編輯:關於Android編程
兩年學習android開發的時候 了解到Service的技術
一直沒抽出時間整理這塊內容 現在終於有時間來詳細的比較深入的編碼 理解這個Service了
一. Service與Activity
android開發是離不開Activity的 Activity相當於WIN的窗口
但是一般只有一個現實在前端 其他的Activity要麼壓到後台的棧中 要麼手動銷毀掉了
而Service是可以啟動多個的 這樣多個Service就是相當是並行狀態
並且 這個Service可以和Activity保持相對獨立
換句話說 可以ActivityA中啟動Service
在ActivityB中給Service發消息
最後在ActivityC中關閉Service
這幾個Activity輪流現實在前端
二. Service與線程
其實 理解線程的話 就很容易理解Service
Activity Service 都是在主線程中執行的 不過Activity對象是只有一個顯示在前端
而Service 不顯示在前端 並可以生成多個對象
這樣存儲在Service的數據 不會像Activity內的數據 隨著Activity銷毀而銷毀
另外可以開啟新的線程 作為後台處理線程
完全獨立於Activity 只處理Activity發來的消息
三. Code
manifest中
注冊2個activity 一個Service
布局activity_main 第一個activity 給三個按鈕 開始Service 結束Service 和下一個界面
activity_sec 第二個activity 也給三個按鈕 退出界面 發送消息2和結束Service
MainActivity的按鈕處理
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
switch (arg0.getId()) {
case (R.id.button_on):
//啟動 Service
this.startService(new Intent(this, PlayService.class));
break;
case (R.id.button_off): {
//停止 Service
this.stopService(new Intent(this,PlayService.class));
}
break;
case (R.id.button_next): {
//打開另一個Activity
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(MainActivity.this, SecActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}SecActivity的按鈕處理
public void onClick(View arg0) {
switch (arg0.getId()) {
case (R.id.button_esc):
//退出Activity
finish();
break;
case (R.id.button_off): {
//關閉Service
this.stopService(new Intent(this,PlayService.class));
}
break;
case (R.id.button_step2): {
//向Service 發消息
Intent intent = new Intent(this, PlayService.class);
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putInt("op", 2);
intent.putExtras(bundle);
this.startService(intent);
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}PlayService完整代碼
public class PlayService extends Service {
private HandlerThread mHandlerThread;
private Handler mPlayHandler;
class PlayHandler extends Handler{
public PlayHandler(){
}
public PlayHandler(Looper lp){
super(lp);
}
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.handleMessage(msg);
//接收到線程處理的數據
// 注意 這裡已經不是主線程上 而是獨立的線程上
System.out.println("PlayHandler handleMessage");
System.out.println("PlayHandler thread id :"+Thread.currentThread().getId());
}
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("PlayService on onBind");
return null;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate();
Toast.makeText(this, "Play Service Created", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
System.out.println("PlayService on onCreate");
//啟動線程
mHandlerThread = new HandlerThread("Play_Service_thread");
mHandlerThread.start();
mPlayHandler = new PlayHandler(mHandlerThread.getLooper());
}
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onStart(intent, startId);
//onStart 可以用於接收Activity發來的消息
//注意 到這裡還是處於主線程上
Toast.makeText(this, "Play Service onStart", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
System.out.println("PlayService on onStart");
System.out.println("PlayService thread id :"+Thread.currentThread().getId());
if (intent != null) {
Bundle bundle = intent.getExtras();
if (bundle != null) {
int op = bundle.getInt("op");
switch (op) {
case 2:
//通過Message對象 轉發給線程處理
System.out.println("PlayService on onStart step2");
Message msg = mPlayHandler.obtainMessage();
msg.sendToTarget();
break;
}
}
}//if
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDestroy();
Toast.makeText(this, "Play Service Stopped", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
System.out.println("PlayService on Destroy");
//退出線程 銷毀數據
mHandlerThread.quit();
mHandlerThread = null;
mPlayHandler = null;
}
}
Service的生成與銷毀都可以在Activity內調用
但是Service的生命周期不等於Activity 而是在主線程 這是得注意的地方
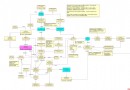 Android MediaPlayer 框架UML圖
Android MediaPlayer 框架UML圖
Android開發交流群:50342056 目的 本文用一個UML類圖,講解mp3文件播放的框架流程。內容以下幾個方面: 1.UML類圖 2.stagefrightPl
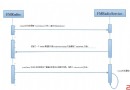 Android FM模塊學習之一 FM啟動流程
Android FM模塊學習之一 FM啟動流程
最近在學習FM模塊,FM是一個值得學習的模塊,可以從上層看到底層。上層就是FM的按扭操作和界面顯示,從而調用到FM底層驅動來實現廣播收聽的功能。 看看
 android開發要避免的那些坑
android開發要避免的那些坑
SparseArray 目前有很多地方從性能優化方說使用SparseArray來替換hashMap,來節省內存,提高性能。Linkify.addLinks() 這個類可以
 Android 關於ViewPager結合碎片Fragment的簡單使用
Android 關於ViewPager結合碎片Fragment的簡單使用
一. 首先在xml添加ViewPager控件 我們希望每個viewpager顯示一張圖片 代碼如下 二.分析