服務端都要添加這兩個響應頭,以保證客戶端和服務端將此下載識別為可以斷點續傳的下載:
* Accept-Ranges:告知下載客戶端這是一個可以恢復續傳的下載,存放本次下載的開始字節位置、文件的字節大小;
* ETag:保存文件的唯一標識(我在用的文件名+文件最後修改時間,以便續傳請求時對文件進行驗證);
* Last-Modified:可選響應頭,存放服務端文件的最後修改時間,用於驗證
*/
boolean isSupportRange = HttpUtils.isSupportRange(response);
if (isSupportRange) {
fileSize += downloadedSize;
// Verify the Content-Range Header, to ensure temporary file is part of the whole file.
// Sometime, temporary file length add response content-length might greater than actual file length,
// in this situation, we consider the temporary file is invalid, then throw an exception.
String realRangeValue = HttpUtils.getHeader(response, "Content-Range");
// response Content-Range may be null when "Range=bytes=0-"
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(realRangeValue)) {
String assumeRangeValue = "bytes " + downloadedSize + "-" + (fileSize - 1);
if (TextUtils.indexOf(realRangeValue, assumeRangeValue) == -1) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"The Content-Range Header is invalid Assume[" + assumeRangeValue + "] vs Real[" + realRangeValue + "], " +
"please remove the temporary file [" + mTemporaryFile + "].");
}
}
}
// Compare the store file size(after download successes have) to server-side Content-Length.
// temporary file will rename to store file after download success, so we compare the
// Content-Length to ensure this request already download or not.
if (fileSize > 0 && mStoreFile.length() == fileSize) {
// Rename the store file to temporary file, mock the download success. ^_^
mStoreFile.renameTo(mTemporaryFile);
// Deliver download progress.
delivery.postDownloadProgress(this, fileSize, fileSize);
return null;
}
//之所以能夠實現斷點續傳的原因所在
RandomAccessFile tmpFileRaf = new RandomAccessFile(mTemporaryFile, "rw");
// If server-side support range download, we seek to last point of the temporary file.
if (isSupportRange) {
//移動文件讀寫指針位置
tmpFileRaf.seek(downloadedSize);
} else {
// If not, truncate the temporary file then start download from beginning.
tmpFileRaf.setLength(0);
downloadedSize = 0;
}
try {
InputStream in = entity.getContent();
// Determine the response gzip encoding, support for HttpClientStack download.
if (HttpUtils.isGzipContent(response) && !(in instanceof GZIPInputStream)) {
in = new GZIPInputStream(in);
}
byte[] buffer = new byte[6 * 1024]; // 6K buffer
int offset;
while ((offset = in.read(buffer)) != -1) {
//寫文件
tmpFileRaf.write(buffer, 0, offset);
downloadedSize += offset;
long currTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
//控制下載進度的速度
if (currTime - lastUpdateTime >= DEFAULT_TIME) {
lastUpdateTime = currTime;
delivery.postDownloadProgress(this, fileSize,
downloadedSize);
}
if (isCanceled()) {
delivery.postCancel(this);
break;
}
}
} finally {
try {
// Close the InputStream and release the resources by "consuming the content".
if (entity != null) entity.consumeContent();
} catch (Exception e) {
// This can happen if there was an exception above that left the entity in
// an invalid state.
NetroidLog.v("Error occured when calling consumingContent");
}
tmpFileRaf.close();
}
return null;
}
實現斷點續傳主要靠的RandomAccessFile,你如果對c語言不陌生的話tmpFileRaf.seek(downloadedSize)和int fseek(FILE *stream, long offset, int fromwhere);是不是有點眼熟,只與RandomAccessFile就不說了。
好了,Netroid的原理基本上就是這些了,講一下我用的時候遇到的兩個問題:
1.下載進度的速度太快,你如果用notifition來顯示,會出現ANR,所以我們要控制一下它的速度,具體方法在上面
//控制下載進度的速度
if (currTime - lastUpdateTime >= DEFAULT_TIME) {
lastUpdateTime = currTime;
delivery.postDownloadProgress(this, fileSize,
downloadedSize);
}
@Override
public void onFinish() {
// we don't inform FINISH when it was cancel.
if (!isCanceled) {
mStatus = STATUS_PAUSE;
mListener.onFinish();
// when request was FINISH, remove the task and re-schedule Task Queue.
// remove(DownloadController.this);
}
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(Void response) {
// we don't inform SUCCESS when it was cancel.
if (!isCanceled) {
mListener.onSuccess(response);
mStatus = STATUS_SUCCESS;
remove(DownloadController.this);
}
}
把onFinish的status改成STATUS_PAUSE,並去掉remove(DownloadController.this);,在onSuccess中再將status修改為STATUS_SUCCESS,並remove,當然這個辦法治標不治本,如果有誰知道請告之,謝謝!
 初始Servlet監聽器
初始Servlet監聽器
Servlet監聽器簡介Servlet監聽器的作用是監聽Web容器的有效事件,由容器管理。利用Listener接口監聽在容器中的某個執行程序,並更具應用程序的需求做出適當
 淺談Android中的MVP
淺談Android中的MVP
前言為什麼使用MVP,網上有很多說法,最主要就是減輕了Activity的責任,相比於MVC中的Activity承擔的責任太多,因此有必要講講MVP。MVP入門在MVC框架
 android開發步步為營之22:處理Activity中的back按鈕事件
android開發步步為營之22:處理Activity中的back按鈕事件
在手機應用中,用戶點擊回退按鈕一般是返回上個頁面,一般頁面不用處理,如果在首頁,點回退,沒任何提示,就把應用給關了,這個用戶體驗就不太好了,所以一般都會給用戶一個確認的提
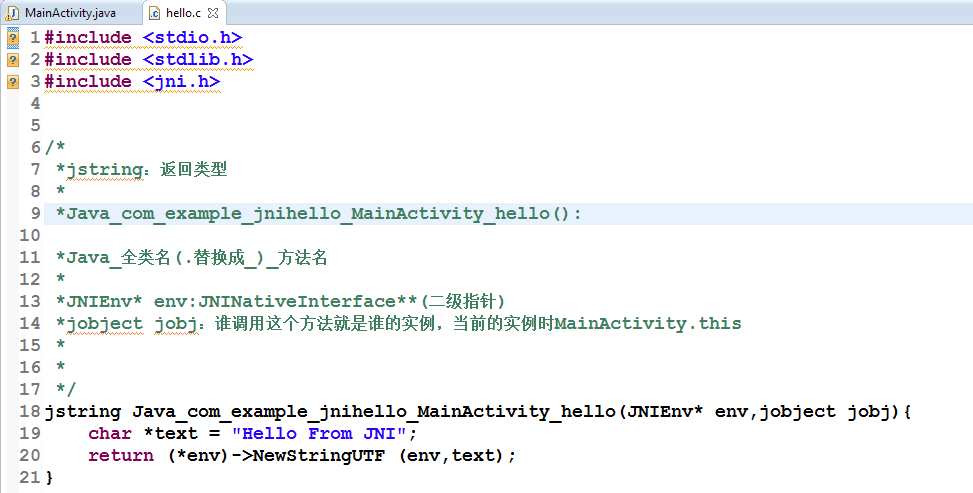 關於JNI
關於JNI
JNINDK開發環境的搭建將NDK的路徑拷貝到環境變量path中 cmd中運行ndk-build可驗證是否添加成功JNI_HelloWorld步驟1.創建Android工