編輯:關於Android編程
先占個位置,下次翻譯~ :p
During normal app use, the foreground activity is sometimes obstructed by other visual components that cause the activity to pause. For example, when a semi-transparent activity opens (such as one in the style of a dialog), the previous activity pauses. As long as the activity is still partially visible but currently not the activity in focus, it remains paused.
However, once the activity is fully-obstructed and not visible, it stops (which is discussed in the next lesson).
As your activity enters the paused state, the system calls the onPause() method
on your Activity, which
allows you to stop ongoing actions that should not continue while paused (such as a video) or persist any information that should be permanently saved in case the user continues to leave your app. If the user returns to your activity from the paused state,
the system resumes it and calls the onResume() method.
Note: When your activity receives a call to onPause(),
it may be an indication that the activity will be paused for a moment and the user may return focus to your activity. However, it's usually the first indication that the user is leaving your activity.
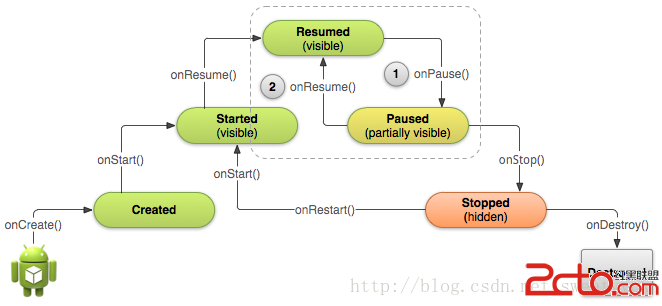
Figure 1. When a semi-transparent activity obscures your activity, the system calls onPause() and
the activity waits in the Paused state (1). If the user returns to the activity while it's still paused, the system calls onResume() (2).
When the system calls onPause() for
your activity, it technically means your activity is still partially visible, but most often is an indication that the user is leaving the activity and it will soon enter the Stopped state. You should usually use the onPause() callback
to:
For example, if your application uses the Camera,
the onPause() method
is a good place to release it.
@Override
public void onPause() {
super.onPause(); // Always call the superclass method first
// Release the Camera because we don't need it when paused
// and other activities might need to use it.
if (mCamera != null) {
mCamera.release()
mCamera = null;
}
}
Generally, you should not use onPause() to
store user changes (such as personal information entered into a form) to permanent storage. The only time you should persist user changes to permanent storage withinonPause() is
when you're certain users expect the changes to be auto-saved (such as when drafting an email). However, you should avoid performing CPU-intensive work during onPause(),
such as writing to a database, because it can slow the visible transition to the next activity (you should instead perform heavy-load shutdown operations during onStop()).
You should keep the amount of operations done in the onPause() method
relatively simple in order to allow for a speedy transition to the user's next destination if your activity is actually being stopped.
Note: When your activity is paused, the Activity instance
is kept resident in memory and is recalled when the activity resumes. You don’t need to re-initialize components that were created during any of the callback methods leading up to the Resumed state.
When the user resumes your activity from the Paused state, the system calls the onResume() method.
Be aware that the system calls this method every time your activity comes into the foreground, including when it's created for the first time. As such, you should implement onResume() to
initialize components that you release during onPause() and
perform any other initializations that must occur each time the activity enters the Resumed state (such as begin animations and initialize components only used while the activity has user focus).
The following example of onResume() is
the counterpart to the onPause() example
above, so it initializes the camera that's released when the activity pauses.
@Override
public void onResume() {
super.onResume(); // Always call the superclass method first
// Get the Camera instance as the activity achieves full user focus
if (mCamera == null) {
initializeCamera(); // Local method to handle camera init
}
}
 《Android源碼設計模式解析與實戰》讀書筆記(十八)
《Android源碼設計模式解析與實戰》讀書筆記(十八)
第十八章、代理模式 代理模式也稱委托模式,是結構型設計模式之一。是應用廣泛的模式之一。1.定義為其他對象提供一種代理以控制對這個對象的訪問。2.使用場景當無法或不想直接訪
 關於Android MVP模式的思考
關於Android MVP模式的思考
最近經常看到各種介紹MVP模式的博客的,之前寫過不少的Android應用,在做那些應用的時候,都是要求快速完成,所以從開始設計到寫代碼就一直考慮著重用。以前寫的項目基本都
 Android Volley小白解析(一)
Android Volley小白解析(一)
做安卓一年有余,意識到網絡請求框架算是很重要的一塊,考慮到Volley是谷歌自帶的,決定好好研究研究源碼,去理理邏輯思路首先呢,Volley去哪裡獲取,看下圖即可,在安卓
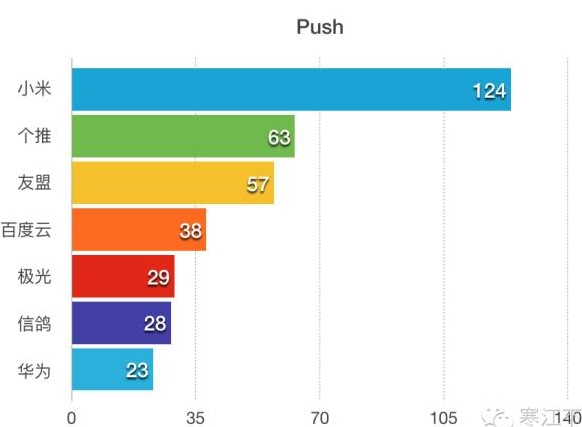 Android幾種消息推送方案總結
Android幾種消息推送方案總結
首先看一張國內Top500 Android應用中它們用到的第三方推送以及所占數量:現在總結下Android平台下幾種推送方案的基本情況以及優缺點:一、使用GCM(Goog