編輯:關於Android編程
title: android.os.Parcelable文檔自譯 date: 2014-12-05 09:16:06
tags:
android.os.Parcelable接口的已知間接子類很多,這裡就不列舉了:
Class Overview
Interface for classes whose instances can be written to and restored from a
Parcel. Classes implementing the Parcelable interface must also have a static
field called CREATOR, which is an object implementing the Parcelable.Creator
interface.
該Interface用於實例可以被寫入,並且可以從Parcel中恢復的classes(對於Parcel暫時只要知道它是一個存 放數據的容器就好了,我會在android IPC中寫到它)。實現android.os.Parcelable接口的類必須持有一個實 現了android.os.Parcelable接口的名為 CREATOR 的靜態字段。
android.os.Parcelable接口典型使用方式,這是官網的例子:
package me.androiddemo.canglangwenyue.androiddemo;
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable;
/**
* Created by canglangwenyue on 12/5/14.
*/
public class MyParcelable implements Parcelable {
private int mData;
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
public void writeToParcel(Parcel out, int flags) {
out.writeInt(mData);
}
public static final Parcelable.Creator
= new Parcelable.Creator
public MyParcelable createFromParcel(Parcel in) {
return new MyParcelable(in);
}
public MyParcelable[] newArray(int size) {
return new MyParcelable[size];
}
};
private MyParcelable(Parcel in) {
mData = in.readInt();
}
}
Summary(簡介)
Nested Classes(嵌套類)
1.interface Parcelable.ClassLoaderCreator
Specialization of Parcelable.Creator that allows you to receive
the ClassLoader the object is being created in.
解析:專業化的 Parcelable.Creator,允許你接收的Object內部創建的 ClassLoader 對象.
2.interface Parcelable.Creator
Interface that must be implemented and provided as a public CREATOR field that
generates instances of your Parcelable class from a Parcel.
解析:該接口必須被子類實現,而且CREATOR 作為公有字段來提供,CREATOR 用於從 Parcel中實例化你的可包裝類.
Constants(常量)
1.int CONTENTS_FILE_DESCRIPTOR
Bit masks for use with describeContents(): each bit represents a kind of object
considered to have potential special significance when marshalled.
解析:用於 describeContents() 的位掩碼,每一位代表它編組時附加的特殊含義。
2.int PARCELABLE_WRITE_RETURN_VALUE
Flag for use with writeToParcel(Parcel, int): the object being written is a
return value, that is the result of a function such as Parcelable
someFunction(), void someFunction(out Parcelable), or void
someFunction(inout Parcelable).
解析:writeToParcel(Parcel, int)的標志位:作為一個返回值,是Parcelable
someFunction(), void someFunction(out Parcelable), or void
someFunction(inout Parcelable)返回的result。
Public Methods(公共method)
1.abstract int describeContents()
Describe the kinds of special objects contained in this Parcelable's marshalled
representation.
解析:描述各種特殊對象,它們包含在可包裝對象的編組形式中.
2.abstract void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags)
Flatten this object in to a Parcel.
解析:將該對象展開到Parcel(存放數據的容器)中。
Parcelable適用於通過Intent來傳遞自定義對象。最後給出一個用Parcelable進行數據傳送的例子
1.發送Object的Activity,內容很簡單,點擊Button,Intent攜帶Object跳轉到MainActivity2(用來接收Object的Activity)。
package me.androiddemo.canglangwenyue.androiddemo;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.support.v7.app.ActionBarActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* @author canglangwenyue
* 用來發送信息的Activity
*/
public class MainActivity extends ActionBarActivity {
private Button sendButton;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
sendButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.send_button);
sendButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent();
Person person = new Person();
person.name = WenYue;
intent.putExtra(WenYue,person);
intent.setClass(MainActivity.this,MainActivity2.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu_main, menu);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
// Handle action bar item clicks here. The action bar will
// automatically handle clicks on the Home/Up button, so long
// as you specify a parent activity in AndroidManifest.xml.
int id = item.getItemId();
//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement
if (id == R.id.action_settings) {
return true;
}
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
}
2.MainActivity2用來接收來自MainActivity的Object,並打印Person.name的長度和content。
package me.androiddemo.canglangwenyue.androiddemo;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.support.v7.app.ActionBarActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
/**
3.Parcelable的實現,具體細節前面已經講到了,就不多說了。
package me.androiddemo.canglangwenyue.androiddemo;
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable;
/**
* Created by canglangwenyue on 12/5/14.
* Parcelable常用於Intent中進行自定義對象的傳遞
*/
public class Person implements Parcelable {
public String name;
@Override
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) {
dest.writeString(name);
}
/*
需要重寫Creator實現android.os.Parcelable接口的類必須持有一個實現了android.os.Parcelable接口的名為 CREATOR 的靜態字段
*/
public static final Creator
/*
重寫Creator方法
*/
@Override
public Person createFromParcel(Parcel source) {
Person person = new Person();
person.name = source.readString();
return person;
}
@Override
public Person[] newArray(int size) {
return new Person[0];
}
};
}
最後給出在MainActivity2中log打印的結果,眼見為實,哈哈:

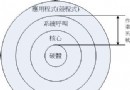 Android系統開發(6)——Linux底層輸入輸出
Android系統開發(6)——Linux底層輸入輸出
一、操作系統的體系結構計算機是由一堆硬件組成的,操作系統是為了有效的控制這些硬件資源的軟件。操作系統除了有效地控制這些硬件資源的分配,並提供計算機運行所需要的功能之外,為
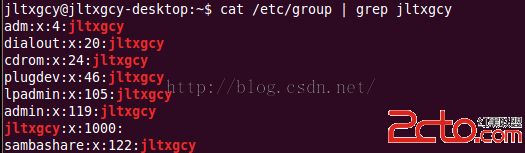 Android中的權限管理(基於uid gid gids setUid)
Android中的權限管理(基於uid gid gids setUid)
我們首先來說一下傳統的Linux基於uid,gid的權限管理機制:1、用戶的uid gid gids:Ubuntu操作系統當前登陸的用戶是jltxgcy,那麼該用戶的ui
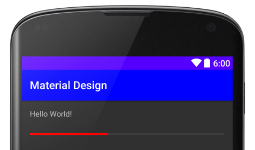 Android5.0美不勝收的新特性 Material Design
Android5.0美不勝收的新特性 Material Design
Google提出了全新的設計規范Material Design,扁平化的設計,加上明亮的色彩,有一種美不勝收的感覺。Material Design翻譯過來叫做&ldquo
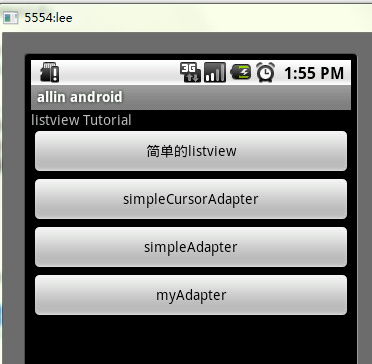 Android ListView詳解
Android ListView詳解
ListView 控件可使用四種不同視圖顯示項目。通過此控件,可將項目組成帶有或不帶有列標頭的列,並顯示伴隨的圖標和文本。 可使用 ListView 控件將稱作 List