編輯:關於Android編程
main(int argc, char **argv) {
......
Device* device = make_device();
ui = device->GetUI();
gCurrentUI = ui;
ui->Init();
ui->SetLocale(locale);
ui->SetBackground(RecoveryUI::NONE);
if (show_text) ui->ShowText(true);
......
if (status != INSTALL_SUCCESS || ui->IsTextVisible()) {
prompt_and_wait(device, status);
}
......
}
1、首先新建了一個Device類的對象, Device類封裝了一些操作,包括UI的操作
2、調用Device類的GetUI()返回一個DefaultUI對象,recovery中涉及到三個UI類,三個類之間為繼承關系,分別為DefaultUI、
ScreenRecoveryUI、RecoveryUI
3、調用DefaultUI類的Init(), DefaultUI類沒有Init()方法,因此將調用它的父類ScreenRecoveryUI的Init()
4、同理,調用ScreenRecoveryUI類的SetLocale()來標識幾個比較特別的區域
5、同理,調用ScreenRecoveryUI類的SetBackground()設置初始狀態的背景圖
6、顯示recovery的主界面,即一個選擇菜單
void ScreenRecoveryUI::Init()
{
gr_init();
gr_font_size(&char_width, &char_height);
text_col = text_row = 0;
text_rows = gr_fb_height() / char_height;
if (text_rows > kMaxRows) text_rows = kMaxRows;
text_top = 1;
text_cols = gr_fb_width() / char_width;
if (text_cols > kMaxCols - 1) text_cols = kMaxCols - 1;
LoadBitmap("icon_installing", &backgroundIcon[INSTALLING_UPDATE]);
backgroundIcon[ERASING] = backgroundIcon[INSTALLING_UPDATE];
LoadBitmap("icon_error", &backgroundIcon[ERROR]);
backgroundIcon[NO_COMMAND] = backgroundIcon[ERROR];
LoadBitmap("progress_empty", &progressBarEmpty);
LoadBitmap("progress_fill", &progressBarFill);
LoadLocalizedBitmap("installing_text", &backgroundText[INSTALLING_UPDATE]);
LoadLocalizedBitmap("erasing_text", &backgroundText[ERASING]);
LoadLocalizedBitmap("no_command_text", &backgroundText[NO_COMMAND]);
LoadLocalizedBitmap("error_text", &backgroundText[ERROR]);
int i;
progressBarIndeterminate = (gr_surface*)malloc(indeterminate_frames *
sizeof(gr_surface));
for (i = 0; i < indeterminate_frames; ++i) {
char filename[40];
// "indeterminate01.png", "indeterminate02.png", ...
sprintf(filename, "indeterminate%02d", i+1);
LoadBitmap(filename, progressBarIndeterminate+i);
}
if (installing_frames > 0) {
installationOverlay = (gr_surface*)malloc(installing_frames *
sizeof(gr_surface));
for (i = 0; i < installing_frames; ++i) {
char filename[40];
// "icon_installing_overlay01.png",
// "icon_installing_overlay02.png", ...
sprintf(filename, "icon_installing_overlay%02d", i+1);
LoadBitmap(filename, installationOverlay+i);
}
} else {
installationOverlay = NULL;
}
pthread_create(&progress_t, NULL, progress_thread, NULL);
RecoveryUI::Init();
}
1、gr_init() 初始化圖形設備,分配Pixelflinger庫渲染的內存
2、gr_font_size() 將字體對應的surface長寬賦值給char_width和char_height
3、LoadBitmap() 將png生成surface, 每個png圖片對應一個surface, 所有surface存放在一個數組中 4、LoadLocalizedBitmap() 將區域文字所在的圖片中的text信息根據當前的locale提取出來,生成對應的surface, 所以 surface也存放在一個數組中 6、pthread_create(&progress_t, NULL, progress_thread, NULL) 創建一個線程,該線程的任務是一個死循環,在該循環中不停 地檢測currentIcon以及progressBarType來決定是不是要更新進度條。 7、調用RecoveryUI的Init(),初始化輸入事件處理。
void ScreenRecoveryUI::SetLocale(const char* locale) {
if (locale) {
char* lang = strdup(locale);
for (char* p = lang; *p; ++p) {
if (*p == '_') {
*p = '\0';
break;
}
}
// A bit cheesy: keep an explicit list of supported languages
// that are RTL.
if (strcmp(lang, "ar") == 0 || // Arabic
strcmp(lang, "fa") == 0 || // Persian (Farsi)
strcmp(lang, "he") == 0 || // Hebrew (new language code)
strcmp(lang, "iw") == 0 || // Hebrew (old language code)
strcmp(lang, "ur") == 0) { // Urdu
rtl_locale = true;
}
free(lang);
}
}
void ScreenRecoveryUI::SetBackground(Icon icon)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&updateMutex);
// Adjust the offset to account for the positioning of the
// base image on the screen.
if (backgroundIcon[icon] != NULL) {
gr_surface bg = backgroundIcon[icon];
gr_surface text = backgroundText[icon];
overlay_offset_x = install_overlay_offset_x + (gr_fb_width() - gr_get_width(bg)) / 2;
overlay_offset_y = install_overlay_offset_y +
(gr_fb_height() - (gr_get_height(bg) + gr_get_height(text) + 40)) / 2;
}
currentIcon = icon;
update_screen_locked();
pthread_mutex_unlock(&updateMutex);
}
SetBackground函數比較簡潔,關鍵部分在update_screen_locked,下面我們重點分析一下。
update_screen_locked和update_progress_locked是recovery的UI部分的關鍵函數,update_screen_locked用來更新背景, update_progress_locked用來更新進度條,因為顯示的畫面會一直在更新,所以這兩個函數會在不同的地方被反復調用
void ScreenRecoveryUI::update_screen_locked()
{
draw_screen_locked();
gr_flip();
}
update_screen_locked包含兩個操作,一是更新screen, 二是切換前後buffer。
void ScreenRecoveryUI::draw_screen_locked()
{
draw_background_locked(currentIcon);
draw_progress_locked();
if (show_text) {
SetColor(TEXT_FILL);
gr_fill(0, 0, gr_fb_width(), gr_fb_height());
int y = 0;
int i = 0;
if (show_menu) {
SetColor(HEADER);
for (; i < menu_top + menu_items; ++i) {
if (i == menu_top) SetColor(MENU);
if (i == menu_top + menu_sel) {
// draw the highlight bar
SetColor(MENU_SEL_BG);
gr_fill(0, y-2, gr_fb_width(), y+char_height+2);
// white text of selected item
SetColor(MENU_SEL_FG);
if (menu[i][0]) gr_text(4, y, menu[i], 1);
SetColor(MENU);
} else {
if (menu[i][0]) gr_text(4, y, menu[i], i < menu_top);
}
y += char_height+4;
}
SetColor(MENU);
y += 4;
gr_fill(0, y, gr_fb_width(), y+2);
y += 4;
++i;
}
SetColor(LOG);
// display from the bottom up, until we hit the top of the
// screen, the bottom of the menu, or we've displayed the
// entire text buffer.
int ty;
int row = (text_top+text_rows-1) % text_rows;
for (int ty = gr_fb_height() - char_height, count = 0;
ty > y+2 && count < text_rows;
ty -= char_height, ++count) {
gr_text(4, ty, text[row], 0);
--row;
if (row < 0) row = text_rows-1;
}
}
}
void ScreenRecoveryUI::draw_progress_locked()
{
if (currentIcon == ERROR) return;
if (currentIcon == INSTALLING_UPDATE || currentIcon == ERASING) {
draw_install_overlay_locked(installingFrame);
}
if (progressBarType != EMPTY) {
int iconHeight = gr_get_height(backgroundIcon[INSTALLING_UPDATE]);
int width = gr_get_width(progressBarEmpty);
int height = gr_get_height(progressBarEmpty);
int dx = (gr_fb_width() - width)/2;
int dy = (3*gr_fb_height() + iconHeight - 2*height)/4;
// Erase behind the progress bar (in case this was a progress-only update)
gr_color(0, 0, 0, 255);
gr_fill(dx, dy, width, height);
if (progressBarType == DETERMINATE) {
float p = progressScopeStart + progress * progressScopeSize;
int pos = (int) (p * width);
if (rtl_locale) {
// Fill the progress bar from right to left.
if (pos > 0) {
gr_blit(progressBarFill, width-pos, 0, pos, height, dx+width-pos, dy);
}
if (pos < width-1) {
gr_blit(progressBarEmpty, 0, 0, width-pos, height, dx, dy);
}
} else {
// Fill the progress bar from left to right.
if (pos > 0) {
gr_blit(progressBarFill, 0, 0, pos, height, dx, dy);
}
if (pos < width-1) {
gr_blit(progressBarEmpty, pos, 0, width-pos, height, dx+pos, dy);
}
}
}
if (progressBarType == INDETERMINATE) {
static int frame = 0;
gr_blit(progressBarIndeterminate[frame], 0, 0, width, height, dx, dy);
// in RTL locales, we run the animation backwards, which
// makes the spinner spin the other way.
if (rtl_locale) {
frame = (frame + indeterminate_frames - 1) % indeterminate_frames;
} else {
frame = (frame + 1) % indeterminate_frames;
}
}
}
}
int gr_init(void); /* 初始化圖形顯示,主要是打開設備、分配內存、初始化一些參數 */ void gr_exit(void); /* 注銷圖形顯示,關閉設備並釋放內存 */ int gr_fb_width(void); /* 獲取屏幕的寬度 */ int gr_fb_height(void); /* 獲取屏幕的高度 */ gr_pixel *gr_fb_data(void); /* 獲取顯示數據緩存的地址 */ void gr_flip(void); /* 刷新顯示內容 */ void gr_fb_blank(bool blank); /* 清屏 */ void gr_color(unsigned char r, unsigned char g, unsigned char b, unsigned char a); /* 設置字體顏色 */ void gr_fill(int x, int y, int w, int h); /* 填充矩形區域,參數分別代表起始坐標、矩形區域大小 */ int gr_text(int x, int y, const char *s); /* 顯示字符串 */ int gr_measure(const char *s); /* 獲取字符串在默認字庫中占用的像素長度 */ void gr_font_size(int *x, int *y); /* 獲取當前字庫一個字符所占的長寬 */ void gr_blit(gr_surface source, int sx, int sy, int w, int h, int dx, int dy); /* 填充由source指定的圖片 */ unsigned int gr_get_width(gr_surface surface); /* 獲取圖片寬度 */ unsigned int gr_get_height(gr_surface surface); /* 獲取圖片高度 */ /* 根據圖片創建顯示資源數據,name為圖片在mk文件指定的相對路徑 */ int res_create_surface(const char* name, gr_surface* pSurface); void res_free_surface(gr_surface surface); /* 釋放資源數據 */
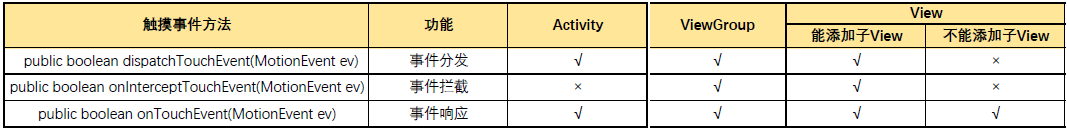 Android的事件分發與消費機制
Android的事件分發與消費機制
一、Touch的三個重要方法在Android中,與觸摸事件也就是 Touch 相關的有三個重要方法,這三個方法共同完成觸摸事件的分發。public boolean dis
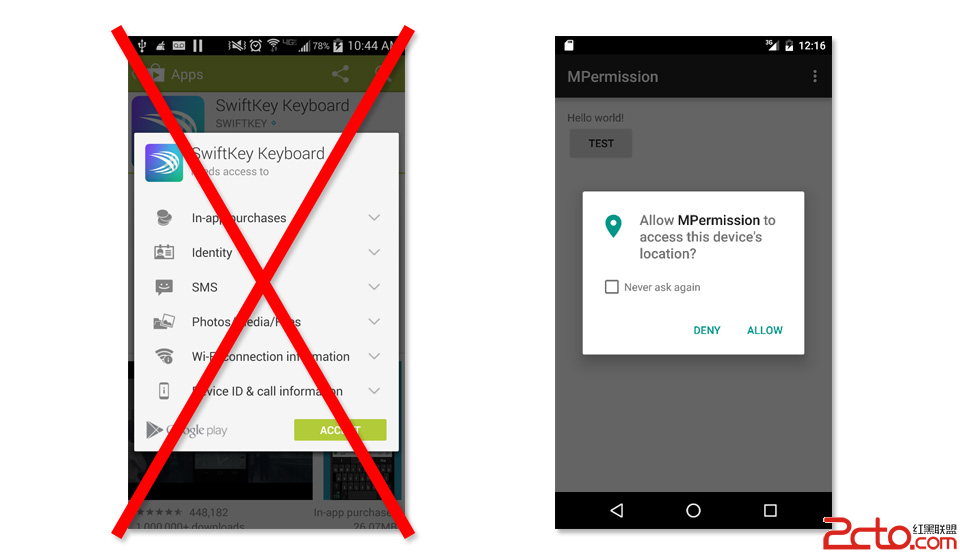 android permission權限與安全機制解析(下)
android permission權限與安全機制解析(下)
android 6.0權限全面詳細分析和解決方案Marshmallow版本權限修改 android的權限系統一直是首要的安全概念,因為這些權限只在安裝的時候被詢問一次。
 android:滑動掛斷自定義View的簡單實現
android:滑動掛斷自定義View的簡單實現
要點: 隨著手指的滑動更新位置 drawText的時候,如何計算開始的位置,使str居中 1.CallSliderEndView.java package net.m
 Android 仿淘寶、京東商品詳情頁向上拖動查看圖文詳情控件DEMO詳解
Android 仿淘寶、京東商品詳情頁向上拖動查看圖文詳情控件DEMO詳解
一、淘寶商品詳情頁效果我們的效果二、實現思路 使用兩個scrollView,兩個scrollView 豎直排列,通過自定義