編輯:關於Android編程
Service是一個android的四大組件之一,它沒有UI界面,可以在後台執行長時間的操作。其他的組件可以start一個Service,service啟動以後會在後台持續運行,不管用戶是否切換到了其他的應用程序。此外,其他的組件還可以綁定到service上,並和service做交互,甚至還可以執行跨進程的操作(IPC)。比如說,Service可以在後台處理網絡請求、播放音樂,執行文件i/o或者跟content provider交互。
有兩種形式的service:
Started
當其他的組件通過調用startService()啟動的service是“Started”。一旦啟動以後,service就在後台無限的運行下去,就算是啟動他的組件已經被銷毀了。通常來說,Started service只會做單一的操作,並且不會返回給調用者返回值。比如:它可以通過網絡下載或者是上傳文件。當操作結束的時候,service要手動把自己停止掉。
Bound
當其他組件通過調用bindService()綁定到service的時候,service就是 bound的。bound service提供了客戶端/服務端的接口,允許組件和service進行交互,發送請求,獲取結果,甚至是做跨進程的操作。bound service只存活於其他組件綁定在它上面的時候,多個組件可以同時綁定到一個service,但是,當所有的組件同時解綁以後,service就被銷毀了。
盡管本文檔是分開討論這兩種類型的service的,但是你的service可以同時支持這兩種類型,service可以是started(無限運行)同時還允許綁定。這僅僅取決於你是否實現了下面的回調:onStartCommand()允許其他的組件start一個service,onBind()允許綁定service。
不管你的service是started還是bound,應用的其他組件都可以使用這個service(甚至是別的應用)。就如同別的組件都可以使用一個Activity一樣,通過Intent來啟動它。但是,你也可以在manifest文件中把service聲明成應用私有的,這就阻止了別的應用訪問它。
更多信息請參考“在manifest文件中聲明service”(http://developer.android.com/guide/components/services.html#Declaring)這一節。
注意:service是運行在宿主進程的主線程的,service並不會創建它自己的線程,並不會運行在單獨的進程中,除非你指定了。這意味著,如果你的service要做一些耗CPU或者是阻塞的操作(比如:播放MP3或者是網絡請求),你需要在service內部手動創建一個新的線程來做這樣的操作。通過使用單獨的線程,會降低ANR的風險,讓主線程可以專注於UI操作。
service基礎
要創建一個service,必須要創建Service(或者是Service子類)的子類。在你的實現中,你要重寫一些回調方法,它們用來處理service的一些關鍵的生命周期,並且提供組件綁定到service的機制,如果合適的話。
要重寫的最重要的回調是:
onStartCommand()
當別的組件通過調用startService()來啟動service的時候,系統會調用這個方法。一旦這個方法開始執行,service就啟動起來並在後台無限運行。如果你覆蓋了這個方法,你還要負責在service的工作結束以後通過調用stopSelf()或者stopService()銷毀掉service。(如果你只是想提供綁定就不需要實現這個方法)
onBind()
當其他的組件通過調用bindService()綁定到service(比如做RPC)的時候,系統會調用這個方法。實現這個方法的時候,必須要通過返回一個IBinder來給客戶端提供一個用來和service進行交互的接口。一般都要實現這個方法,但是如果你不允許綁定的話,可以返回null。
onCreate()
當service首次啟動的時候,系統會調用這個方法,只會執行一次(在調用onStartCommand()或者onBind()之前)。如果service已經在運行了,這個方法是不會被調用的。
onDestroy()
當service不再被使用或者是被銷毀的時候系統會調用這個方法。你的service要實現這個方法來做一些清理資源的工作,比如:線程啊,監聽啊,廣播接收器啊等等。這是service收到的最後一個回調。
如果一個組件通過startService()啟動一個service(會導致系統調用onStartCommand()),service會一直運行,一直到它調用stopSelf()或者是別的組件調用stopService()來把它停止掉。
如果一個組件通過bindService()啟動一個service(onStartCommand()不會被調用),service只存活於綁定到它的組件上。一旦service跟所有的客戶端解綁,它就會被系統結束掉。
Android系統只會在系統的內存不夠用的時候才會強制殺掉service,系統必須能夠給擁有用戶焦點的activity提供系統資源。
如果service被綁定到了擁有用戶焦點的activity上,它很可能不會被殺死。
如果service聲明成了前台運行的,一般不會被殺死。
其他情況下,如果service是被started並且是長時間運行的,系統會隨著時間的推移把它放到後台任務列表的靠後的位置,它就會變得易於被殺掉。
如果你的service是被started,你必須要讓它能優雅的處理系統的restart。
如果系統殺掉了你的service,一旦資源可用,系統會立馬restart被殺掉的service(當然這也取決於onStartCommand()的返回值)。
想了解更多關於系統可能會殺掉service的信息,參考:進程和線程(http://developer.android.com/guide/components/processes-and-threads.html)。
下面的章節,你會學到如何創建各種類型的service,還有如何在其他組件中使用service。
在manifest文件中聲明service
跟Activity類似(還有其他組件),你必須要在manifest文件中聲明所有的service。
要聲明一個service,添加
...
...
想了解更多關於在manifest聲明service的信息,參考
為了確保你的應用是安全的,當start或者是bind一個service的時候總是使用明確的intent,並且不要給service聲明intent filter。如果允許不明確的方式來啟動service非常重要,你可以給service提供intent filter,排除掉某些組件名字。但是,你必須要用setPackage()給intent設置pachage,這給要調用的目標service提供了足夠的確定性。
此外,你也可以用過引入android:exported這個屬性,並把它的值設置為false來確保你的service只是對你的應用可用。這就有效地防止了其他的應用啟動你的service,就算是使用明確intent也沒有用。
創建一個Started Service
如果別的組件通過調用startService()啟動service的話,service就是一個started service,這會導致系統調用servicve的onStartCommand()方法。
當service啟動以後,它的生命周期跟啟動它的組件的生命周期是相互獨立的,service可以在後台無限的運行,就算啟動它的組件已經銷毀了。這種情況下,當它的任務完成以後,service就需要調用stopSelf()來停掉自己,其他的組件可以調用stopService()來停掉service。
應用程序的組件比如Activity可以通過調用 startService()來啟動一個service,並且給service傳遞一個Intent,Intent就指定了要啟動的service和傳遞給service使用的數據。service會在onStartCommand()方法中收到這個Intent。
舉個例子,假如一個Activity需要把數據保存到網絡的數據庫上,Activity可以啟動一個service,通過intent傳遞給service要保存的數據。service在onStartCommand()方法中收到intent,連上網絡,做數據庫操作。當操作完成以後,service要停掉自己,然後servive就被銷毀了。
注意:service是運行在應用的同一個進程中,默認是運行在應用的主線程的。因此,如果當用戶跟應用進行交互的時候,service做一些耗時或者是阻塞的操作的話,service會拖慢Activity的性能。為了避免影響應用的性能,你要在service內部新開一個線程。
一般來說,可以通過繼承兩個類來創建started service:
一個是繼承Service
Service是所有service的基類。當你繼承這個類的時候,要在service內部新開一個線程做繁重的操作,因為service默認是運行在應用的主線程的,它會影響應用的性能。
還一個是繼承IntentService
它是Service的子類,它內部使用了一個工作線程來處理所有的請求,一次一個。如果你的service不需要同步與處理多個請求的話,這將是最佳的選擇。你所要做的僅僅是實現onHandleIntent()方法,它會接收請求的intent,因此你就可以做後台任務。
下面的章節講述了如何用這兩個類實現service。
繼承IntentService類
因為大多數的started service都不需要處理並發的請求,因此使用IntentService可能是最優的方案。
IntentService會做如下的事情:
(1)創建一個默認的工作線程,它用來執行傳遞到onStartCommand()的intent,並且是跟應用的主線程獨立的。
(2)創建一個工作隊列。每次只傳遞一個intent到onHandleIntent()方法,因此就不需要擔心多線程的問題了。
(3)當所有的請求都處理完以後,service會自動停止掉,因此不需要調用stopSelf()。
(4)提供了onBind()的默認實現,方法會返回null。
(5)提供了 onStartCommand()的默認實現,會把intent發送到工作隊列,然後發送給onHandleIntent()。
所有這些以後,你所需要做的僅僅是實現onHandleIntent()來完成客戶的工作(當然你也可以給service提供構造函數)。
下面是一個實現了IntentService的例子:
public class HelloIntentService extends IntentService {
/**
* A constructor is required, and must call the super IntentService(String)
* constructor with a name for the worker thread.
*/
public HelloIntentService() {
super(HelloIntentService);
}
/**
* The IntentService calls this method from the default worker thread with
* the intent that started the service. When this method returns, IntentService
* stops the service, as appropriate.
*/
@Override
protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) {
// Normally we would do some work here, like download a file.
// For our sample, we just sleep for 5 seconds.
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis() + 5*1000;
while (System.currentTimeMillis() < endTime) {
synchronized (this) {
try {
wait(endTime - System.currentTimeMillis());
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
}
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Toast.makeText(this, service starting, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return super.onStartCommand(intent,flags,startId);
}
public class HelloService extends Service {
private Looper mServiceLooper;
private ServiceHandler mServiceHandler;
// Handler that receives messages from the thread
private final class ServiceHandler extends Handler {
public ServiceHandler(Looper looper) {
super(looper);
}
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
// Normally we would do some work here, like download a file.
// For our sample, we just sleep for 5 seconds.
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis() + 5*1000;
while (System.currentTimeMillis() < endTime) {
synchronized (this) {
try {
wait(endTime - System.currentTimeMillis());
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
// Stop the service using the startId, so that we don't stop
// the service in the middle of handling another job
stopSelf(msg.arg1);
}
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
// Start up the thread running the service. Note that we create a
// separate thread because the service normally runs in the process's
// main thread, which we don't want to block. We also make it
// background priority so CPU-intensive work will not disrupt our UI.
HandlerThread thread = new HandlerThread(ServiceStartArguments,
Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
thread.start();
// Get the HandlerThread's Looper and use it for our Handler
mServiceLooper = thread.getLooper();
mServiceHandler = new ServiceHandler(mServiceLooper);
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Toast.makeText(this, service starting, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
// For each start request, send a message to start a job and deliver the
// start ID so we know which request we're stopping when we finish the job
Message msg = mServiceHandler.obtainMessage();
msg.arg1 = startId;
mServiceHandler.sendMessage(msg);
// If we get killed, after returning from here, restart
return START_STICKY;
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// We don't provide binding, so return null
return null;
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Toast.makeText(this, service done, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
Intent intent = new Intent(this, HelloService.class); startService(intent);
前台service是被認為是用戶可感知的,當系統內存低的時候不是候選被殺掉的service。前台service必須在狀態欄有提醒,放在“正在進行”的頭部之下,也就是說,提醒不會消失除非service被停止或者被從前台移除。
比如說,service的音樂播放器應該運行在前台,因為用戶明確感知到它的操作,狀態欄的提醒可以表明當前正在播放的歌曲,並且允許用戶跳轉到音樂播放器的Activity做一些交互。
讓service運行在前台需要調用startForeground()方法。這個方法接受2個參數,一個唯一標識提醒的整數,一個是狀態欄的提醒。比如:
Notification notification = new Notification(R.drawable.icon, getText(R.string.ticker_text),System.currentTimeMillis()); Intent notificationIntent = new Intent(this, ExampleActivity.class); PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, notificationIntent, 0); notification.setLatestEventInfo(this, getText(R.string.notification_title),getText(R.string.notification_message), pendingIntent); startForeground(ONGOING_NOTIFICATION_ID, notification);
(2)bound service
當其他組件(客戶端)調用bindService()時候service被創建出來,然後客戶端通過IBinder接口跟service進行交互。客戶端可以調用unbindService()來關掉與service的連接。多個客戶端可以同時連接到一個service上,當所有的客戶端都解綁以後,系統會銷毀掉service(service不需要自己手動去停掉)。
這兩種形式並不是完全獨立的。也就是說,你可以綁定到一個用startService()啟動的started service上。比如:後台的音樂service可以通過startService()傳遞要播放的歌曲的intent來啟動起來,然後,當用戶希望對播放器做一些操作或者是獲取當前歌曲的信息的時候,可以把Activity通過bindService()綁定到service上。這種情況下,stopService()或者stopSelf()並不會停掉service,直到所有的客戶端都解綁以後。
實現生命周期回調
類似於Activity,service也有生命收起回調函數可以讓你來監控service的狀態,並在適當的時候做一些事情。
下面的例子展示了每一個生命周期函數:
public class ExampleService extends Service {
int mStartMode; // indicates how to behave if the service is killed
IBinder mBinder; // interface for clients that bind
boolean mAllowRebind; // indicates whether onRebind should be used
@Override
public void onCreate() {
// The service is being created
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
// The service is starting, due to a call to startService()
return mStartMode;
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// A client is binding to the service with bindService()
return mBinder;
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
// All clients have unbound with unbindService()
return mAllowRebind;
}
@Override
public void onRebind(Intent intent) {
// A client is binding to the service with bindService(),
// after onUnbind() has already been called
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
// The service is no longer used and is being destroyed
}
}
 Android - Manifest 文件 詳解
Android - Manifest 文件 詳解
Manifest 文件 詳解 本文地址: http://blog.csdn.net/caroline_wendy/article/details/20899281
 android開發步步為營之53:viewpager+fragment構造可左右滑動標簽頁效果
android開發步步為營之53:viewpager+fragment構造可左右滑動標簽頁效果
可滑動的標簽頁是很多應用的用來做外面框架的,比如微信,微博等等,我這裡實現的效果是下面是主標簽頁,然後中間一個的標簽頁裡面又可以繼續左右滑動,等於是標簽頁內部再嵌套標簽頁
 ShareSDK集成
ShareSDK集成
第一步:下載SDK:1下載地址:http://www.mob.com/ 根據需求選擇需要的平台:第二步:申請ShareSDK的AppKey把鼠標移到頭像上,點擊進入後台:
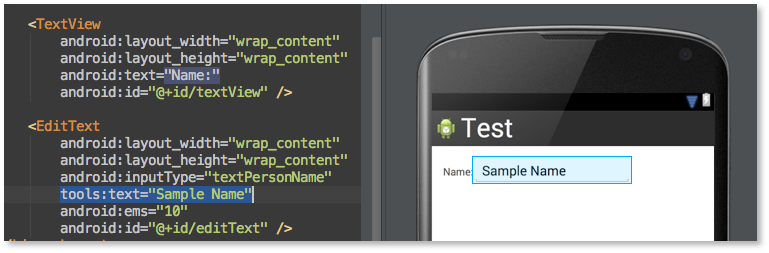 Android Studio使用小技巧:布局預覽時填充數據
Android Studio使用小技巧:布局預覽時填充數據
我們都知道Android Studio用起來很棒,其中布局預覽更棒。我們在調UI的時候基本是需要實時預覽來看效果的,在Android Studio中只需要切換到Desig