編輯:關於Android編程
有時候,看到一些界面上的色彩,心情可能會很舒暢,有時候,看到一些其他色彩,就覺得很討厭,不爽,看到android L Palette 從圖片中提取篩選出來的顏色,覺得都挺好看的,就去了解了下Palette調色板。
看了代碼,根據我的理解,大概說說主要的步驟:
第一步,將圖片縮小,再整個過程中,可以降低計算量和減少內存的使用,跟不縮小也能達到一樣的效果
/**
* Scale the bitmap down so that it's smallest dimension is
* {@value #CALCULATE_BITMAP_MIN_DIMENSION}px. If {@code bitmap} is smaller than this, than it
* is returned.
*/
private static Bitmap scaleBitmapDown(Bitmap bitmap) {
final int minDimension = Math.min(bitmap.getWidth(), bitmap.getHeight());
if (minDimension <= CALCULATE_BITMAP_MIN_DIMENSION) {
// If the bitmap is small enough already, just return it
return bitmap;
}
final float scaleRatio = CALCULATE_BITMAP_MIN_DIMENSION / (float) minDimension;
return Bitmap.createScaledBitmap(bitmap,
Math.round(bitmap.getWidth() * scaleRatio),
Math.round(bitmap.getHeight() * scaleRatio),
false);
}
第二步,將縮小後的圖片數據,放在一個int 數組裡
/**
* Factory-method to generate a {@link ColorCutQuantizer} from a {@link Bitmap} object.
*
* @param bitmap Bitmap to extract the pixel data from
* @param maxColors The maximum number of colors that should be in the result palette.
*/
static ColorCutQuantizer fromBitmap(Bitmap bitmap, int maxColors) {
final int width = bitmap.getWidth();
final int height = bitmap.getHeight();
final int[] pixels = new int[width * height];
bitmap.getPixels(pixels, 0, width, 0, 0, width, height);
return new ColorCutQuantizer(new ColorHistogram(pixels), maxColors);
}
第三步,將這個int 數組由小到大排序,就相當於,將一張圖片一樣的顏色堆在一起,然後計算共有多少種顏色,每種顏色它是多大,這些是在一個叫ColorHistogram(顏色直方圖)類裡面計算的,用顏色直方圖來說,就是共有多少柱顏色,每柱顏色有多高
/**
* Class which provides a histogram for RGB values.
*/
final class ColorHistogram {
private final int[] mColors;
private final int[] mColorCounts;
private final int mNumberColors;
/**
* A new {@link ColorHistogram} instance.
*
* @param pixels array of image contents
*/
ColorHistogram(final int[] pixels) {
// Sort the pixels to enable counting below
Arrays.sort(pixels);
// Count number of distinct colors
mNumberColors = countDistinctColors(pixels);
// Create arrays
mColors = new int[mNumberColors];
mColorCounts = new int[mNumberColors];
// Finally count the frequency of each color
countFrequencies(pixels);
}
/**
* @return 獲取共用多少柱不同顏色 number of distinct colors in the image.
*/
int getNumberOfColors() {
return mNumberColors;
}
/**
* @return 獲取排好序後的不同顏色的數組 an array containing all of the distinct colors in the image.
*/
int[] getColors() {
return mColors;
}
/**
* @return 獲取保存每一柱有多高的數組 an array containing the frequency of a distinct colors within the image.
*/
int[] getColorCounts() {
return mColorCounts;
}
//計算共用多少柱不同顏色
private static int countDistinctColors(final int[] pixels) {
if (pixels.length < 2) {
// If we have less than 2 pixels we can stop here
return pixels.length;
}
// If we have at least 2 pixels, we have a minimum of 1 color...
int colorCount = 1;
int currentColor = pixels[0];
// Now iterate from the second pixel to the end, counting distinct colors
for (int i = 1; i < pixels.length; i++) {
// If we encounter a new color, increase the population
if (pixels[i] != currentColor) {
currentColor = pixels[i];
colorCount++;
}
}
return colorCount;
}
//計算每一柱有多高
private void countFrequencies(final int[] pixels) {
if (pixels.length == 0) {
return;
}
int currentColorIndex = 0;
int currentColor = pixels[0];
mColors[currentColorIndex] = currentColor;
mColorCounts[currentColorIndex] = 1;
Log.i(pixels.length,+ pixels.length);
if (pixels.length == 1) {
// If we only have one pixel, we can stop here
return;
}
// Now iterate from the second pixel to the end, population distinct colors
for (int i = 1; i < pixels.length; i++) {
if (pixels[i] == currentColor) {
// We've hit the same color as before, increase population
mColorCounts[currentColorIndex]++;
} else {
// We've hit a new color, increase index
currentColor = pixels[i];
currentColorIndex++;
mColors[currentColorIndex] = currentColor;
mColorCounts[currentColorIndex] = 1;
}
}
}
}
第四步,將各種顏色,根據RGB轉HSL算法,得出對應的HSL(H: Hue 色相,S:Saturation 飽和度L Lightness 明度),根據特定的條件,比如是明度L是否接近白色,黑色,還有一個判斷叫isNearRedILine,解釋是@return true if the color lies close to the red side of the I line(接近紅色私密區域附近?).,然後根據這三個條件,過濾掉這些顏色,什麼是HSL和RGB轉HSL算法可以查看下百科,比較有詳細說明
/**
* Private constructor.
*
* @param colorHistogram histogram representing an image's pixel data
* @param maxColors The maximum number of colors that should be in the result palette.
*/
private ColorCutQuantizer(ColorHistogram colorHistogram, int maxColors) {
final int rawColorCount = colorHistogram.getNumberOfColors();
final int[] rawColors = colorHistogram.getColors();//顏色數組
final int[] rawColorCounts = colorHistogram.getColorCounts();//對應rawColors每一個顏色數組的大小
// First, lets pack the populations into a SparseIntArray so that they can be easily
// retrieved without knowing a color's index
mColorPopulations = new SparseIntArray(rawColorCount);
for (int i = 0; i < rawColors.length; i++) {
mColorPopulations.append(rawColors[i], rawColorCounts[i]);
}
// Now go through all of the colors and keep those which we do not want to ignore
mColors = new int[rawColorCount];
int validColorCount = 0;
for (int color : rawColors) {
if (!shouldIgnoreColor(color)) {
mColors[validColorCount++] = color;
}
}
Log.d(mColors length, +mColors.length);
if (validColorCount <= maxColors) {
// The image has fewer colors than the maximum requested, so just return the colors
mQuantizedColors = new ArrayList();
for (final int color : mColors) {
mQuantizedColors.add(new Swatch(color, mColorPopulations.get(color)));
}
} else {
// We need use quantization to reduce the number of colors
mQuantizedColors = quantizePixels(validColorCount - 1, maxColors);
}
}
這裡截了張圖看看

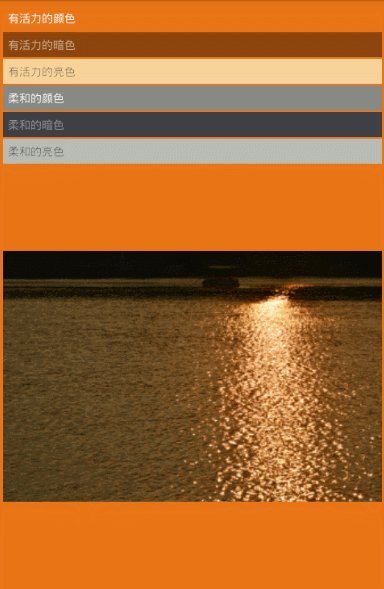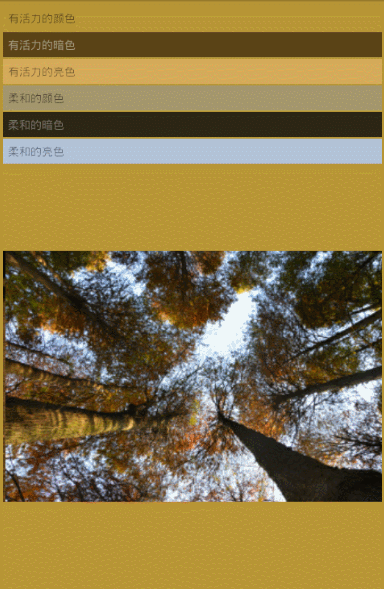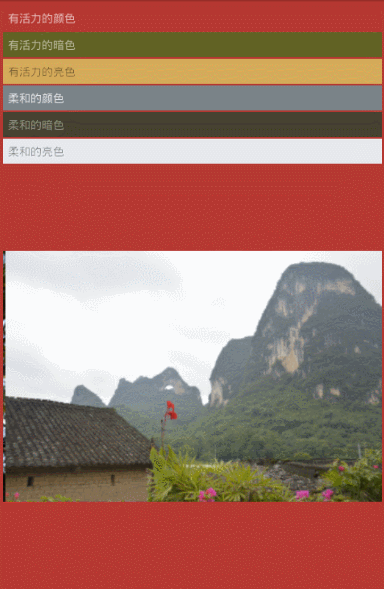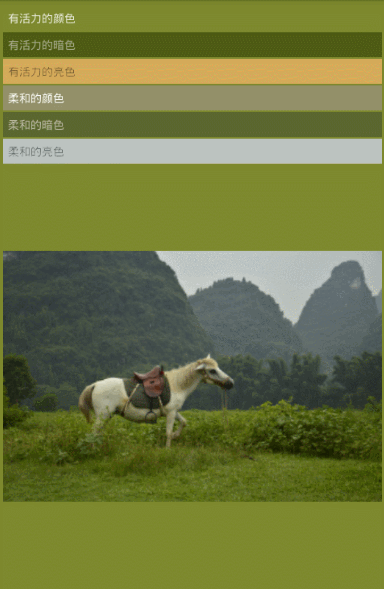
第五步,根據是各種亮度,飽和度的取值范圍,比如有活力的暗色,有活力的亮色,柔和的顏色,柔和的暗色,柔和的亮色,找到對應的顏色
private Swatch findColor(float targetLuma, float minLuma, float maxLuma,
float targetSaturation, float minSaturation, float maxSaturation) {
Swatch max = null;
float maxValue = 0f;
for (Swatch swatch : mSwatches) {
final float sat = swatch.getHsl()[1];
final float luma = swatch.getHsl()[2];
if (sat >= minSaturation && sat <= maxSaturation &&
luma >= minLuma && luma <= maxLuma &&
!isAlreadySelected(swatch)) {
float thisValue = createComparisonValue(sat, targetSaturation, luma, targetLuma,
swatch.getPopulation(), mHighestPopulation);
if (max == null || thisValue > maxValue) {
max = swatch;
maxValue = thisValue;
}
}
}
return max;
}
看下效果圖
 Android shape和selector 結合使用實例代碼
Android shape和selector 結合使用實例代碼
shape和selector是Android UI設計中經常用到的,比如我們要自定義一個圓角Button,點擊Button有些效果的變化,就要用到shape和select
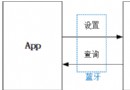 【Android藍牙開發】手機藍牙與下位機HC-05藍牙模塊通信系統
【Android藍牙開發】手機藍牙與下位機HC-05藍牙模塊通信系統
本文根據自己的實踐總結而來,參考前人博客之余,也自己總結和開發了一些功能,在這裡給自己備份也分享給大家。不同之處在於:自動打開並搜索藍牙、修改藍牙名字、完整接收藍牙傳輸
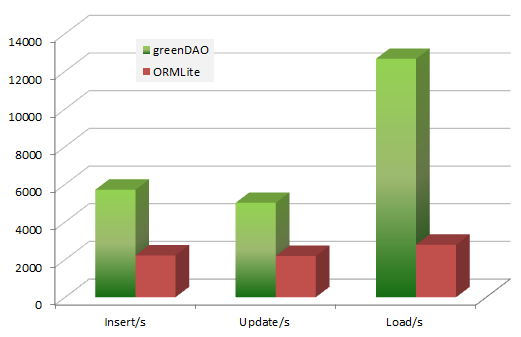 Android ORM數據庫之GreenDao使用教程及源碼分析
Android ORM數據庫之GreenDao使用教程及源碼分析
一、簡介1.Android ORM介紹?在平時的開發過程中,大家一定會或多或少地接觸到 SQLite。然而在使用它時,我們往往需要做許多額外的工作,像編寫 SQL 語句與
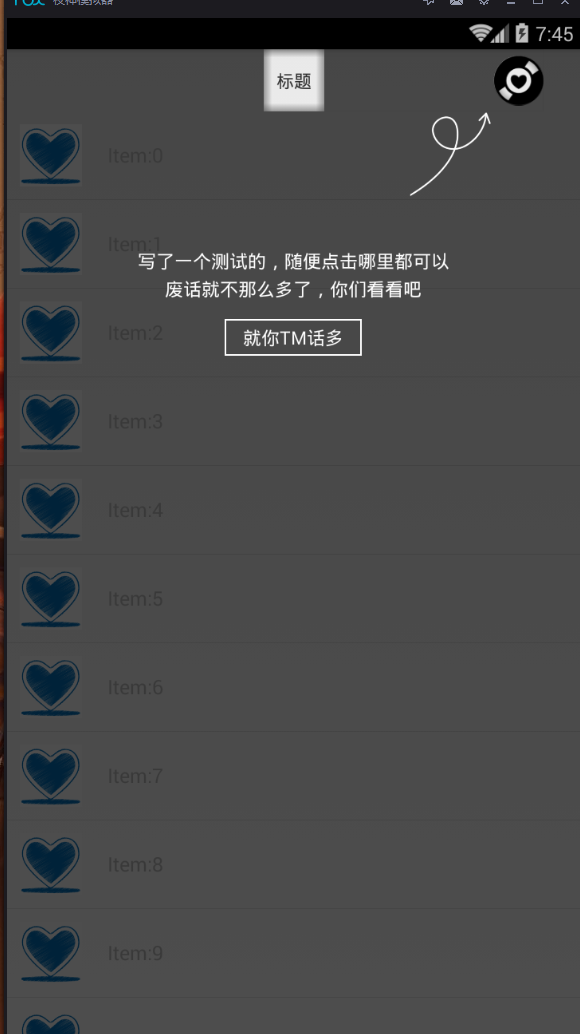 實現app第一次安裝浮層引導View!
實現app第一次安裝浮層引導View!
在我們第一次安裝app的時候,有一些app會出現一個覆蓋在我們原來View上面的浮層view,用來做一個app的指示,讓用戶更快的知道app的整體架構和功能點。下面大家看