編輯:關於Android編程
要自己寫一個相機應用直接使用相機硬件,首先應用需要一個權限設置,在AndroidManifest.xml中加上使用設備相機的權限:
為你的應用創建自定義的相機,一般步驟如下:
1.檢測相機硬件並獲取訪問
2.建立一個Preview類:需要一個相機預覽的類,繼承 SurfaceView 類,並實現SurfaceHolder接口。
3.建立預覽的布局。
4.為拍照建立監聽。
5.拍照並且存儲文件。
6.釋放相機。
因為相機是一個共享資源,所以應該被謹慎管理,這樣應用之間才不會發生沖突。
所以使用完相機之後應該調用 Camera.release()來釋放相機對象。
如果不釋放,後續的使用相機請求(其他應用或本應用)都會失敗。
PackageManager.hasSystemFeature() 方法。比如:
/** Check if this device has a camera */
private boolean checkCameraHardware(Context context)
{
if (context.getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature(
PackageManager.FEATURE_CAMERA))
{
// this device has a camera
return true;
}
else
{
// no camera on this device
return false;
}
}
設備上可能有多個相機,Android 2.3以後可以使用 Camera.getNumberOfCameras()來查看相機的數目。
如下面這段程序用於檢測設備中的相機,並得到默認相機的索引號:
private int getDefaultCameraId()
{
int defaultId = -1;
// Find the total number of cameras available
mNumberOfCameras = Camera.getNumberOfCameras();
// Find the ID of the default camera
CameraInfo cameraInfo = new CameraInfo();
for (int i = 0; i < mNumberOfCameras; i++)
{
Camera.getCameraInfo(i, cameraInfo);
if (cameraInfo.facing == CameraInfo.CAMERA_FACING_BACK)
{
defaultId = i;
}
}
if (-1 == defaultId)
{
if (mNumberOfCameras > 0)
{
// 如果沒有後向攝像頭
defaultId = 0;
}
else
{
// 沒有攝像頭
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), R.string.no_camera,
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
return defaultId;
}
看了Camera類的代碼實現後,其中不帶參數的open()方法:默認是調用後置攝像頭
public static Camera open()
{
int numberOfCameras = getNumberOfCameras();
CameraInfo cameraInfo = new CameraInfo();
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfCameras; i++)
{
getCameraInfo(i, cameraInfo);
if (cameraInfo.facing == CameraInfo.CAMERA_FACING_BACK)
{
return new Camera(i);
}
}
return null;
}
要獲取主要的相機,可以使用 Camera.open() 方法,注意異常處理。
在使用這個方法的時候一定要檢查異常,如果相機正在被使用或者不存在,沒有處理異常,將會使得應用被系統關閉。
如:
/** A safe way to get an instance of the Camera object. */
public static Camera getCameraInstance()
{
Camera c = null;
try
{
c = Camera.open(); // attempt to get a Camera instance
}
catch (Exception e)
{
// Camera is not available (in use or does not exist)
}
return c; // returns null if camera is unavailable
}
Android 2.3之後,可以使用Camera.open(int)來獲取特定的相機。
可以使用Camera.getParameters()方法來檢查相機的特性。
API Level 9之後,可以使用 Camera.getCameraInfo()來查看相機是在設備前面還是後面,還可以得到圖像的方向。
為了有效地拍照或錄像,用戶必須要看到相機能看到的圖像。
相機的preview類是一個 SurfaceView ,展示了相機正在捕捉的圖像。
下面是一個預覽類的例子(來自官網):
/** A basic Camera preview class */
public class CameraPreview extends SurfaceView implements SurfaceHolder.Callback {
private SurfaceHolder mHolder;
private Camera mCamera;
public CameraPreview(Context context, Camera camera) {
super(context);
mCamera = camera;
// Install a SurfaceHolder.Callback so we get notified when the
// underlying surface is created and destroyed.
mHolder = getHolder();
mHolder.addCallback(this);
// deprecated setting, but required on Android versions prior to 3.0
mHolder.setType(SurfaceHolder.SURFACE_TYPE_PUSH_BUFFERS);
}
public void surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder holder) {
// The Surface has been created, now tell the camera where to draw the preview.
try {
mCamera.setPreviewDisplay(holder);
mCamera.startPreview();
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.d(TAG, Error setting camera preview: + e.getMessage());
}
}
public void surfaceDestroyed(SurfaceHolder holder) {
// empty. Take care of releasing the Camera preview in your activity.
}
public void surfaceChanged(SurfaceHolder holder, int format, int w, int h) {
// If your preview can change or rotate, take care of those events here.
// Make sure to stop the preview before resizing or reformatting it.
if (mHolder.getSurface() == null){
// preview surface does not exist
return;
}
// stop preview before making changes
try {
mCamera.stopPreview();
} catch (Exception e){
// ignore: tried to stop a non-existent preview
}
// set preview size and make any resize, rotate or
// reformatting changes here
// start preview with new settings
try {
mCamera.setPreviewDisplay(mHolder);
mCamera.startPreview();
} catch (Exception e){
Log.d(TAG, Error starting camera preview: + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
注意要設置尺寸的話需要放在surfaceChanged()方法裡,調用 setPreviewSize()方法,並且應該使用 getSupportedPreviewSizes()返回的值,而不要使用任意的尺寸。
布局時可以使用FrameLayout,這樣其他的按鈕或者元素可以疊加在預覽圖像上。
對於大多數設備來說,相機預覽的默認方向是橫放的(landscape)。
從Android 2.2 (API Level 8)開始,可以使用 setDisplayOrientation()來設置預覽圖像的方向。
如果需要在用戶改變設備方向的時候改變預覽圖像的方向,可以在 surfaceChanged()方法中,首先用 Camera.stopPreview() 停止預覽,改變方向,然後用Camera.startPreview()開啟新的預覽。
當然你也可以直接在manifest中設置好方向,如下:
在應用裡面,必須為用戶控制加上監聽,來響應用戶拍照的動作。
為了得到圖像,要使用 Camera.takePicture()方法。
這個方法接收三個參數,用於從相機獲取圖像。
為了接收到JPEG格式的數據,需要實現Camera.PictureCallback接口用來接收圖像數據並且寫入文件。
下面的代碼展示了一個最基本的實現:
private PictureCallback mPicture = new PictureCallback() {
@Override
public void onPictureTaken(byte[] data, Camera camera) {
File pictureFile = getOutputMediaFile(MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE);
if (pictureFile == null){
Log.d(TAG, Error creating media file, check storage permissions: +
e.getMessage());
return;
}
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(pictureFile);
fos.write(data);
fos.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
Log.d(TAG, File not found: + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.d(TAG, Error accessing file: + e.getMessage());
}
}
};
// Add a listener to the Capture button
Button captureButton = (Button) findViewById(id.button_capture);
captureButton.setOnClickListener(
new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// get an image from the camera
mCamera.takePicture(null, null, mPicture);
}
}
);
相機是設備資源,被所有應用共享,當應用不使用相機時應當及時釋放,應當在Activity.onPause()中釋放。
如果不及時釋放,後續的相機請求(包括你自己的應用和其他的應用發出的)都將失敗並且導致應用退出。
完整的照相程序需要考慮相機切換、預覽圖像的尺寸設置、焦距變換、縮放、白平衡的相機參數設置。
請查閱文後的參考資料進行進一步學習。
附上一個粗糙待完善的自定義相機程序(2013/4/6)
預覽圖像類:
package com.example.hellocustomcamera;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import android.R.integer;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.ImageFormat;
import android.graphics.PixelFormat;
import android.hardware.Camera;
import android.hardware.Camera.CameraInfo;
import android.hardware.Camera.Size;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.SurfaceHolder;
import android.view.SurfaceView;
/**
* 相機圖片預覽類
*
* @author
*
*/
public class CameraPreview extends SurfaceView implements
SurfaceHolder.Callback
{
private SurfaceHolder mHolder;
private Camera mCamera;
Size mPreviewSize;
List mSupportedPreviewSizes;
public CameraPreview(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle)
{
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
init();
}
public CameraPreview(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
{
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public CameraPreview(Context context)
{
super(context);
init();
}
/**
* 初始化工作
*
*/
private void init()
{
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG, CameraPreview initialize);
// Install a SurfaceHolder.Callback so we get notified when the
// underlying surface is created and destroyed.
mHolder = getHolder();
mHolder.addCallback(this);
// deprecated setting, but required on Android versions prior to 3.0
mHolder.setType(SurfaceHolder.SURFACE_TYPE_PUSH_BUFFERS);
}
public void setCamera(Camera camera)
{
mCamera = camera;
if (mCamera != null)
{
mSupportedPreviewSizes = mCamera.getParameters()
.getSupportedPreviewSizes();
requestLayout();
}
}
@Override
public void surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder holder)
{
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG, surfaceCreated);
// The Surface has been created, now tell the camera where to draw the
// preview.
try
{
if (null != mCamera)
{
mCamera.setPreviewDisplay(holder);
}
}
catch (IOException e1)
{
e1.printStackTrace();
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG,
Error setting camera preview display: + e1.getMessage());
}
try
{
if (null != mCamera)
{
mCamera.startPreview();
}
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG, surfaceCreated successfully! );
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG,
Error setting camera preview: + e.getMessage());
}
}
@Override
public void surfaceChanged(SurfaceHolder holder, int format, int width,
int height)
{
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG, surface changed);
// If your preview can change or rotate, take care of those events here.
// Make sure to stop the preview before resizing or reformatting it.
if (null == mHolder.getSurface())
{
// preview surface does not exist
return;
}
// stop preview before making changes
try
{
if (null != mCamera)
{
mCamera.stopPreview();
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
// ignore: tried to stop a non-existent preview
}
// set preview size and make any resize, rotate or
// reformatting changes here
if (null != mCamera)
{
Camera.Parameters parameters = mCamera.getParameters();
parameters.setPreviewSize(mPreviewSize.width, mPreviewSize.height);
requestLayout();
mCamera.setParameters(parameters);
mCamera.setDisplayOrientation(90);
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG, camera set parameters successfully!:
+ parameters);
}
// 這裡可以用來設置尺寸
// start preview with new settings
try
{
if (null != mCamera)
{
mCamera.setPreviewDisplay(mHolder);
mCamera.startPreview();
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG,
Error starting camera preview: + e.getMessage());
}
}
@Override
public void surfaceDestroyed(SurfaceHolder holder)
{
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG, surfaceDestroyed);
if (null != mCamera)
{
mCamera.stopPreview();
}
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
{
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// We purposely disregard child measurements because act as a
// wrapper to a SurfaceView that centers the camera preview instead
// of stretching it.
final int width = resolveSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(),
widthMeasureSpec);
final int height = resolveSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(),
heightMeasureSpec);
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
if (mSupportedPreviewSizes != null)
{
mPreviewSize = getOptimalPreviewSize(mSupportedPreviewSizes, width,
height);
}
}
private Size getOptimalPreviewSize(List sizes, int w, int h)
{
final double ASPECT_TOLERANCE = 0.1;
double targetRatio = (double) w / h;
if (sizes == null)
return null;
Size optimalSize = null;
double minDiff = Double.MAX_VALUE;
int targetHeight = h;
// Try to find an size match aspect ratio and size
for (Size size : sizes)
{
double ratio = (double) size.width / size.height;
if (Math.abs(ratio - targetRatio) > ASPECT_TOLERANCE)
continue;
if (Math.abs(size.height - targetHeight) < minDiff)
{
optimalSize = size;
minDiff = Math.abs(size.height - targetHeight);
}
}
// Cannot find the one match the aspect ratio, ignore the requirement
if (optimalSize == null)
{
minDiff = Double.MAX_VALUE;
for (Size size : sizes)
{
if (Math.abs(size.height - targetHeight) < minDiff)
{
optimalSize = size;
minDiff = Math.abs(size.height - targetHeight);
}
}
}
return optimalSize;
}
}
package com.example.hellocustomcamera;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager;
import android.hardware.Camera;
import android.hardware.Camera.CameraInfo;
import android.hardware.Camera.PictureCallback;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.Display;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.Window;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.FrameLayout;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class HelloCustomCameraActivity extends Activity
{
private Camera mCamera;
private CameraPreview mPreview;
int mNumberOfCameras;
int mCameraCurrentlyLocked;
// The first rear facing camera
int mDefaultCameraId;
int mScreenWidth, mScreenHeight;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG, onCreate);
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// 無標題欄的窗口
requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);
getWindow().addFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN);
// 設置布局
setContentView(R.layout.activity_hello_custom_camera);
// 得到屏幕的大小
WindowManager wManager = (WindowManager) getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
Display display = wManager.getDefaultDisplay();
mScreenHeight = display.getHeight();
mScreenWidth = display.getWidth();
// Create our Preview view and set it as the content of our activity.
mPreview = new CameraPreview(this);
FrameLayout preview = (FrameLayout) findViewById(R.id.camera_preview);
// 將相機預覽圖加入幀布局裡面
preview.addView(mPreview, 0);
// 使用按鈕進行拍攝動作監聽
Button captureButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button_capture);
captureButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener()
{
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
// get an image from the camera
mCamera.takePicture(null, null, mPicture);
}
});
// 得到默認的相機ID
mDefaultCameraId = getDefaultCameraId();
mCameraCurrentlyLocked = mDefaultCameraId;
}
@Override
protected void onResume()
{
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG, onResume);
super.onResume();
// Open the default i.e. the first rear facing camera.
mCamera = getCameraInstance(mCameraCurrentlyLocked);
mPreview.setCamera(mCamera);
}
@Override
protected void onPause()
{
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG, onPause);
super.onPause();
// Because the Camera object is a shared resource, it's very
// important to release it when the activity is paused.
if (mCamera != null)
{
mPreview.setCamera(null);
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG, onPause --> Realease camera);
mCamera.release();
mCamera = null;
}
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy()
{
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG, onDestroy);
super.onDestroy();
}
/**
* 得到默認相機的ID
*
* @return
*/
private int getDefaultCameraId()
{
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG, getDefaultCameraId);
int defaultId = -1;
// Find the total number of cameras available
mNumberOfCameras = Camera.getNumberOfCameras();
// Find the ID of the default camera
CameraInfo cameraInfo = new CameraInfo();
for (int i = 0; i < mNumberOfCameras; i++)
{
Camera.getCameraInfo(i, cameraInfo);
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG, camera info: + cameraInfo.orientation);
if (cameraInfo.facing == CameraInfo.CAMERA_FACING_BACK)
{
defaultId = i;
}
}
if (-1 == defaultId)
{
if (mNumberOfCameras > 0)
{
// 如果沒有後向攝像頭
defaultId = 0;
}
else
{
// 沒有攝像頭
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), R.string.no_camera,
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
return defaultId;
}
/** A safe way to get an instance of the Camera object. */
public static Camera getCameraInstance(int cameraId)
{
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG, getCameraInstance);
Camera c = null;
try
{
c = Camera.open(cameraId); // attempt to get a Camera instance
}
catch (Exception e)
{
// Camera is not available (in use or does not exist)
e.printStackTrace();
Log.e(AppConstants.LOG_TAG, Camera is not available);
}
return c; // returns null if camera is unavailable
}
public static final int MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE = 1;
public static final int MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO = 2;
/** Create a File for saving an image or video */
private static File getOutputMediaFile(int type)
{
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG, getOutputMediaFile);
// To be safe, you should check that the SDCard is mounted
// using Environment.getExternalStorageState() before doing this.
File mediaStorageDir = null;
try
{
// This location works best if you want the created images to be
// shared
// between applications and persist after your app has been
// uninstalled.
mediaStorageDir = new File(
Environment
.getExternalStoragePublicDirectory(Environment.DIRECTORY_PICTURES),
MyCameraApp);
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG,
Successfully created mediaStorageDir: + mediaStorageDir);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG, Error in Creating mediaStorageDir:
+ mediaStorageDir);
}
// Create the storage directory if it does not exist
if (!mediaStorageDir.exists())
{
if (!mediaStorageDir.mkdirs())
{
// 在SD卡上創建文件夾需要權限:
//
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG,
failed to create directory, check if you have the WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE permission);
return null;
}
}
// Create a media file name
String timeStamp = new SimpleDateFormat(yyyyMMdd_HHmmss)
.format(new Date());
File mediaFile;
if (type == MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE)
{
mediaFile = new File(mediaStorageDir.getPath() + File.separator
+ IMG_ + timeStamp + .jpg);
}
else if (type == MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO)
{
mediaFile = new File(mediaStorageDir.getPath() + File.separator
+ VID_ + timeStamp + .mp4);
}
else
{
return null;
}
return mediaFile;
}
private PictureCallback mPicture = new PictureCallback()
{
@Override
public void onPictureTaken(byte[] data, Camera camera)
{
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG, onPictureTaken);
File pictureFile = getOutputMediaFile(MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE);
if (pictureFile == null)
{
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG,
Error creating media file, check storage permissions: );
return;
}
try
{
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(pictureFile);
fos.write(data);
fos.close();
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e)
{
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG, File not found: + e.getMessage());
}
catch (IOException e)
{
Log.d(AppConstants.LOG_TAG,
Error accessing file: + e.getMessage());
}
// 拍照後重新開始預覽
mCamera.stopPreview();
mCamera.startPreview();
}
};
/** Check if this device has a camera */
private boolean checkCameraHardware(Context context)
{
if (context.getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature(
PackageManager.FEATURE_CAMERA))
{
// this device has a camera
return true;
}
else
{
// no camera on this device
return false;
}
}
}
 Android高仿QQ6.0側滑刪除實例代碼
Android高仿QQ6.0側滑刪除實例代碼
推薦閱讀:先給大家分享一下,側滑刪除,布局也就是前面一個item,然後有兩個隱藏的按鈕(TextView也可以),然後我們可以向左側滑動,然後顯示出來,然後對delete
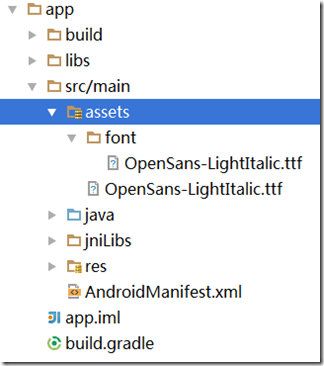 AndroidStudio 實現加載字體資源的方法
AndroidStudio 實現加載字體資源的方法
AndroidStudio 實現加載字體資源的方法在android中字體的格式總是不能盡善盡美的顯示出來 , 於是要求我們使用一些有美感的字體,加載的方式(就
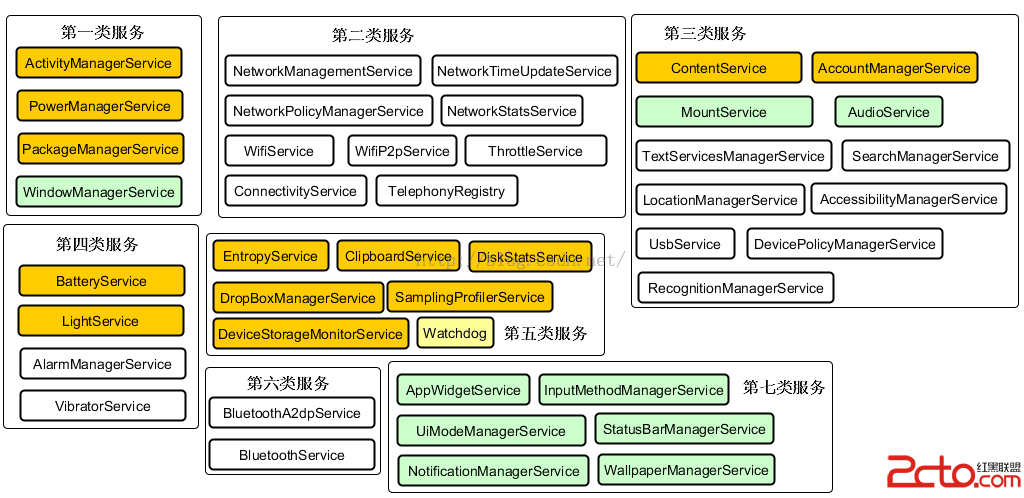 深入理解Android之AOP
深入理解Android之AOP
深入理解Android之AOP 一、閒談AOP大家都知道OOP,即ObjectOriented Programming,面向對象編程。而本文要介紹的是AOP。A
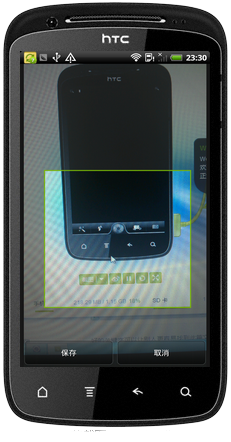 Android開發從相機或相冊獲取圖片裁剪
Android開發從相機或相冊獲取圖片裁剪
廢話不多說了,直接給大家貼代碼了。package com.only.android.app;import java.io.File;import android.app.