編輯:關於Android編程
Rect位於android.graphics下,表示一個矩形,由四條邊的坐標組成,提供了一些設置方法,都比較簡單,源碼如下:
/*
* Copyright (C) 2006 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package android.graphics;
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* Rect holds four integer coordinates for a rectangle. The rectangle is
* represented by the coordinates of its 4 edges (left, top, right bottom).
* These fields can be accessed directly. Use width() and height() to retrieve
* the rectangle's width and height. Note: most methods do not check to see that
* the coordinates are sorted correctly (i.e. left <= right and top <= bottom).
*/
public final class Rect implements Parcelable {
public int left;
public int top;
public int right;
public int bottom;
private static final Pattern FLATTENED_PATTERN = Pattern.compile(
"(-?\\d+) (-?\\d+) (-?\\d+) (-?\\d+)");
/**
* Create a new empty Rect. All coordinates are initialized to 0.
*/
public Rect() {}
/**
* Create a new rectangle with the specified coordinates. Note: no range
* checking is performed, so the caller must ensure that left <= right and
* top <= bottom.
*
* @param left The X coordinate of the left side of the rectangle
* @param top The Y coordinate of the top of the rectangle
* @param right The X coordinate of the right side of the rectangle
* @param bottom The Y coordinate of the bottom of the rectangle
*/
public Rect(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
this.left = left;
this.top = top;
this.right = right;
this.bottom = bottom;
}
/**
* Create a new rectangle, initialized with the values in the specified
* rectangle (which is left unmodified).
*
* @param r The rectangle whose coordinates are copied into the new
* rectangle.
*/
public Rect(Rect r) {
if (r == null) {
left = top = right = bottom = 0;
} else {
left = r.left;
top = r.top;
right = r.right;
bottom = r.bottom;
}
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Rect r = (Rect) o;
return left == r.left && top == r.top && right == r.right && bottom == r.bottom;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = left;
result = 31 * result + top;
result = 31 * result + right;
result = 31 * result + bottom;
return result;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(32);
sb.append("Rect("); sb.append(left); sb.append(", ");
sb.append(top); sb.append(" - "); sb.append(right);
sb.append(", "); sb.append(bottom); sb.append(")");
return sb.toString();
}
/**
* Return a string representation of the rectangle in a compact form.
*/
public String toShortString() {
return toShortString(new StringBuilder(32));
}
/**
* Return a string representation of the rectangle in a compact form.
* @hide
*/
public String toShortString(StringBuilder sb) {
sb.setLength(0);
sb.append('['); sb.append(left); sb.append(',');
sb.append(top); sb.append("]["); sb.append(right);
sb.append(','); sb.append(bottom); sb.append(']');
return sb.toString();
}
/**
* Return a string representation of the rectangle in a well-defined format.
*
* You can later recover the Rect from this string through
* {@link #unflattenFromString(String)}.
*
* @return Returns a new String of the form "left top right bottom"
*/
public String flattenToString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(32);
// WARNING: Do not change the format of this string, it must be
// preserved because Rects are saved in this flattened format.
sb.append(left);
sb.append(' ');
sb.append(top);
sb.append(' ');
sb.append(right);
sb.append(' ');
sb.append(bottom);
return sb.toString();
}
/**
* Returns a Rect from a string of the form returned by {@link #flattenToString},
* or null if the string is not of that form.
*/
public static Rect unflattenFromString(String str) {
Matcher matcher = FLATTENED_PATTERN.matcher(str);
if (!matcher.matches()) {
return null;
}
return new Rect(Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(1)),
Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(2)),
Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(3)),
Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(4)));
}
/**
* Print short representation to given writer.
* @hide
*/
public void printShortString(PrintWriter pw) {
pw.print('['); pw.print(left); pw.print(',');
pw.print(top); pw.print("]["); pw.print(right);
pw.print(','); pw.print(bottom); pw.print(']');
}
/**
* Returns true if the rectangle is empty (left >= right or top >= bottom)
*/
public final boolean isEmpty() {
return left >= right || top >= bottom;
}
/**
* @return the rectangle's width. This does not check for a valid rectangle
* (i.e. left <= right) so the result may be negative.
*/
public final int width() {
return right - left;
}
/**
* @return the rectangle's height. This does not check for a valid rectangle
* (i.e. top <= bottom) so the result may be negative.
*/
public final int height() {
return bottom - top;
}
/**
* @return the horizontal center of the rectangle. If the computed value
* is fractional, this method returns the largest integer that is
* less than the computed value.
*/
public final int centerX() {
return (left + right) >> 1;
}
/**
* @return the vertical center of the rectangle. If the computed value
* is fractional, this method returns the largest integer that is
* less than the computed value.
*/
public final int centerY() {
return (top + bottom) >> 1;
}
/**
* @return the exact horizontal center of the rectangle as a float.
*/
public final float exactCenterX() {
return (left + right) * 0.5f;
}
/**
* @return the exact vertical center of the rectangle as a float.
*/
public final float exactCenterY() {
return (top + bottom) * 0.5f;
}
/**
* Set the rectangle to (0,0,0,0)
*/
public void setEmpty() {
left = right = top = bottom = 0;
}
/**
* Set the rectangle's coordinates to the specified values. Note: no range
* checking is performed, so it is up to the caller to ensure that
* left <= right and top <= bottom.
*
* @param left The X coordinate of the left side of the rectangle
* @param top The Y coordinate of the top of the rectangle
* @param right The X coordinate of the right side of the rectangle
* @param bottom The Y coordinate of the bottom of the rectangle
*/
public void set(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
this.left = left;
this.top = top;
this.right = right;
this.bottom = bottom;
}
/**
* Copy the coordinates from src into this rectangle.
*
* @param src The rectangle whose coordinates are copied into this
* rectangle.
*/
public void set(Rect src) {
this.left = src.left;
this.top = src.top;
this.right = src.right;
this.bottom = src.bottom;
}
/**
* Offset the rectangle by adding dx to its left and right coordinates, and
* adding dy to its top and bottom coordinates.
*
* @param dx The amount to add to the rectangle's left and right coordinates
* @param dy The amount to add to the rectangle's top and bottom coordinates
*/
public void offset(int dx, int dy) {
left += dx;
top += dy;
right += dx;
bottom += dy;
}
/**
* Offset the rectangle to a specific (left, top) position,
* keeping its width and height the same.
*
* @param newLeft The new "left" coordinate for the rectangle
* @param newTop The new "top" coordinate for the rectangle
*/
public void offsetTo(int newLeft, int newTop) {
right += newLeft - left;
bottom += newTop - top;
left = newLeft;
top = newTop;
}
/**
* Inset the rectangle by (dx,dy). If dx is positive, then the sides are
* moved inwards, making the rectangle narrower. If dx is negative, then the
* sides are moved outwards, making the rectangle wider. The same holds true
* for dy and the top and bottom.
*
* @param dx The amount to add(subtract) from the rectangle's left(right)
* @param dy The amount to add(subtract) from the rectangle's top(bottom)
*/
public void inset(int dx, int dy) {
left += dx;
top += dy;
right -= dx;
bottom -= dy;
}
/**
* Returns true if (x,y) is inside the rectangle. The left and top are
* considered to be inside, while the right and bottom are not. This means
* that for a x,y to be contained: left <= x < right and top <= y < bottom.
* An empty rectangle never contains any point.
*
* @param x The X coordinate of the point being tested for containment
* @param y The Y coordinate of the point being tested for containment
* @return true iff (x,y) are contained by the rectangle, where containment
* means left <= x < right and top <= y < bottom
*/
public boolean contains(int x, int y) {
return left < right && top < bottom // check for empty first
&& x >= left && x < right && y >= top && y < bottom;
}
/**
* Returns true iff the 4 specified sides of a rectangle are inside or equal
* to this rectangle. i.e. is this rectangle a superset of the specified
* rectangle. An empty rectangle never contains another rectangle.
*
* @param left The left side of the rectangle being tested for containment
* @param top The top of the rectangle being tested for containment
* @param right The right side of the rectangle being tested for containment
* @param bottom The bottom of the rectangle being tested for containment
* @return true iff the the 4 specified sides of a rectangle are inside or
* equal to this rectangle
*/
public boolean contains(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
// check for empty first
return this.left < this.right && this.top < this.bottom
// now check for containment
&& this.left <= left && this.top <= top
&& this.right >= right && this.bottom >= bottom;
}
/**
* Returns true iff the specified rectangle r is inside or equal to this
* rectangle. An empty rectangle never contains another rectangle.
*
* @param r The rectangle being tested for containment.
* @return true iff the specified rectangle r is inside or equal to this
* rectangle
*/
public boolean contains(Rect r) {
// check for empty first
return this.left < this.right && this.top < this.bottom
// now check for containment
&& left <= r.left && top <= r.top && right >= r.right && bottom >= r.bottom;
}
/**
* If the rectangle specified by left,top,right,bottom intersects this
* rectangle, return true and set this rectangle to that intersection,
* otherwise return false and do not change this rectangle. No check is
* performed to see if either rectangle is empty. Note: To just test for
* intersection, use {@link #intersects(Rect, Rect)}.
*
* @param left The left side of the rectangle being intersected with this
* rectangle
* @param top The top of the rectangle being intersected with this rectangle
* @param right The right side of the rectangle being intersected with this
* rectangle.
* @param bottom The bottom of the rectangle being intersected with this
* rectangle.
* @return true if the specified rectangle and this rectangle intersect
* (and this rectangle is then set to that intersection) else
* return false and do not change this rectangle.
*/
public boolean intersect(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
if (this.left < right && left < this.right && this.top < bottom && top < this.bottom) {
if (this.left < left) this.left = left;
if (this.top < top) this.top = top;
if (this.right > right) this.right = right;
if (this.bottom > bottom) this.bottom = bottom;
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* If the specified rectangle intersects this rectangle, return true and set
* this rectangle to that intersection, otherwise return false and do not
* change this rectangle. No check is performed to see if either rectangle
* is empty. To just test for intersection, use intersects()
*
* @param r The rectangle being intersected with this rectangle.
* @return true if the specified rectangle and this rectangle intersect
* (and this rectangle is then set to that intersection) else
* return false and do not change this rectangle.
*/
public boolean intersect(Rect r) {
return intersect(r.left, r.top, r.right, r.bottom);
}
/**
* If rectangles a and b intersect, return true and set this rectangle to
* that intersection, otherwise return false and do not change this
* rectangle. No check is performed to see if either rectangle is empty.
* To just test for intersection, use intersects()
*
* @param a The first rectangle being intersected with
* @param b The second rectangle being intersected with
* @return true iff the two specified rectangles intersect. If they do, set
* this rectangle to that intersection. If they do not, return
* false and do not change this rectangle.
*/
public boolean setIntersect(Rect a, Rect b) {
if (a.left < b.right && b.left < a.right && a.top < b.bottom && b.top < a.bottom) {
left = Math.max(a.left, b.left);
top = Math.max(a.top, b.top);
right = Math.min(a.right, b.right);
bottom = Math.min(a.bottom, b.bottom);
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* Returns true if this rectangle intersects the specified rectangle.
* In no event is this rectangle modified. No check is performed to see
* if either rectangle is empty. To record the intersection, use intersect()
* or setIntersect().
*
* @param left The left side of the rectangle being tested for intersection
* @param top The top of the rectangle being tested for intersection
* @param right The right side of the rectangle being tested for
* intersection
* @param bottom The bottom of the rectangle being tested for intersection
* @return true iff the specified rectangle intersects this rectangle. In
* no event is this rectangle modified.
*/
public boolean intersects(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
return this.left < right && left < this.right && this.top < bottom && top < this.bottom;
}
/**
* Returns true iff the two specified rectangles intersect. In no event are
* either of the rectangles modified. To record the intersection,
* use {@link #intersect(Rect)} or {@link #setIntersect(Rect, Rect)}.
*
* @param a The first rectangle being tested for intersection
* @param b The second rectangle being tested for intersection
* @return true iff the two specified rectangles intersect. In no event are
* either of the rectangles modified.
*/
public static boolean intersects(Rect a, Rect b) {
return a.left < b.right && b.left < a.right && a.top < b.bottom && b.top < a.bottom;
}
/**
* Update this Rect to enclose itself and the specified rectangle. If the
* specified rectangle is empty, nothing is done. If this rectangle is empty
* it is set to the specified rectangle.
*
* @param left The left edge being unioned with this rectangle
* @param top The top edge being unioned with this rectangle
* @param right The right edge being unioned with this rectangle
* @param bottom The bottom edge being unioned with this rectangle
*/
public void union(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
if ((left < right) && (top < bottom)) {
if ((this.left < this.right) && (this.top < this.bottom)) {
if (this.left > left) this.left = left;
if (this.top > top) this.top = top;
if (this.right < right) this.right = right;
if (this.bottom < bottom) this.bottom = bottom;
} else {
this.left = left;
this.top = top;
this.right = right;
this.bottom = bottom;
}
}
}
/**
* Update this Rect to enclose itself and the specified rectangle. If the
* specified rectangle is empty, nothing is done. If this rectangle is empty
* it is set to the specified rectangle.
*
* @param r The rectangle being unioned with this rectangle
*/
public void union(Rect r) {
union(r.left, r.top, r.right, r.bottom);
}
/**
* Update this Rect to enclose itself and the [x,y] coordinate. There is no
* check to see that this rectangle is non-empty.
*
* @param x The x coordinate of the point to add to the rectangle
* @param y The y coordinate of the point to add to the rectangle
*/
public void union(int x, int y) {
if (x < left) {
left = x;
} else if (x > right) {
right = x;
}
if (y < top) {
top = y;
} else if (y > bottom) {
bottom = y;
}
}
/**
* Swap top/bottom or left/right if there are flipped (i.e. left > right
* and/or top > bottom). This can be called if
* the edges are computed separately, and may have crossed over each other.
* If the edges are already correct (i.e. left <= right and top <= bottom)
* then nothing is done.
*/
public void sort() {
if (left > right) {
int temp = left;
left = right;
right = temp;
}
if (top > bottom) {
int temp = top;
top = bottom;
bottom = temp;
}
}
/**
* Parcelable interface methods
*/
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
/**
* Write this rectangle to the specified parcel. To restore a rectangle from
* a parcel, use readFromParcel()
* @param out The parcel to write the rectangle's coordinates into
*/
public void writeToParcel(Parcel out, int flags) {
out.writeInt(left);
out.writeInt(top);
out.writeInt(right);
out.writeInt(bottom);
}
public static final Parcelable.Creator CREATOR = new Parcelable.Creator() {
/**
* Return a new rectangle from the data in the specified parcel.
*/
public Rect createFromParcel(Parcel in) {
Rect r = new Rect();
r.readFromParcel(in);
return r;
}
/**
* Return an array of rectangles of the specified size.
*/
public Rect[] newArray(int size) {
return new Rect[size];
}
};
/**
* Set the rectangle's coordinates from the data stored in the specified
* parcel. To write a rectangle to a parcel, call writeToParcel().
*
* @param in The parcel to read the rectangle's coordinates from
*/
public void readFromParcel(Parcel in) {
left = in.readInt();
top = in.readInt();
right = in.readInt();
bottom = in.readInt();
}
/**
* Scales up the rect by the given scale.
* @hide
*/
public void scale(float scale) {
if (scale != 1.0f) {
left = (int) (left * scale + 0.5f);
top = (int) (top * scale + 0.5f);
right = (int) (right * scale + 0.5f);
bottom = (int) (bottom * scale + 0.5f);
}
}
}
下面寫了一個簡單的測試示例,對這些方法進行測試,代碼如下:
package com.home.rect;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
public class MyView extends View {
Paint paint = new Paint();
Rect r1;
Rect r2;
Rect r3;
public MyView(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
private void init() {
// 兩個構造方法
r1 = new Rect(10, 10, 100, 100);
r2 = new Rect(new Rect(110, 110, 170, 170));
// 判斷是否相等,重寫了equals
Log.i("equals", r1.equals(r2) + "");
// 重寫了toString
Log.i("toString", r1.toString());
Log.i("toShortString", r1.toShortString());
Log.i("flattenToString", r1.flattenToString());
r3 = Rect.unflattenFromString("180 180 280 280");
// 判斷是否為空
Log.i("isEmpty", r1.isEmpty() + "");
// 寬
Log.i("width", r1.width() + "");
// 高
Log.i("height", r1.height() + "");
// 中心X坐標
Log.i("centerX", r1.centerX() + "");
// 中心Y坐標
Log.i("centerY", r1.centerY() + "");
// 精確的中心X坐標
Log.i("exactCenterX", r1.exactCenterX() + "");
// 精確的中心Y坐標
Log.i("exactCenterY", r1.exactCenterY() + "");
// 重置為空
r2.setEmpty();
// 設置坐標
r2.set(40, 40, 70, 70);
printCoordinates(r2);
// 使用已有的Rect進行設置
r2.set(r1);
printCoordinates(r2);
// 偏移
r1.offset(20, 20);
printCoordinates(r1);
r1.offsetTo(40, 40);
printCoordinates(r1);
r1.inset(20, 30);
printCoordinates(r1);
// 判斷包含性
Log.i("contains", r1.contains(20, 20) + "");
Log.i("contains", r1.contains(20, 20, 40, 40) + "");
Log.i("contains", r1.contains(r2) + "");
// 判斷相交
Log.i("intersect", r1.intersect(30, 30, 30, 30) + "");
Log.i("intersect", r1.intersect(r2) + "");
Log.i("intersects", r1.intersects(30, 30, 30, 30) + "");
Log.i("intersects", Rect.intersects(r2, r3) + "");
// 取相交部分
Log.i("setIntersect", r1.setIntersect(r2, r3) + "");
// 取並
r1.union(r2);
printCoordinates(r1);
r1.union(30, 30);
printCoordinates(r1);
r1.union(20, 30, 30, 30);
printCoordinates(r1);
// 交換
r1.sort();
printCoordinates(r1);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
canvas.drawRect(r1, paint);
canvas.drawRect(r2, paint);
canvas.drawRect(r3, paint);
}
/**
* 打印坐標
*
* @param rect
*/
private void printCoordinates(Rect rect) {
Log.i("left", rect.left + "");
Log.i("top", rect.top + "");
Log.i("right", rect.right + "");
Log.i("bottom", rect.bottom + "");
}
}
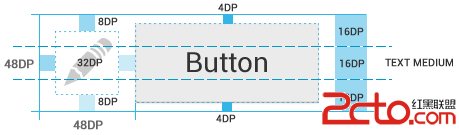 淺談android適配(下)
淺談android適配(下)
上一篇我們主要了解了為什麼適配,以及怎麼適配,同時給出了部分切圖規范,和在開發過程中需要的一些注意事項,這一遍主要從官方給出的指導建議出發,從視覺的角度來說說怎麼適配。度
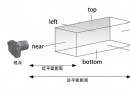 THREE.js-照相機(Camera)
THREE.js-照相機(Camera)
既然是通過相機來渲染場景,那麼沒有相機,我們也就什麼看不到了。THREE.js中提供了Camera類對相機這個角色進行抽象。相機將三維的場景投影到二維的屏幕,根據投影的方
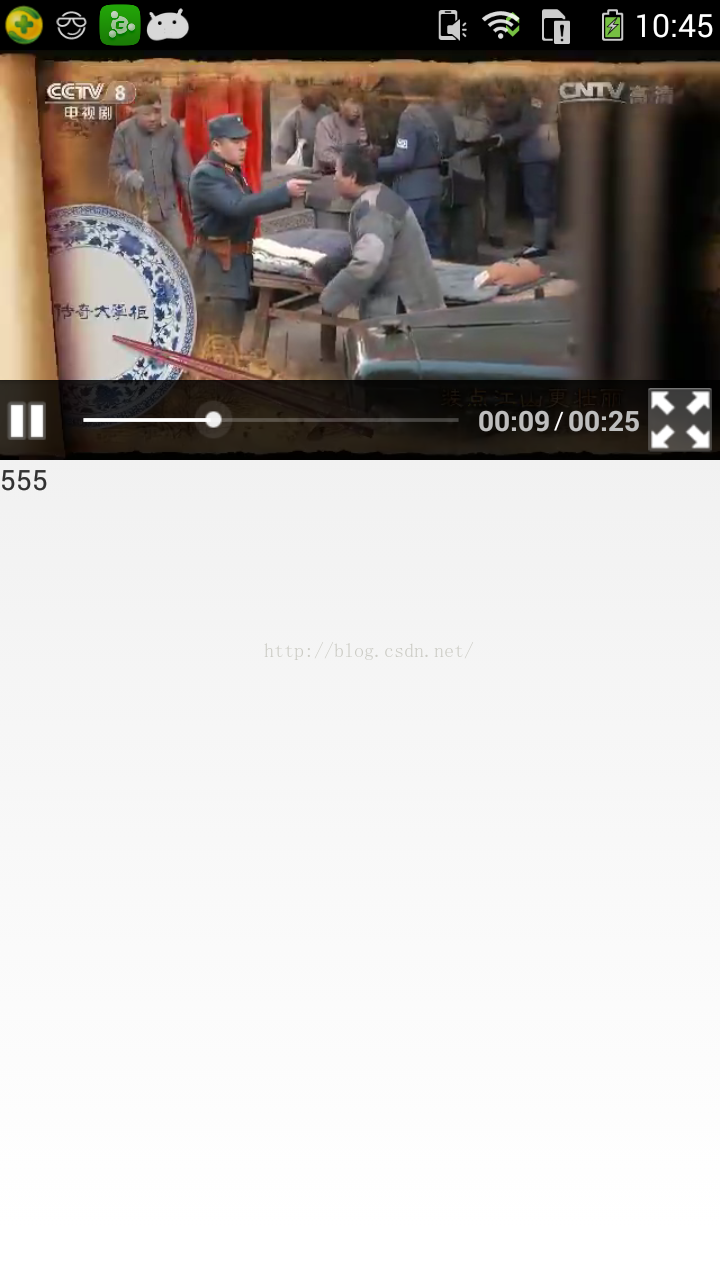 自定義MediaController來實現修改底部布局作以及實現vedioview半屏與全屏的切換
自定義MediaController來實現修改底部布局作以及實現vedioview半屏與全屏的切換
因為直接使用系統vedioview,底部的MediaController布局有點不好看,尤其是進度條,不能實現辦半屏與全屏的切換,自己網上看了下別人的資料,整理了下,做以
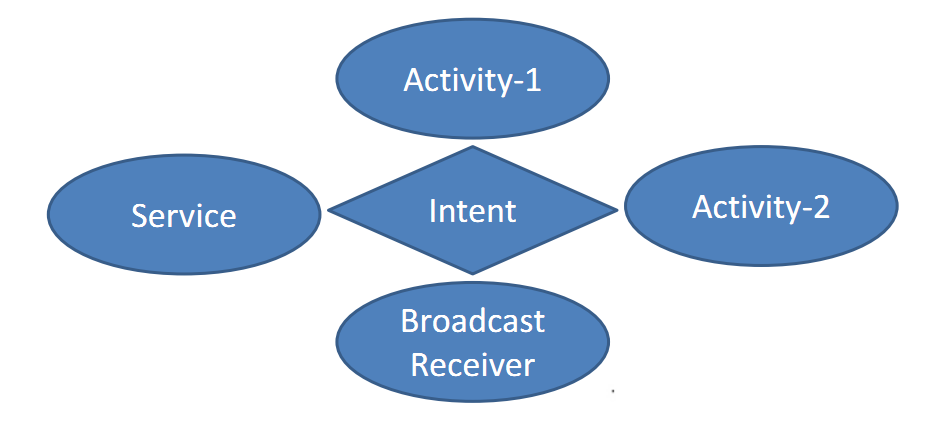 Android——Intent總結
Android——Intent總結
Intent組件雖然不是四大組件,但卻是連接四大組件的橋梁,學習好這個知識,也非常的重要。一、什麼是Intent1、Intent的概念:Android中提供了Intent