編輯:關於Android編程

/**
* Set the scrolled position of your view. This will cause a call to
* {@link #onScrollChanged(int, int, int, int)} and the view will be
* invalidated.
* @param x the x position to scroll to
* @param y the y position to scroll to
*/
public void scrollTo(int x, int y) {
if (mScrollX != x || mScrollY != y) {
int oldX = mScrollX;
int oldY = mScrollY;
mScrollX = x;
mScrollY = y;
invalidateParentCaches();
onScrollChanged(mScrollX, mScrollY, oldX, oldY);
if (!awakenScrollBars()) {
postInvalidateOnAnimation();
}
}
}還有一個是
/**
* Move the scrolled position of your view. This will cause a call to
* {@link #onScrollChanged(int, int, int, int)} and the view will be
* invalidated.
* @param x the amount of pixels to scroll by horizontally
* @param y the amount of pixels to scroll by vertically
*/
public void scrollBy(int x, int y) {
scrollTo(mScrollX + x, mScrollY + y);
}我們仔細的來解讀一下上面的函數。這個源碼我是摘自5.0的源碼。我們看到ScrollBy這個函數也是調用的ScrollTo我們就來分析一下ScrollTo這個函數到底做了什麼工作?很簡單的幾句代碼,最重要的一句就是這一句 postInvalidateOnAnimation();這一句代碼會去回調我們的ondraw函數,在ondraw函數裡面繪制我們的可見區域,然後我們在來看看VIew的draw的方法
* Manually render this view (and all of its children) to the given Canvas.
* The view must have already done a full layout before this function is
* called. When implementing a view, implement
* {@link #onDraw(android.graphics.Canvas)} instead of overriding this method.
* If you do need to override this method, call the superclass version.
*
* @param canvas The Canvas to which the View is rendered.
*/
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
if (mClipBounds != null) {
canvas.clipRect(mClipBounds);
}
final int privateFlags = mPrivateFlags;
final boolean dirtyOpaque = (privateFlags & PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) == PFLAG_DIRTY_OPAQUE &&
(mAttachInfo == null || !mAttachInfo.mIgnoreDirtyState);
mPrivateFlags = (privateFlags & ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) | PFLAG_DRAWN;
/*
* Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed
* in the appropriate order:
*
* 1. Draw the background
* 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading
* 3. Draw view's content
* 4. Draw children
* 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers
* 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance)
*/
// Step 1, draw the background, if needed
int saveCount;
if (!dirtyOpaque) {
final Drawable background = mBackground;
if (background != null) {
final int scrollX = mScrollX;
final int scrollY = mScrollY;
if (mBackgroundSizeChanged) {
background.setBounds(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop);
mBackgroundSizeChanged = false;
}
if ((scrollX | scrollY) == 0) {
background.draw(canvas);
} else {
canvas.translate(scrollX, scrollY);
background.draw(canvas);
canvas.translate(-scrollX, -scrollY);
}
}
}
// skip step 2 & 5 if possible (common case)
final int viewFlags = mViewFlags;
boolean horizontalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_HORIZONTAL) != 0;
boolean verticalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_VERTICAL) != 0;
if (!verticalEdges && !horizontalEdges) {
// Step 3, draw the content
if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas);
// Step 4, draw the children
dispatchDraw(canvas);
// Step 6, draw decorations (scrollbars)
onDrawScrollBars(canvas);
if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas);
}
// we're done...
return;
}
/*
* Here we do the full fledged routine...
* (this is an uncommon case where speed matters less,
* this is why we repeat some of the tests that have been
* done above)
*/
boolean drawTop = false;
boolean drawBottom = false;
boolean drawLeft = false;
boolean drawRight = false;
float topFadeStrength = 0.0f;
float bottomFadeStrength = 0.0f;
float leftFadeStrength = 0.0f;
float rightFadeStrength = 0.0f;
// Step 2, save the canvas' layers
int paddingLeft = mPaddingLeft;
final boolean offsetRequired = isPaddingOffsetRequired();
if (offsetRequired) {
paddingLeft += getLeftPaddingOffset();
}
int left = mScrollX + paddingLeft;
int right = left + mRight - mLeft - mPaddingRight - paddingLeft;
int top = mScrollY + getFadeTop(offsetRequired);
int bottom = top + getFadeHeight(offsetRequired);
if (offsetRequired) {
right += getRightPaddingOffset();
bottom += getBottomPaddingOffset();
}
final ScrollabilityCache scrollabilityCache = mScrollCache;
final float fadeHeight = scrollabilityCache.fadingEdgeLength;
int length = (int) fadeHeight;
// clip the fade length if top and bottom fades overlap
// overlapping fades produce odd-looking artifacts
if (verticalEdges && (top + length > bottom - length)) {
length = (bottom - top) / 2;
}
// also clip horizontal fades if necessary
if (horizontalEdges && (left + length > right - length)) {
length = (right - left) / 2;
}
if (verticalEdges) {
topFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getTopFadingEdgeStrength()));
drawTop = topFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f;
bottomFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getBottomFadingEdgeStrength()));
drawBottom = bottomFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f;
}
if (horizontalEdges) {
leftFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getLeftFadingEdgeStrength()));
drawLeft = leftFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f;
rightFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getRightFadingEdgeStrength()));
drawRight = rightFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f;
}
saveCount = canvas.getSaveCount();
int solidColor = getSolidColor();
if (solidColor == 0) {
final int flags = Canvas.HAS_ALPHA_LAYER_SAVE_FLAG;
if (drawTop) {
canvas.saveLayer(left, top, right, top + length, null, flags);
}
if (drawBottom) {
canvas.saveLayer(left, bottom - length, right, bottom, null, flags);
}
if (drawLeft) {
canvas.saveLayer(left, top, left + length, bottom, null, flags);
}
if (drawRight) {
canvas.saveLayer(right - length, top, right, bottom, null, flags);
}
} else {
scrollabilityCache.setFadeColor(solidColor);
}
// Step 3, draw the content
if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas);
// Step 4, draw the children
dispatchDraw(canvas);
// Step 5, draw the fade effect and restore layers
final Paint p = scrollabilityCache.paint;
final Matrix matrix = scrollabilityCache.matrix;
final Shader fade = scrollabilityCache.shader;
if (drawTop) {
matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * topFadeStrength);
matrix.postTranslate(left, top);
fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix);
canvas.drawRect(left, top, right, top + length, p);
}
if (drawBottom) {
matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * bottomFadeStrength);
matrix.postRotate(180);
matrix.postTranslate(left, bottom);
fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix);
canvas.drawRect(left, bottom - length, right, bottom, p);
}
if (drawLeft) {
matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * leftFadeStrength);
matrix.postRotate(-90);
matrix.postTranslate(left, top);
fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix);
canvas.drawRect(left, top, left + length, bottom, p);
}
if (drawRight) {
matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * rightFadeStrength);
matrix.postRotate(90);
matrix.postTranslate(right, top);
fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix);
canvas.drawRect(right - length, top, right, bottom, p);
}
canvas.restoreToCount(saveCount);
// Step 6, draw decorations (scrollbars)
onDrawScrollBars(canvas);
if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas);
}
} LinearLayout linearLayout = new LinearLayout(this);
linearLayout.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(2000, 2000));//這裡我把寬高設置大點好做測試因為我的手機是1920*1080所以設置得大一點
linearLayout.setOrientation(LinearLayout.HORIZONTAL);
TextView textView1 = new TextView(this);
textView1.setText("hello i am text 1");
textView1.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(1000, 2000));
linearLayout.addView(textView1);
TextView textView2 = new TextView(this);
textView2.setText("hello i am text 2");
textView2.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(1000, 2000));
linearLayout.addView(textView2);
setContentView(linearLayout);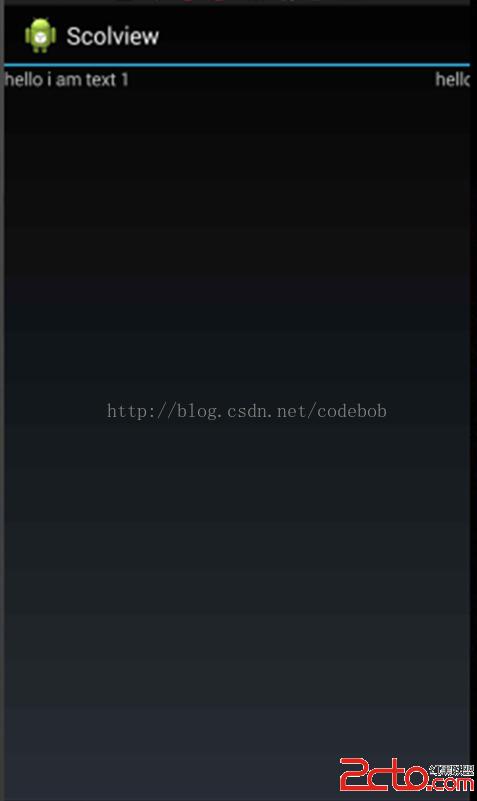 可以很清晰的看到我們的TextView2沒有顯示出來,這裡也就很明了了,因為超出了屏幕,然後我們重新加一句代碼。
可以很清晰的看到我們的TextView2沒有顯示出來,這裡也就很明了了,因為超出了屏幕,然後我們重新加一句代碼。
LinearLayout linearLayout = new LinearLayout(this);
linearLayout.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(2000, 2000));//這裡我把寬高設置大點好做測試因為我的手機是1920*1080所以設置得大一點
linearLayout.setOrientation(LinearLayout.HORIZONTAL);
TextView textView1 = new TextView(this);
textView1.setText("hello i am text 1");
textView1.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(1000, 2000));
linearLayout.addView(textView1);
TextView textView2 = new TextView(this);
textView2.setText("hello i am text 2");
textView2.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(1000, 2000));
linearLayout.addView(textView2);
linearLayout.scrollTo(1000, 0);//我們加了這一句代碼
setContentView(linearLayout);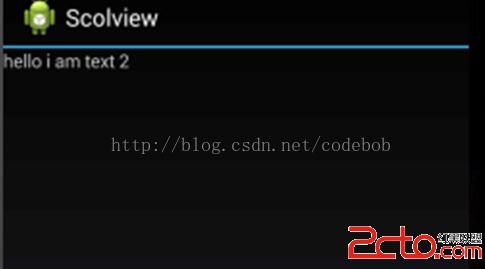 可以看到text2顯示完全了,這也很明顯因為我們把視圖向左滾動了。在後面講的UI控件的系列教程這兩個scrollTo和scrollBy函數用得很頻繁,所以這裡從源頭把它給分析了一次,幫助我們後面好理解。
可以看到text2顯示完全了,這也很明顯因為我們把視圖向左滾動了。在後面講的UI控件的系列教程這兩個scrollTo和scrollBy函數用得很頻繁,所以這裡從源頭把它給分析了一次,幫助我們後面好理解。 Android 高仿微信實時聊天 基於百度雲推送
Android 高仿微信實時聊天 基於百度雲推送
一直在仿微信界面,今天終於有幸利用百度雲推送仿一仿微信聊天了~~~ 首先特別感謝:weidi1989分享的Android之基於百度雲推送IM ,大家可以直接
 Android自定義View基礎開發之圖片加載進度條
Android自定義View基礎開發之圖片加載進度條
學會了Paint,Canvas的基本用法之後,我們就可以動手開始實踐了,先寫個簡單的圖片加載進度條看看。 按照慣例,先看效果圖,再決定要不要往下看:既然看到這裡了,應該是
 關於Android端配置極光推送
關於Android端配置極光推送
因為業務需要,android客戶端需要加推送,原來采用的百度推送,但是小米手機有時候收不到,後來換成了極光推送,極光的話所有設備都能收到推送,但是在高峰的時候會推遲,博主
 android 在有 簽名文件的情況下,找回 password 和 alias
android 在有 簽名文件的情況下,找回 password 和 alias
哈哈,這種需求我也是醉了。今天有個搞ios的朋友(以前公司同事,現在是Leader)問我他們公司安卓要做版本升級,然後簽名文件有但是password 和 alias忘記