Layout Parameters(布局參數):
在XML文件中,我們經常會看到類似於layout_width這樣的布局屬性(layout attributes),這些屬性通常是用來定義
View的布局參數,為了讓它適應於ViewGroup。
每個ViewGroup類都實現了一個繼承自ViewGroup.LayoutParams的嵌套類。
子類包含定義每個子View大小和位置的屬性類型,為了讓它適應於ViewGroup。
下面我們通過官方文檔的一張圖片以及一個XML文件來具體學習一下:
1 <!-- activity的根布局是LinearLayout 也就是線性布局 -->
2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
3 xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
4 android:layout_width="match_parent"
5 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
6 android:background="#0f0"
7 android:orientation="vertical" >
8 <!-- LinearLayout有個子View是RelativeLayout -->
9 <RelativeLayout
10 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
11 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
12 android:background="#f00"
13 >
14 <TextView
15 android:id="@+id/textView1InRL"
16 android:background="#fff"
17 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
18 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
19 android:text="TextView" />
20
21 <TextView
22 android:id="@+id/textView2InRL"
23 android:background="#fff"
24 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
25 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
26 android:text="TextView2"
27 android:layout_toRightOf="@id/textView1InRL"
28 />
29 <TextView
30 android:background="#fff"
31 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
32 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
33 android:text="TextView3"
34 android:layout_below="@id/textView2InRL"
35 />
36 </RelativeLayout>
37 <Button
38 android:text="Button1InLinearLayout"
39 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
40 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
41 />
42 <Button
43 android:text="Button2InLinearLayout"
44 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
45 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
46 />
47 </LinearLayout>
從上,我們可以看出。布局中的子元素都必須定義使他合適於它的父布局的布局參數,盡管它可能為它的子元素定義不同的布局參數。比如上圖中的RelativeLayout,它受父Layout:LinearLayout影響,然後它的布局參數則影響到了它的子元素:三個TextView。
常見的布局(Common Layouts):
下面介紹Android中常用的布局:
1.線性布局(Linear Layout)
將子元素按垂直方向或水平方向線性排列。(如果窗口的長度超過了屏幕的長度,則可以生成一個滾動條)
窗口長度超過屏幕長度,生成滾動條(srollbar)的方法:
用ScrollView包裹線性布局:
1 <LinearLayout
2 android:layout_width="fill_parent"
3 android:layout_height="fill_parent"
4 xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
5 <ScrollView
6 android:layout_width="fill_parent"
7 android:layout_height="wrap_content">
8 <LinearLayout
9 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
10 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
11 android:orientation="vertical">
12 <!-- 這裡放線性布局中的內容 -->
13 </LinearLayout>
14 </ScrollView>
15 </LinearLayout>
通過一個例子來深入學習一下線性布局:
1 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
2 xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
3 android:layout_width="match_parent"
4 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
5 android:paddingLeft="20dp"
6 android:paddingRight="20dp"
7 android:orientation="vertical" >
8 <ScrollView
9 android:layout_width="fill_parent"
10 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
11 >
12 <LinearLayout
13 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
14 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
15 android:orientation="vertical"
16 >
17 <EditText
18 android:layout_width="match_parent"
19 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
20 android:hint="帳號:" />
21 <EditText
22 android:layout_width="match_parent"
23 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
24 android:hint="密碼:" />
25 <LinearLayout
26 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
27 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
28 android:orientation="horizontal"
29 >
30 <Button
31 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
32 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
33 android:layout_marginLeft="30dp"
34 android:text="登錄"
35 />
36 <Button
37 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
38 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
39 android:layout_marginLeft="100dp"
40 android:text="注冊"
41 />
42 </LinearLayout>
43 <ImageView
44 android:layout_width="match_parent"
45 android:layout_height="500dp"
46 android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher"
47 />
48 <TextView
49 android:layout_width="match_parent"
50 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
51 android:text="LinearLayout大小超過屏幕大小的測試"
52 />
53 </LinearLayout>
54 </ScrollView>
55 </LinearLayout>
2.相關布局(Relative Layout)
正如其名,相關布局。我們可以通過讓子元素互相相關(比如Button A在TextView B的下面)或與父布局互相相關來指定
它們在布局中的位置。
默認地,所有的子View都被放置在布局的左上方(top-left)。
設置子View之間和子View與父母之間關系的參數如下圖所示:
同樣通過一個例子來學習一下相關布局:
1 <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
2 xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
3 android:layout_width="match_parent"
4 android:layout_height="match_parent"
5 tools:context=".MainActivity" >
6
7 <!--android:layout_centerHorizontal 設置TextView在水平中心-->
8 <TextView
9 android:id="@+id/login"
10 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
11 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
12 android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
13 android:textSize="20sp"
14 android:text="登錄界面" />
15 <!--android:layout_marginTop="24dp" 設置了EditText的頂部上面的空閒空間是24dp -->
16 <EditText
17 android:id="@+id/editText1"
18 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
19 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
20 android:layout_below="@id/login"
21 android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
22 android:layout_marginTop="24dp"
23 android:hint="username"
24 android:ems="10" >
25
26 <requestFocus />
27 </EditText>
28 <!-- android:layout_below="@+id/editText1"editText2在editText1下面 -->
29 <EditText
30 android:id="@+id/editText2"
31 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
32 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
33 android:layout_below="@+id/editText1"
34 android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
35 android:layout_marginTop="27dp"
36 android:ems="10"
37 android:hint="password"
38 android:inputType="textPassword" />
39 <!-- android:layout_alignRight="@id/editText2"設置cancelButton與
40 editText2的右邊緣對齊-->
41 <Button
42 android:id="@+id/cancelButton"
43 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
44 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
45 android:layout_below="@id/editText2"
46 android:layout_alignRight="@id/editText2"
47 android:text="取消"
48 />
49 <!-- android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/cancelButton"設置確定按鈕在取消按鈕的左邊 -->
50 <Button
51 android:id="@+id/confirmButton"
52 android:layout_width="wrap_content"
53 android:layout_height="wrap_content"
54 android:layout_below="@id/editText2"
55 android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/cancelButton"
56 android:text="確定"
57 />
58
59 </RelativeLayout>
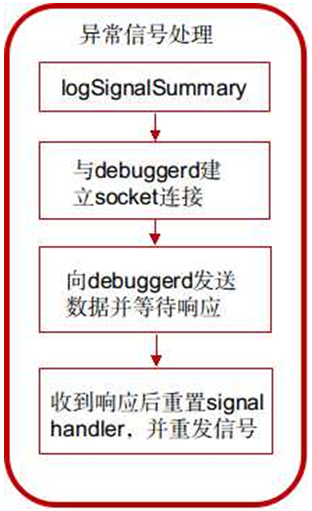 Android debuggerd 源碼分析
Android debuggerd 源碼分析
 Android組件ViewStub基本使用方法詳解
Android組件ViewStub基本使用方法詳解
 Android中標簽容器控件的實例詳解
Android中標簽容器控件的實例詳解
 詳解Android中Activity運行時屏幕方向與顯示方式
詳解Android中Activity運行時屏幕方向與顯示方式