編輯:關於Android編程
public class ShapeSelectorView extends View {
// We must provide a constructor that takes a Context and an AttributeSet.
// This constructor allows the UI to create and edit an instance of your view.
public ShapeSelectorView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
}
添加視圖到布局中
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > <com.codepath.example.customviewdemo.ShapeSelectorView android:id="@+id/shapeSelector" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" /> </RelativeLayout>
接下來我們定義一個命名空間app,這個命名空間允許Android自動解析而不需要指定具體的包名。 自定義屬性 視圖可以通過XML來配置屬性和樣式,你需要想清楚要添加那些自定義的屬性,比如我們想讓用戶可以選擇形狀的顏色、是否顯示形狀的名稱,比如我們想讓視圖可以像下面一樣配置:
<com.codepath.example.customviewdemo.ShapeSelectorView app:shapeColor="#7f0000" app:displayShapeName="true" android:id="@+id/shapeSelector" ... />
為了能夠定義shapeColor和displayShapeName,我們需要在res/values/attrs.xml中配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="ShapeSelectorView">
<attr name="shapeColor" format="color" />
<attr name="displayShapeName" format="boolean" />
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
對於每個你想自定義的屬性你需要定義attr節點,每個節點有name和format屬性,format屬性是我們期望的值的類型,比如color,dimension,boolean,integer,float等。一旦定義好了屬性,你可以像使用自帶屬性一樣使用他們,唯一的區別在於你的自定義屬性屬於一個不同的命名空間,你可以在根視圖的layout裡面定義命名空間,一般情況下你只需要這樣子指定:http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/<package_name>,但是你可以使用
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > <com.codepath.example.customviewdemo.ShapeSelectorView app:shapeColor="#7f0000" app:displayShapeName="true" android:id="@+id/shapeSelector" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_above="@+id/btnSelect" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_below="@+id/tvPrompt" /> </RelativeLayout>
應用自定義屬性 在前面我們定義了shapeColor和displayShapeName兩個屬性值,我們需要提取這兩個屬性值來用在自定義的視圖中,可以使用TypedArray和obtainStyledAttributes方法來完成,如下所示:
public class ShapeSelectorView extends View {
private int shapeColor;
private boolean displayShapeName;
public ShapeSelectorView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
setupAttributes(attrs);
}
private void setupAttributes(AttributeSet attrs) {
// Obtain a typed array of attributes
TypedArray a = getContext().getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.ShapeSelectorView, 0, 0);
// Extract custom attributes into member variables
try {
shapeColor = a.getColor(R.styleable.ShapeSelectorView_shapeColor, Color.BLACK);
displayShapeName = a.getBoolean(R.styleable.ShapeSelectorView_displayShapeName, false);
} finally {
// TypedArray objects are shared and must be recycled.
a.recycle();
}
}
}
接下來添加一些getter和setter方法:
public class ShapeSelectorView extends View {
// ...
public boolean isDisplayingShapeName() {
return displayShapeName;
}
public void setDisplayingShapeName(boolean state) {
this.displayShapeName = state;
invalidate();
requestLayout();
}
public int getShapeColor() {
return shapeColor;
}
public void setShapeColor(int color) {
this.shapeColor = color;
invalidate();
requestLayout();
}
}
當視圖屬性發生改變的時候可能需要重新繪圖,你需要調用invalidate()和requestLayout()來刷新顯示。 畫圖 假設我們要使用前面的屬性畫一個長方形,所有的繪圖都是在onDraw方法裡執行,使用Canvas對象來繪圖,如下所示:
public class ShapeSelectorView extends View {
// ...
private int shapeWidth = 100;
private int shapeHeight = 100;
private int textXOffset = 0;
private int textYOffset = 30;
private Paint paintShape;
// ...
public ShapeSelectorView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
setupAttributes(attrs);
setupPaint();
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
canvas.drawRect(0, 0, shapeWidth, shapeHeight, paintShape);
if (displayShapeName) {
canvas.drawText("Square", shapeWidth + textXOffset, shapeHeight + textXOffset, paintShape);
}
}
private void setupPaint() {
paintShape = new Paint();
paintShape.setStyle(Style.FILL);
paintShape.setColor(shapeColor);
paintShape.setTextSize(30);
}
}
這段代碼就會根據XML裡設置的shapeColor來畫圖,根據displayShapeName屬性來決定是否顯示圖形的名稱,結果如下圖: 更多畫圖的教程可以參考這裡 Custom 2D Drawing Tutorial 計算尺寸 為了更好的理解自定義視圖的寬度和高度,我們需要定義onMeasure方法,這個方法根據視圖的內容來決定它的寬度和高度,在這裡寬度和高度是由形狀和下面的文本決定的,如下所示:
public class ShapeSelectorView extends View {
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// Defines the extra padding for the shape name text
int textPadding = 10;
int contentWidth = shapeWidth;
// Resolve the width based on our minimum and the measure spec
int minw = contentWidth + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();
int w = resolveSizeAndState(minw, widthMeasureSpec, 0);
// Ask for a height that would let the view get as big as it can
int minh = shapeHeight + getPaddingBottom() + getPaddingTop();
if (displayShapeName) {
minh += textYOffset + textPadding;
}
int h = resolveSizeAndState(minh, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
// Calling this method determines the measured width and height
// Retrieve with getMeasuredWidth or getMeasuredHeight methods later
setMeasuredDimension(w, h);
}
}
寬度和高度都是基於MeasureSpec來討論的,一個MeasureSpec封裝了父布局傳遞給子布局的布局要求,每個MeasureSpec代表了一組寬度和高度的要求。一個MeasureSpec由大小和模式組成。它有三種模式:UNSPECIFIED(未指定),父元素未給子元素施加任何束縛,子元素可以得到任意想要的大小;EXACTLY(完全),父元素決定子元素的確切大小,子元素將被限定在給定的邊界裡而忽略它本身大小;AT_MOST(至多),子元素至多達到指定大小的值。resolveSizeAndState()方法根據視圖想要的大小和MeasureSpec返回一個合適的值,最後你需要調用setMeasureDimension()方法生效。 不同形狀之間切換 如果想實現用戶點擊之後改變形狀,需要在onTouchEvent方法裡添加自定義邏輯:
public class ShapeSelectorView extends View {
// ...
private String[] shapeValues = { "square", "circle", "triangle" };
private int currentShapeIndex = 0;
// Change the currentShapeIndex whenever the shape is clicked
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
boolean result = super.onTouchEvent(event);
if (event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
currentShapeIndex ++;
if (currentShapeIndex > (shapeValues.length - 1)) {
currentShapeIndex = 0;
}
postInvalidate();
return true;
}
return result;
}
}
現在不管什麼時候視圖被單擊,選擇的形狀的下標會改變,調用postInvalisate()方法後會顯示一個不同的形狀,接下來更新onDraw()方法來實現更改形狀的邏輯:
public class ShapeSelectorView extends View {
// ...
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
String shapeSelected = shapeValues[currentShapeIndex];
if (shapeSelected.equals("square")) {
canvas.drawRect(0, 0, shapeWidth, shapeHeight, paintShape);
textXOffset = 0;
} else if (shapeSelected.equals("circle")) {
canvas.drawCircle(shapeWidth / 2, shapeHeight / 2, shapeWidth / 2, paintShape);
textXOffset = 12;
} else if (shapeSelected.equals("triangle")) {
canvas.drawPath(getTrianglePath(), paintShape);
textXOffset = 0;
}
if (displayShapeName) {
canvas.drawText(shapeSelected, 0 + textXOffset, shapeHeight + textYOffset, paintShape);
}
}
protected Path getTrianglePath() {
Point p1 = new Point(0, shapeHeight), p2 = null, p3 = null;
p2 = new Point(p1.x + shapeWidth, p1.y);
p3 = new Point(p1.x + (shapeWidth / 2), p1.y - shapeHeight);
Path path = new Path();
path.moveTo(p1.x, p1.y);
path.lineTo(p2.x, p2.y);
path.lineTo(p3.x, p3.y);
return path;
}
// ...
}
現在每次點擊都會顯示一個不同的形狀,結果如下: 接下來添加一個獲取形狀的方法:
public class ShapeSelectorView extends View {
// ...
// Returns selected shape name
public String getSelectedShape() {
return shapeValues[currentShapeIndex];
}
}
保存視圖的狀態 當配置發生改變的時候(比如屏幕旋轉)視圖需要保存它們的狀態,你可以實現onSaveInstanceState()和onRestoreInstanceState()方法來保存和恢復視圖狀態,如下所示:
public class ShapeSelectorView extends View {
// This is the view state for this shape selector
private int currentShapeIndex = 0;
@Override
public Parcelable onSaveInstanceState() {
// Construct bundle
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
// Store base view state
bundle.putParcelable("instanceState", super.onSaveInstanceState());
// Save our custom view state to bundle
bundle.putInt("currentShapeIndex", this.currentShapeIndex);
// ... store any other custom state here ...
// Return the bundle
return bundle;
}
@Override
public void onRestoreInstanceState(Parcelable state) {
// Checks if the state is the bundle we saved
if (state instanceof Bundle) {
Bundle bundle = (Bundle) state;
// Load back our custom view state
this.currentShapeIndex = bundle.getInt("currentShapeIndex");
// ... load any other custom state here ...
// Load base view state back
state = bundle.getParcelable("instanceState");
}
// Pass base view state on to super
super.onRestoreInstanceState(state);
}
}
一旦你實現了這些保存和恢復的邏輯,當手機配置改變的時候你的視圖能夠自動保存狀態。
 Android自定義View之圖形圖像Bitmap
Android自定義View之圖形圖像Bitmap
概述:BitMap代表一張位圖,擴展名可以是.bmp或者.dib。位圖是Windows標准格式圖形文件,它將圖像定義為由點(像素)組成,每個點可以由多種色彩表示,包括2、
 Android開發中下拉刷新如何實現
Android開發中下拉刷新如何實現
因為最近的開發涉及到了網絡讀取數據,那麼自然少不了的就是下拉刷新的功能,搜索的方法一般是自己去自定義ListView或者RecyclerView來重寫OnTouch或者O
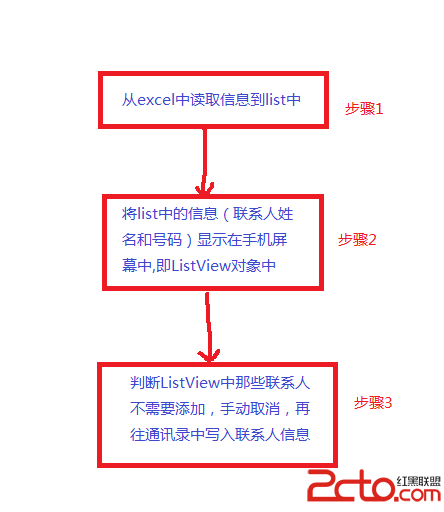 android批量添加聯系人
android批量添加聯系人
研究生期間就沒寫過Java代碼了,這幾天由於想做一個統計網頁詞頻的工具,但是使用C++不是很方便,於是又用Java做了一個小工具。翻開電腦中以前的文件,發現之前還做過一個
 androidLayout之layout_weight小解
androidLayout之layout_weight小解
一.兄弟Layout_height為fill_parent本來准備編寫一款簡單的計算器,來學習android,遇到了多個兄弟Layout區域按照一個比例大小來顯示的技術問