編輯:關於Android編程
不時的回過頭來看看自己的Andriod學習、實踐之路,總發現有些以前不明白的,現在清楚緣由;也會發現一些之前沒怎麼關注的,現在看到了 ,非常想去深刻了解的。
比如:Bundle。
在一個Activity的生命周期中,首先要執行的是onCreate方法
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_modifyheadphoto);
}
在默認情況下,上面紅色部分 是 onCreate方法的參數 , 默認執行的方法, 都會自動添加,而這部分一般情況,我都不去關注,你呢?
今天,就來搞清楚這個Bundle的作用,以及和Intent的區別。
一、Bundle:A mapping from String values to various Parcelable types
鍵值對的集合
類繼承關系:
java.lang.Object
android.os.Bundle
Bundle類是一個final類:
public final class Bundle extends Objectimplements Parcelable Cloneable
作用:可以用作是兩個Activity間的通訊。
用法:
①、裝載數據:
Bundle mBundle = new Bundle();
mBundle.putString("DataTag", "要傳過去的數據");
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(MainActivity.this, Destion.class);
intent.putExtras(mBundle);
②、目標Activity解析數據
Bundle bundle = getIntent().getExtras(); //得到傳過來的bundle
String data = bundle.getString("DataTag");//讀出數據
二、Intent的含義和作用 就略了。。。直接上二者比較:
兩個Activity之間傳遞數據,數據的附加有兩種方式:
一種是直接 intent.putxx();
另一種是 先bundle.putxx(), 然後再調用public Intent putExtras (Bundle extras) 添加bundle.
其實兩種的本質是一樣的。
先看Intent的方法:
public Intent putExtra(String name, boolean value) {
if (mExtras == null) {
mExtras = new Bundle();
}
mExtras.putBoolean(name, value);
return this;
}
其中mExtras是intent內部定義的一個private Bundle變量。
可以看到,intent其實是調用了bundle相應的put函數,也就是說,intent內部還是用bundle來實現數據傳遞的,只是封裝了一層而已。
而使用Bundle傳值的話最後調用的方法:Intent.putExtras(Bundle extras):
public Intent putExtras(Bundle extras) {
if (mExtras == null) {
mExtras = new Bundle();
}
mExtras.putAll(extras);
return this;
}
可以看到,其實是把之前那個bundle中的數據批量添加到intent內部的bundle中。
其實是和上面的直接用Intent傳鍵值對是一樣的原理。
總之呢,Intent旨在數據傳遞,bundle旨在存取數據,當然intent也提供一部分數據的存取,但比起bundle就顯得不專業,不靈活的多
 MIUI 8和MIUI 7有什麼區別 MIUI 8和MIUI 7區別對比
MIUI 8和MIUI 7有什麼區別 MIUI 8和MIUI 7區別對比
期待已久的MIUI 8終於上線啦!經過全新設計的MIUI 8靈感來源於變幻萬千的“萬花筒”,在色彩、交互動畫、系統字體等方面的大膽改
 【Android圖像處理】底片(濾鏡)效果
【Android圖像處理】底片(濾鏡)效果
底片效果是怎麼實現的?先看看代碼://底片 public static Bitmap Negative(Bitmap bm){ int Width = bm.getWi
 Android 中使用ExpandableListView 實現分組的實例
Android 中使用ExpandableListView 實現分組的實例
Android 中使用ExpandableListView 實現分組一個視圖顯示垂直滾動兩級列表中的條目。這不同於列表視圖,允許兩個層次,類似於QQ的好友分組
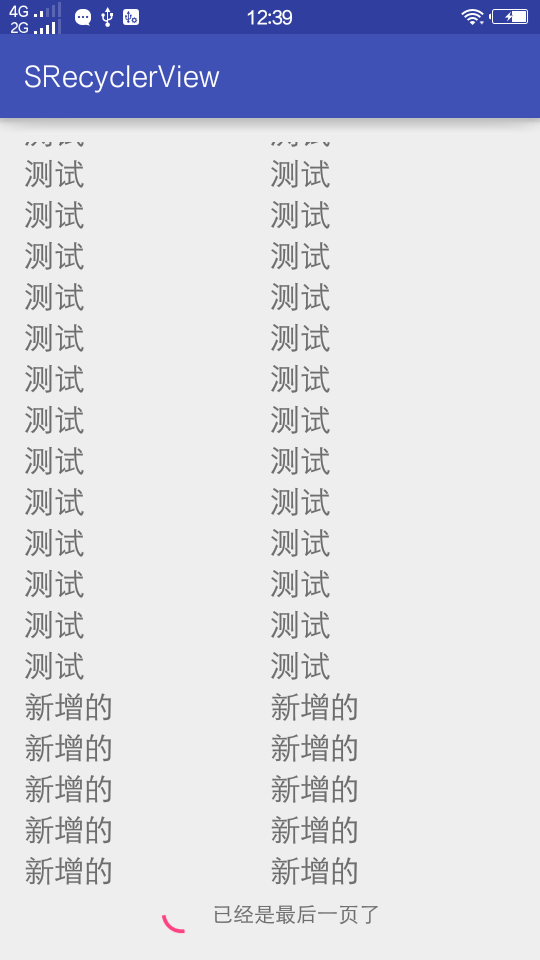 Android RecyclerView 上拉加載更多及下拉刷新功能的實現方法
Android RecyclerView 上拉加載更多及下拉刷新功能的實現方法
RecyclerView 已經出來很久了,但是在項目中之前都使用的是ListView,最近新的項目上了都大量的使用了RecycleView.尤其是瀑布流的下拉刷新,網上吧