編輯:關於Android編程
Android系統較為龐大,要搞清楚系統運行原理需要長期努力。系統啟動部分看了幾遍但沒有總結,今天簡單總結一下。
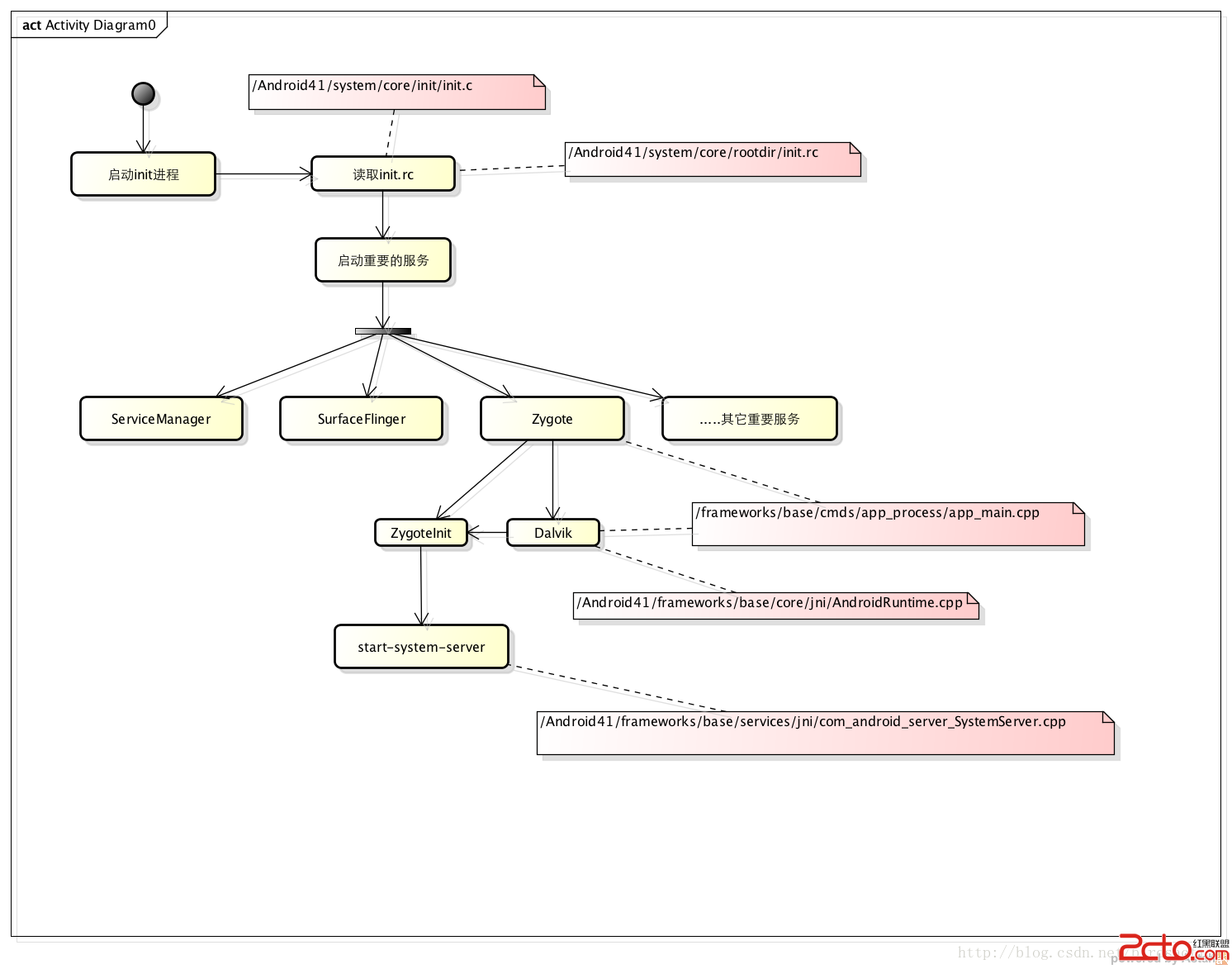
Android首先重點是啟動zygote進程,這個進程來源於init.rc的讀取,zygote進程主要用於孵化新的app程序,還包括啟動android大量的服務SystemService
本人研究的源碼是4.1的,其它版本的可能略有差異。
init.rc 文件作為啟動配置重要的入口出,init.c將會讀取這個文件,核心的相關進程也將開啟。
/Android41/system/core/init/init.c
重點是解析了init.rc文件,並且開始處理相關指令。找到main入口,貼出部分代碼
mkdir(/dev, 0755);
mkdir(/proc, 0755);
mkdir(/sys, 0755);
mount(tmpfs, /dev, tmpfs, MS_NOSUID, mode=0755);
mkdir(/dev/pts, 0755);
mkdir(/dev/socket, 0755);
mount(devpts, /dev/pts, devpts, 0, NULL);
mount(proc, /proc, proc, 0, NULL);
mount(sysfs, /sys, sysfs, 0, NULL);
/* indicate that booting is in progress to background fw loaders, etc */
close(open(/dev/.booting, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT, 0000));
/* We must have some place other than / to create the
* device nodes for kmsg and null, otherwise we won't
* be able to remount / read-only later on.
* Now that tmpfs is mounted on /dev, we can actually
* talk to the outside world.
*/
open_devnull_stdio();
klog_init();
property_init();
get_hardware_name(hardware, &revision);
process_kernel_cmdline();
#ifdef HAVE_SELINUX
INFO(loading selinux policy
);
selinux_load_policy();
#endif
is_charger = !strcmp(bootmode, charger);
INFO(property init
);
if (!is_charger)
property_load_boot_defaults();
INFO(reading config file
);
init_parse_config_file(/init.rc); //讀取rc文件
找到Android41/system/core/rootdir/init.rc
這個文件裡面還包括,ServiceManager IPC服務管理者啟動,surfaceflinger圖像服務,bootanim啟動動畫,media媒體服務等。
service zygote /system/bin/app_process -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
class main
socket zygote stream 660 root system
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
app_process啟動代碼在 frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp
main中的主要代碼。
while (i < argc) {
const char* arg = argv[i++];
if (!parentDir) {
parentDir = arg;
} else if (strcmp(arg, --zygote) == 0) {
zygote = true;
niceName = zygote;
} else if (strcmp(arg, --start-system-server) == 0) {
startSystemServer = true;
} else if (strcmp(arg, --application) == 0) {
application = true;
} else if (strncmp(arg, --nice-name=, 12) == 0) {
niceName = arg + 12;
} else {
className = arg;
break;
}
}
if (niceName && *niceName) {
setArgv0(argv0, niceName);
set_process_name(niceName);
}
runtime.mParentDir = parentDir;
if (zygote) {
runtime.start(com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit,
startSystemServer ? start-system-server : );
} else if (className) {
// Remainder of args get passed to startup class main()
runtime.mClassName = className;
runtime.mArgC = argc - i;
runtime.mArgV = argv + i;
runtime.start(com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit,
application ? application : tool);
} else {
fprintf(stderr, Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.
);
app_usage();
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL(app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.);
return 10;
}
虛擬機的啟動在/Android41/frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp 裡面包含了大量的初始化比如heap大小內存分配等,這裡暫時不說。
先看ZygoteInit代碼
/Android41/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
public static void main(String argv[]) {
try {
// Start profiling the zygote initialization.
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
registerZygoteSocket();
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
preload();
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
// Finish profiling the zygote initialization.
SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeZygoteSnapshot();
// Do an initial gc to clean up after startup
gc();
// If requested, start system server directly from Zygote
if (argv.length != 2) {
throw new RuntimeException(argv[0] + USAGE_STRING);
}
if (argv[1].equals(start-system-server)) {
startSystemServer();
} else if (!argv[1].equals()) {
throw new RuntimeException(argv[0] + USAGE_STRING);
}
Log.i(TAG, Accepting command socket connections);
if (ZYGOTE_FORK_MODE) {
runForkMode();
} else {
runSelectLoopMode();
}
closeServerSocket();
} catch (MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
caller.run();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
Log.e(TAG, Zygote died with exception, ex);
closeServerSocket();
throw ex;
}
}
下面看看啟動SystemService
private static boolean startSystemServer()
throws MethodAndArgsCaller, RuntimeException {
/* Hardcoded command line to start the system server */
String args[] = {
--setuid=1000,
--setgid=1000,
--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007,
--capabilities=130104352,130104352,
--runtime-init,
--nice-name=system_server,
com.android.server.SystemServer,
};
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs = null;
int pid;
try {
parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args);
ZygoteConnection.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
ZygoteConnection.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
/* Request to fork the system server process */
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.debugFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
/* For child process */
if (pid == 0) {
handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}
return true;
}
/Android41/libcore/dalvik/src/main/java/dalvik/system/Zygote.java 其實是需要調用對應的native方法.
forkSystemServer fork一個獨立進程用於SystemServer
native方法在 /Android41/dalvik/vm/native/dalvik_system_zygote.cpp
fork成功後,就調用傳入的參數com.android.server.SystemServer.java
SystemServer開啟了Android應用層的大部分服務,包括電源管理,電池,網絡 AMS WMS等。
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer 目錄下面也包含了大量的相應的服務代碼。
public static final void init2() {
Slog.i(TAG, Entered the Android system server!);
Thread thr = new ServerThread();
thr.setName(android.server.ServerThread);
thr.start();
}
有 native public static void init1(String[] args);調用。
找到對應的底層代碼。
/AndroidSource/Android41/frameworks/base/services/jni/com_android_server_SystemServer.cpp
namespace android {
extern C int system_init();
static void android_server_SystemServer_init1(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz)
{
system_init();
}
/*
* JNI registration.
*/
static JNINativeMethod gMethods[] = {
/* name, signature, funcPtr */
{ init1, ([Ljava/lang/String;)V, (void*) android_server_SystemServer_init1 },//注冊了init1方法
};
int register_android_server_SystemServer(JNIEnv* env)
{
return jniRegisterNativeMethods(env, com/android/server/SystemServer,
gMethods, NELEM(gMethods));
}
}; // namespace android
system_init()是個外部函數,到那找到函數體?
/AndroidSource/Android41/frameworks/base/services/jni/Android.mk文件中有添加靜態Library
LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES :=
libandroid_runtime
libandroidfw
libcutils
libhardware
libhardware_legacy
libnativehelper
libsystem_server
libutils
libui
libinput
libskia
libgui
libusbhost
libsuspend
system_server 在 /AndroidSource/Android41/frameworks/base/cmds/system_server 可以找到,可以看Android.mk文件知道模塊都編譯了那些文件
看System_init.cpp代碼方法
extern C status_t system_init()
{
ALOGI(Entered system_init());
sp proc(ProcessState::self());
sp sm = defaultServiceManager();
ALOGI(ServiceManager: %p
, sm.get());
sp grim = new GrimReaper();
sm->asBinder()->linkToDeath(grim, grim.get(), 0);
char propBuf[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
property_get(system_init.startsurfaceflinger, propBuf, 1);
if (strcmp(propBuf, 1) == 0) {
// Start the SurfaceFlinger
SurfaceFlinger::instantiate();
}
property_get(system_init.startsensorservice, propBuf, 1);
if (strcmp(propBuf, 1) == 0) {
// Start the sensor service
SensorService::instantiate();
}
// And now start the Android runtime. We have to do this bit
// of nastiness because the Android runtime initialization requires
// some of the core system services to already be started.
// All other servers should just start the Android runtime at
// the beginning of their processes's main(), before calling
// the init function.
ALOGI(System server: starting Android runtime.
);
AndroidRuntime* runtime = AndroidRuntime::getRuntime();
ALOGI(System server: starting Android services.
);
JNIEnv* env = runtime->getJNIEnv();
if (env == NULL) {
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
jclass clazz = env->FindClass(com/android/server/SystemServer);
if (clazz == NULL) {
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
jmethodID methodId = env->GetStaticMethodID(clazz, init2, ()V);
if (methodId == NULL) {
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(clazz, methodId);
ALOGI(System server: entering thread pool.
);
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
ALOGI(System server: exiting thread pool.
);
return NO_ERROR;
}
init2方法啟動了線程開始了Android服務的加載和啟動。
基本流程就是啟動Zygote進程,虛擬機的創建,然後是SystemServer加載服務,當然還同時啟動了其它服務包括ServiceManager,SurfaceFlinger程序。
下一部分詳細分析SystemServer啟動和ActivityManagerService啟動應用程序。
畫個圖容易記住。
 Android開發實現高德地圖定位
Android開發實現高德地圖定位
一、 要實現高德地圖定位呢,首先需要做好以下幾步准備:1. 在高德開放平台注冊帳號注冊地址:http://lbs.amap.com2. 在開發中下載Android平台下的
 (Android review) 任務棧與啟動模式
(Android review) 任務棧與啟動模式
這一個知識點主要以理解為主:一、任務棧(task stack)1、作用:就是用來管理activity的進入,退出。記錄了用戶的行為。2、舉例:假如要進行一下操作:這時候,
 Android百度地圖(四)如何引入離線地圖包
Android百度地圖(四)如何引入離線地圖包
本篇我們准備為地圖添加:引入離線地圖包官方文檔:http://lbsyun.baidu.com/index.php?title=androidsdk/guide/offl
 Android官方開發文檔之從Eclipse遷移到Android Studio開發篇
Android官方開發文檔之從Eclipse遷移到Android Studio開發篇
1、前言從Eclipse遷移項目到Android Studio需要適應一個新的項目結構,建立系統和IDE的功能。為了簡化遷移過程,Android Studio提供了重要工