編輯:關於Android編程
在Android常用編程中,Handler在進行異步操作並處理返回結果時經常被使用。通常我們的代碼會這樣實現。
public class SampleActivity extends Activity {
private final Handler mLeakyHandler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
// ...
}
}
}
但是,其實上面的代碼可能導致內存洩露,當你使用Android lint工具的話,會得到這樣的警告
This Handler class should be static or leaks might occur (com.example.multifragment.SampleActivity.1) Issue: Ensures that Handler classes do not hold on to a reference to an outer class Id: HandlerLeak Since this Handler is declared as an inner class, it may prevent the outer class from being garbage collected. If the Handler is using a Looper or MessageQueue for a thread other than the main thread, then there is no issue. If the Handler is using the Looper or MessageQueue of the main thread, you need to fix your Handler declaration, as follows: Declare the Handler as a static class; In the outer class, instantiate a WeakReference to the outer class and pass this object to your Handler when you instantiate the Handler; Make all references to members of the outer class using the WeakReference object.
看到這裡,可能還是有一些搞不清楚,代碼中哪裡可能導致內存洩露,又是如何導致內存洩露的呢?那我們就慢慢分析一下。
1.當一個Android應用啟動的時候,會自動創建一個供應用主線程使用的Looper實例。Looper的主要工作就是一個一個處理消息隊列中的消息對象。在Android中,所有Android框架的事件(比如Activity的生命周期方法調用和按鈕點擊等)都是放入到消息中,然後加入到Looper要處理的消息隊列中,由Looper負責一條一條地進行處理。主線程中的Looper生命周期和當前應用一樣長。
2.當一個Handler在主線程進行了初始化之後,我們發送一個target為這個Handler的消息到Looper處理的消息隊列時,實際上已經發送的消息已經包含了一個Handler實例的引用,只有這樣Looper在處理到這條消息時才可以調用Handler#handleMessage(Message)完成消息的正確處理。
3.在Java中,非靜態的內部類和匿名內部類都會隱式地持有其外部類的引用。靜態的內部類不會持有外部類的引用。
確實上面的代碼示例有點難以察覺內存洩露,那麼下面的例子就非常明顯了
public class SampleActivity extends Activity {
private final Handler mLeakyHandler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
// ...
}
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// Post a message and delay its execution for 10 minutes.
mLeakyHandler.postDelayed(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() { /* ... */ }
}, 1000 * 60 * 10);
// Go back to the previous Activity.
finish();
}
}
分析一下上面的代碼,當我們執行了Activity的finish方法,被延遲的消息會在被處理之前存在於主線程消息隊列中10分鐘,而這個消息中又包含了Handler的引用,而Handler是一個匿名內部類的實例,其持有外面的SampleActivity的引用,所以這導致了SampleActivity無法回收,進行導致SampleActivity持有的很多資源都無法回收,這就是我們常說的內存洩露。
注意上面的new Runnable這裡也是匿名內部類實現的,同樣也會持有SampleActivity的引用,也會阻止SampleActivity被回收。
要解決這種問題,思路就是不適用非靜態內部類,繼承Handler時,要麼是放在單獨的類文件中,要麼就是使用靜態內部類。因為靜態的內部類不會持有外部類的引用,所以不會導致外部類實例的內存洩露。當你需要在靜態內部類中調用外部的Activity時,我們可以使用弱引用來處理。另外關於同樣也需要將Runnable設置為靜態的成員屬性。注意:一個靜態的匿名內部類實例不會持有外部類的引用。 修改後不會導致內存洩露的代碼如下
public class SampleActivity extends Activity {
/**
* Instances of static inner classes do not hold an implicit
* reference to their outer class.
*/
private static class MyHandler extends Handler {
private final WeakReference mActivity;
public MyHandler(SampleActivity activity) {
mActivity = new WeakReference(activity);
}
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
SampleActivity activity = mActivity.get();
if (activity != null) {
// ...
}
}
}
private final MyHandler mHandler = new MyHandler(this);
/**
* Instances of anonymous classes do not hold an implicit
* reference to their outer class when they are static.
*/
private static final Runnable sRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() { /* ... */ }
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// Post a message and delay its execution for 10 minutes.
mHandler.postDelayed(sRunnable, 1000 * 60 * 10);
// Go back to the previous Activity.
finish();
}
}
其實在Android中很多的內存洩露都是由於在Activity中使用了非靜態內部類導致的,就像本文提到的一樣,所以當我們使用時要非靜態內部類時要格外注意,如果其實例的持有對象的生命周期大於其外部類對象,那麼就有可能導致內存洩露。個人傾向於使用文章的靜態類和弱引用的方法解決這種問題。
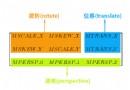 安卓自定義View進階-Matrix原理
安卓自定義View進階-Matrix原理
前言畫布操作 有重疊的部分,本文會讓你更加深入的了解其中的原理。本篇的主角Matrix,是一個一直在後台默默工作的勞動模范,雖然我們所有看到View背後都有著Matrix
 淺談談Android 圖片選擇器
淺談談Android 圖片選擇器
ImageSelector 簡介Android自定義相冊,實現了拍照、圖片選擇(單選/多選)、ImageLoader無綁定 任由開發者選擇https://github.c
 Android游戲開發之碰撞檢測(矩形碰撞、圓形碰撞、像素碰撞)
Android游戲開發之碰撞檢測(矩形碰撞、圓形碰撞、像素碰撞)
本文為大家分享了Android游戲開發之碰撞檢測,供大家參考,具體內容如下矩形碰撞 原理: 兩個矩形位置 的四種情況 不是這四中情況 則碰撞圓形碰撞 原理: 利用兩個圓心
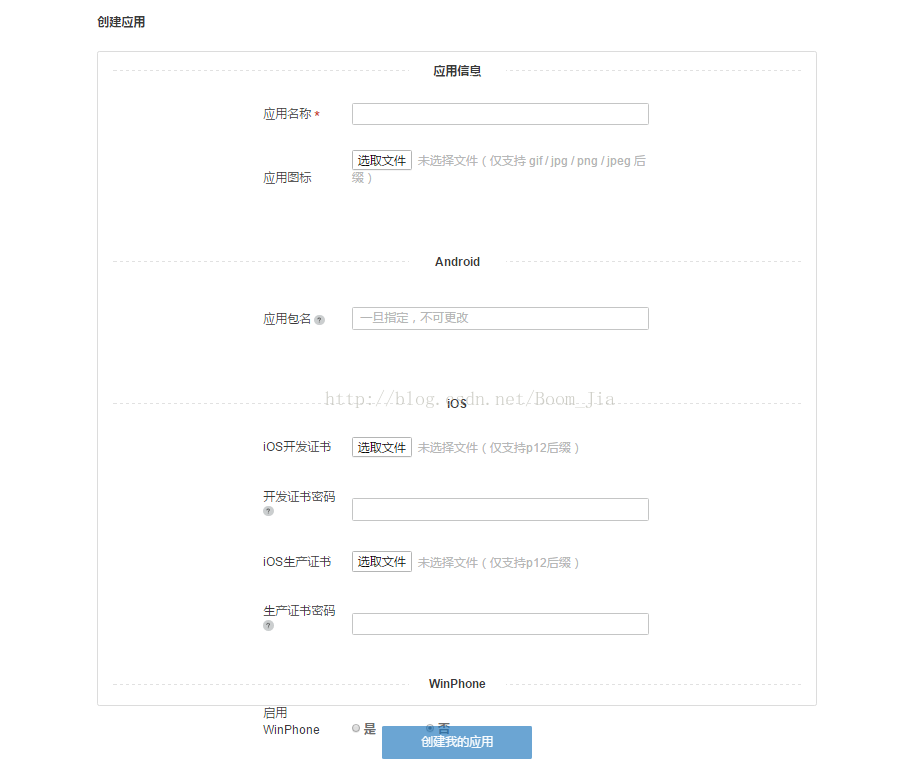 Android如何集成極光短信驗證
Android如何集成極光短信驗證
先借助Android studio工具新建一個新的空項目。步驟一(獲取appkey)1.在極光官網平台上新建短信應用(根據要求包名和應用名稱填寫好)2.獲取得到Jpush