編輯:關於Android編程
關於判斷手機是否已經root的方法。如果app有一些特殊功能需要root權限,則需要判斷是否root。比如一些市場下載完app後自動安裝。
/**
* @author Kevin Kowalewski
*
*/
public class Root {
private static String LOG_TAG = Root.class.getName();
public boolean isDeviceRooted() {
if (checkRootMethod1()){return true;}
if (checkRootMethod2()){return true;}
if (checkRootMethod3()){return true;}
return false;
}
public boolean checkRootMethod1(){
String buildTags = android.os.Build.TAGS;
if (buildTags != null && buildTags.contains("test-keys")) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean checkRootMethod2(){
try {
File file = new File("/system/app/Superuser.apk");
if (file.exists()) {
return true;
}
} catch (Exception e) { }
return false;
}
public boolean checkRootMethod3() {
if (new ExecShell().executeCommand(SHELL_CMD.check_su_binary) != null){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
/**
* @author Kevin Kowalewski
*
*/
public class ExecShell {
private static String LOG_TAG = ExecShell.class.getName();
public static enum SHELL_CMD {
check_su_binary(new String[] {"/system/xbin/which","su"}),
;
String[] command;
SHELL_CMD(String[] command){
this.command = command;
}
}
public ArrayList executeCommand(SHELL_CMD shellCmd){
String line = null;
ArrayList fullResponse = new ArrayList();
Process localProcess = null;
try {
localProcess = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(shellCmd.command);
} catch (Exception e) {
return null;
//e.printStackTrace();
}
BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(localProcess.getOutputStream()));
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(localProcess.getInputStream()));
try {
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
Log.d(LOG_TAG, "--> Line received: " + line);
fullResponse.add(line);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Log.d(LOG_TAG, "--> Full response was: " + fullResponse);
return fullResponse;
}
}
代碼來自stackoverflow,向作者致敬。
方法2:
The RootTools library offers simple methods to check for root:
一個開源項目:http://code.google.com/p/roottools/
RootTools.isRootAvailable()判斷是否root
RootTools.isAccessGiven()返回true那麼手機已經root並且app也被授予root權限。
另外:據那片帖子的一個回貼人說使用
String commandToExecute = "su";
executeShellCommand(commandToExecute);
private boolean executeShellCommand(String command){
Process process = null;
try{
process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
} finally{
if(process != null){
try{
process.destroy();
}catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
}
會引起非常嚴重的性能問題,將手機系統拖的非常慢,當應用多次啟動後會創建出很多個僵死的進程耗用內存。
參考http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1101380/determine-if-running-on-a-rooted-device
To sum up; I have no advice for you to determine if device is rooted or not. But if I were you I would not use Runtime.getRuntime().exec().
By the way; RootTools.isRootAvailable() causes same problem.
The RootTools library offers simple methods to check for root:
 Android N 之 重要的開發者功能
Android N 之 重要的開發者功能
FrameMetricsListener APIAndroid N 仍處於活動的開發狀態,但現在您可以將其作為 N Developer Preview 的一部分進行試用。
 電池越來越大安卓仍然耗電大的原因
電池越來越大安卓仍然耗電大的原因
相信你和我一樣有這種疑問:本帥的安卓手機電池容量高達3000mAh了,而蘋果iPhone6才1810mAh,可卻不如人家耐用,為什麼?那麼,下面我們就聊一聊
 Android中關於Volley的使用(一)加載圖片
Android中關於Volley的使用(一)加載圖片
在Android中,如果我們要展示的圖片是存儲在網絡上的時候,我們就必須通過HttpClient或者HttpUrlConnection這兩個類來進行關於網絡方面的操作,比
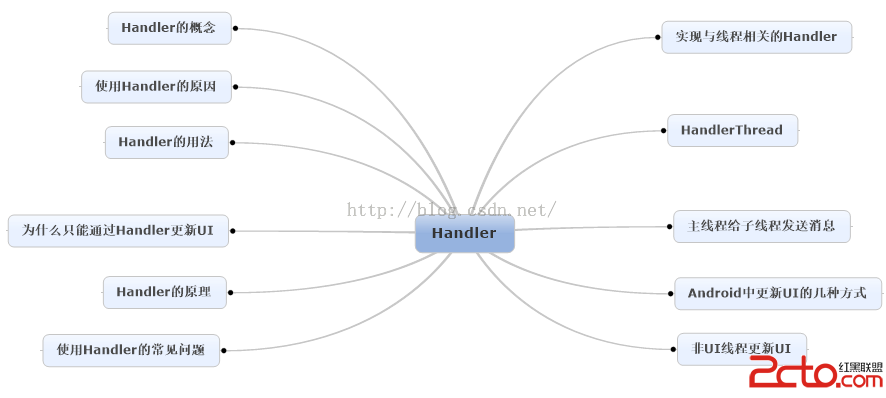 Android消息機制Handler解析(源碼+Demo)
Android消息機制Handler解析(源碼+Demo)
Handler是開發人員在面試過程中最常見的問題之一了,這篇文章將較為全面地對Handler進行解讀,包括源碼層,以及使用方法。如果看完文章有疑問,歡迎在評論中一起探討基