編輯:關於Android編程
大家都知道在Android中通過AIDL可以跨進程調用Service中的數據,網上也有很多實例,但是大部分實例都是關於基本數據類型的遠程調用,很少講到復雜數據的調用,今天我用一個例子來演示一下怎樣用AIDL Service 傳遞復雜數據。
我們分2步開始:
第一步:部署我們的服務端,也就是Service端:
1:在Service端我先自定義2個類型:Person和Pet。因為我們需要跨進程傳遞Person對象和Pet對象,所以Person類和Pet類都必須實現Parcelable接口,並要求在實現類中定義一個名為CREATER,類型為Parcelable.creator的靜態Field。
代碼如下:
1 package com.example.remoteservice;
2
3 import android.os.Parcel;
4 import android.os.Parcelable;
5
6 public class Person implements Parcelable {
7 int id;
8 String name;
9 String pass;
10
11 public Person() {
12
13 }
14
15 public Person(int id, String name, String pass) {
16 this.id = id;
17 this.name = name;
18 this.pass = pass;
19 }
20
21 @Override
22 public boolean equals(Object o) {
23 if (this == o) {
24 return true;
25 }
26 if (o == null) {
27 return false;
28 }
29
30 if (getClass() != o.getClass()) {
31 return false;
32 }
33 Person other = (Person) o;
34
35 if (name == null) {
36 if (other.name != null) {
37 return false;
38 }
39 } else if (!name.equals(other.name)) {
40 return false;
41 }
42
43 if (pass == null) {
44 if (other.pass != null) {
45 return false;
46 }
47 } else if (!pass.equals(other.pass)) {
48 return false;
49 }
50
51 return true;
52 }
53
54 @Override
55 public int hashCode() {
56 final int prime = 31;
57 int result = 1;
58 result = prime * result + (name == null ? 0 : name.hashCode());
59 result = prime * result + (pass == null ? 0 : pass.hashCode());
60 return result;
61 }
62
63 @Override
64 public int describeContents() {
65
66 return 0;
67 }
68
69 @Override
70 public void writeToParcel(Parcel arg0, int arg1) {
71 arg0.writeInt(id);
72 arg0.writeString(name);
73 arg0.writeString(pass);
74 }
75
76 public static final Parcelable.Creator CREATOR = new Creator() {
77
78 @Override
79 public Person createFromParcel(Parcel source) {
80
81 return new Person(source.readInt(), source.readString(), source.readString());
82 }
83
84 @Override
85 public Person[] newArray(int size) {
86
87 return new Person[size];
88 }
89 };
90
91 public int getId() {
92 return id;
93 }
94
95 public void setId(int id) {
96 this.id = id;
97 }
98
99 public String getName() {
100 return name;
101 }
102
103 public void setName(String name) {
104 this.name = name;
105 }
106
107 public String getPass() {
108 return pass;
109 }
110
111 public void setPass(String pass) {
112 this.pass = pass;
113 }
114
115 }

因為我們會對Person進行比較,所以在Person類中我重寫了
public int hashCode() 和 public boolean equals(Object o)方法

1 package com.example.remoteservice;
2
3 import android.os.Parcel;
4 import android.os.Parcelable;
5
6 public class Pet implements Parcelable {
7 String name;
8 float weight;
9
10 public Pet(String name, float weight) {
11 this.name = name;
12 this.weight = weight;
13 }
14
15 public String getName() {
16 return name;
17 }
18
19 public void setName(String name) {
20 this.name = name;
21 }
22
23 public float getWeight() {
24 return weight;
25 }
26
27 public void setWeight(float weight) {
28 this.weight = weight;
29 }
30
31 @Override
32 public int describeContents() {
33
34 return 1;
35 }
36
37 @Override
38 public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) {
39 dest.writeString(name);
40 dest.writeFloat(weight);
41
42 }
43
44 public static final Parcelable.Creator CREATOR = new Creator() {
45
46 @Override
47 public Pet createFromParcel(Parcel source) {
48
49 return new Pet(source.readString(), source.readFloat());
50 }
51
52 @Override
53 public Pet[] newArray(int size) {
54
55 return new Pet[size];
56 }
57 };
58
59 @Override
60 public String toString() {
61
62 return name: + this.name + ;weight: + this.weight;
63 }
64
65 }

2:創建完自定義類型之後還需要用AIDL來定義它們,Person.aidl和Pet.aidl的代碼如下:
1 package com.example.remoteservice; 2 parcelable Person;
1 package com.example.remoteservice; 2 parcelable Pet;
3:完成1,2之後就可以使用AIDL定義通信接口了,在這裡我定義一個IPet.aidl的接口,代碼如下:

1 package com.example.remoteservice; //必須導入包
2 import com.example.remoteservice.Person; //指定自定義類的位置
3 import com.example.remoteservice.Pet;
4
5 interface IPet
6 {
7 List getPets(in Person owner);//這裡的in表示Person對象是輸入的參數
8 }

4:服務端的最後一步就是實現Service了,當然不要忘了注冊Service,代碼如下:

1 package com.example.remoteservice;
2
3 import com.example.remoteservice.IPet.Stub;
4
5 import java.util.ArrayList;
6 import java.util.HashMap;
7 import java.util.List;
8 import java.util.Map;
9
10 import android.app.Service;
11 import android.content.Intent;
12 import android.os.IBinder;
13 import android.os.RemoteException;
14 import android.util.Log;
15
16 public class RemoteService extends Service {
17
18 private PetBinder petBinder;
19
20 private static Map> pets = new HashMap>();
21 static {
22 ArrayList list1 = new ArrayList();
23 list1.add(new Pet(candy, 2.2f));
24 list1.add(new Pet(sandy, 4.2f));
25 pets.put(new Person(1, sun, sun), list1);
26
27 ArrayList list2 = new ArrayList();
28 list2.add(new Pet(moon, 5.2f));
29 list2.add(new Pet(hony, 6.2f));
30 pets.put(new Person(1, csx, csx), list2);
31
32 }
33
34 public class PetBinder extends Stub {// 繼承IPet接口中的Stub類,Stub類繼承了Binder類,所有PetBinder也間接的繼承了Binder類
35
36 @Override
37 public List getPets(Person owner) throws RemoteException {
38
39 return pets.get(owner);
40 }
41
42 }
43
44 @Override
45 public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
46
47 Log.i(csx, onBind);
48 return petBinder;
49 }
50
51 @Override
52 public void onCreate() {
53
54 super.onCreate();
55 Log.i(csx, onCreate);
56 petBinder = new PetBinder();// 實例化Binder
57
58 }
59
60 @Override
61 public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
62
63 Log.i(csx, onUnbind);
64 return super.onUnbind(intent);
65 }
66
67 @Override
68 public void onDestroy() {
69
70 super.onDestroy();
71 Log.i(csx, onDestroy);
72 }
73
74 }

這是我Service端的部署情況(其中MainActivity可以不用去實現,因為我們只提供服務,沒有窗口顯示):

第二步:部署客戶端:
1.在客戶端新建一個包,命名需要和服務端放置aidl文件的包名相同(我這裡是com.example.remoteservice),然後把服務端的Person.java,Pet.java,Person.aidl,Pet.aidl,IPet.aidl復制到這個包下面

2.在activity中綁定遠程服務進行數據交換,layout布局和activity代碼如下:

110 11 15 16 20 21 27 28 29



1 package com.example.remoteclient;
2
3 import android.app.Service;
4 import android.content.ComponentName;
5 import android.content.Intent;
6 import android.content.ServiceConnection;
7 import android.os.Bundle;
8 import android.os.IBinder;
9 import android.os.RemoteException;
10 import android.support.v7.app.ActionBarActivity;
11 import android.util.Log;
12 import android.view.View;
13 import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
14 import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
15 import android.widget.Button;
16 import android.widget.EditText;
17 import android.widget.ListView;
18
19 import com.example.remoteservice.IPet;
20 import com.example.remoteservice.Person;
21 import com.example.remoteservice.Pet;
22
23 import java.util.List;
24
25 public class RemoteClient extends ActionBarActivity {
26
27 public static final String REMOTE_SERVICE_ACTION = com.example.remoteservice.RemoteService.ACTION;
28 EditText editText;
29 Button button;
30 ListView listView;
31
32 IPet petService;// 聲明IPet接口
33 List pets;
34 ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection() {
35
36 @Override
37 public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
38 Log.i(csx, onServiceDisconnected);
39 conn = null;
40 }
41
42 @Override
43 public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
44 Log.i(csx, onServiceConnected);
45 petService = IPet.Stub.asInterface(service);// 通過遠程服務的Binder實現接口
46
47 }
48 };
49
50 @Override
51 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
52 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
53 setContentView(R.layout.remote_client_layout);
54 editText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText_person);
55 button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button_ok);
56 listView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.listView_pet);
57
58 Intent service = new Intent();
59 service.setAction(REMOTE_SERVICE_ACTION);
60
61 bindService(service, conn, Service.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);// 綁定遠程服務
62
63 button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
64
65 @Override
66 public void onClick(View v) {
67 String personName = editText.getText().toString();
68 if (personName == null || personName.equals()) {
69
70 return;
71 }
72
73 try {
74 pets = petService.getPets(new Person(1, personName, personName));// 調用遠程service的getPets方法
75 updataListView();
76
77 } catch (RemoteException e) {
78
79 e.printStackTrace();
80 } catch (NullPointerException e) {
81 e.printStackTrace();
82 }
83
84 }
85 });
86
87 }
88
89 public void updataListView() {
90 listView.setAdapter(null);
91
92 if (pets == null || pets.isEmpty()) {
93 return;
94
95 }
96 ArrayAdapter adapter = new ArrayAdapter(RemoteClient.this,
97 android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, pets);
98 listView.setAdapter(adapter);
99
100 }
101
102 @Override
103 protected void onDestroy() {
104
105 unbindService(conn);// 解除綁定
106 super.onDestroy();
107 }
108
109 }

到此為止所有的工作都完成了,下面我們看一下效果:我在編輯框中輸入“csx”,點擊確定,就會顯示出服務端RemoteService中pets的相應數據。

 andriod 利用ExpandableList做三級樹
andriod 利用ExpandableList做三級樹
源碼DEMO 等待審核中....... --------------------------------------------------------------
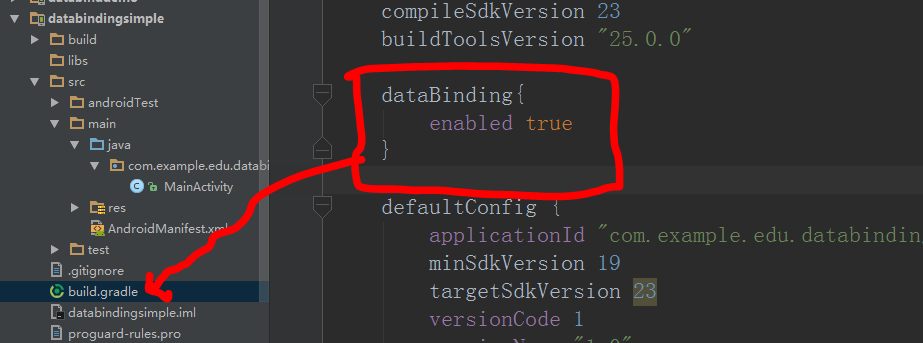 Android之DataBinding初體驗(一)
Android之DataBinding初體驗(一)
DataBinding是谷歌推出的一個官方的數據綁定框架,所以我們有必要學下怎麼使用它。如果你英文足夠好就可以去官網看。https://developer.android
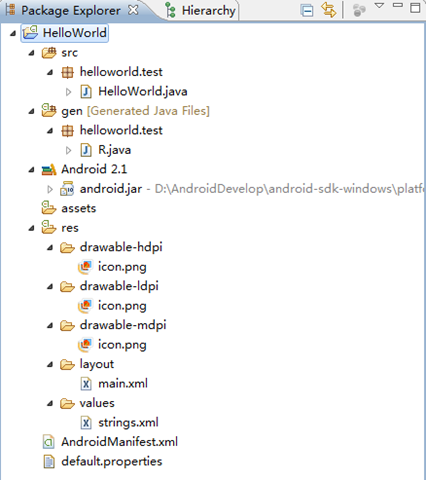 Android編程入門之HelloWorld項目目錄結構分析
Android編程入門之HelloWorld項目目錄結構分析
本文實例講述了Android編程入門之HelloWorld項目目錄結構。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:我們介紹了如何搭建Android開發環境及簡單地建立一個Hello
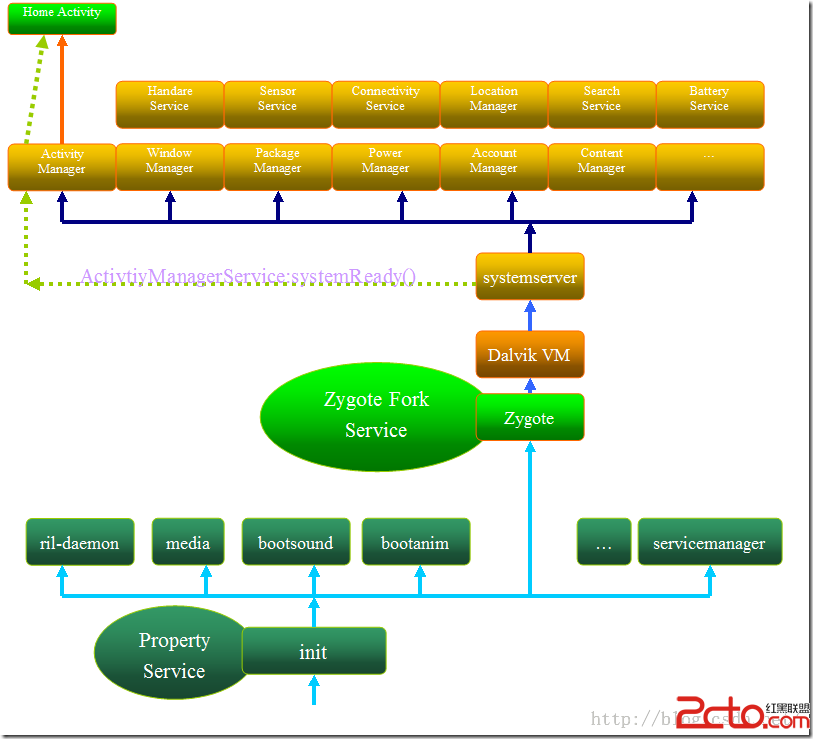 Android 框架啟動流程
Android 框架啟動流程
As we all know,Android手機系統本質上是一個基於Linux的應用程序,它以Linux系統為內核。因此系統的啟動過程包括Linux內核啟動和Androi