編輯:關於Android編程
今天在網上看到一篇文章寫關於Android實現3D旋轉(http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/opensource/os-cn-android-anmt2/index.html?ca=drs-),出於好奇就寫了一個,運行效果如下:
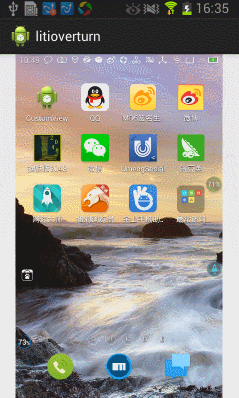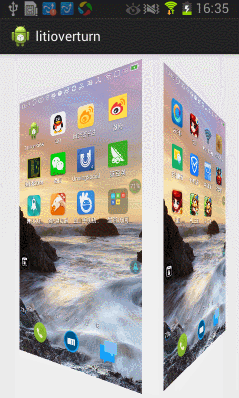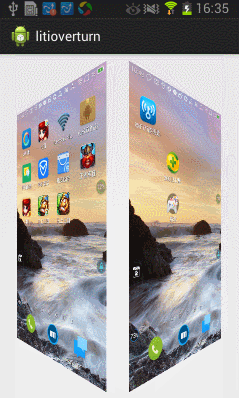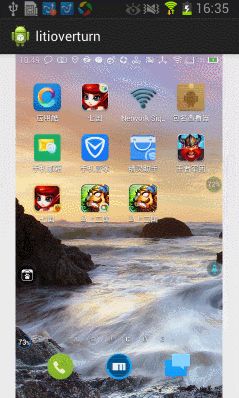
下面我們就開始一步步完成這個效果吧。
package com.example.rotation3dview;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewDebug.HierarchyTraceType;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.ImageView;
public class Rote3DView extends ViewGroup{
public Rote3DView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initScreens();
}
public void initScreens(){
ViewGroup.LayoutParams p = new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
this.addView(new ImageView(this.getContext()), i, p);
}
((ImageView)this.getChildAt(0)).setImageResource(R.drawable.page1);
((ImageView)this.getChildAt(1)).setImageResource(R.drawable.page2);
((ImageView)this.getChildAt(2)).setImageResource(R.drawable.page3);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int childLeft = 0;
final int childCount = getChildCount();
for(int i = 0; i< childCount; i++){
final View childView = getChildAt(i);
if(childView.getVisibility() != View.GONE){
final int childWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth();
childView.layout(childLeft, 0, childLeft + childWidth, childView.getMeasuredHeight());
childLeft += childWidth;
}
}
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
final int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
final int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
if(widthMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){
throw new IllegalStateException(僅支持精確尺寸);
}
final int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
if(heightMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){
throw new IllegalStateException(僅支持精確尺寸);
}
final int count = getChildCount();
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++){
getChildAt(i).measure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
private float mDownX;
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
float x = event.getX();
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
mDownX = x;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
int disX = (int)(mDownX - x);
mDownX = x;
scrollBy(disX, 0);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
break;
default:
break;
}
return true;
}
}
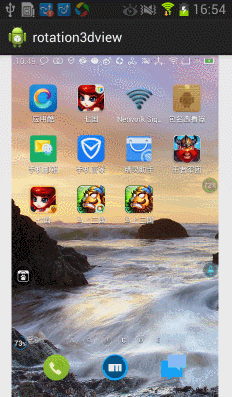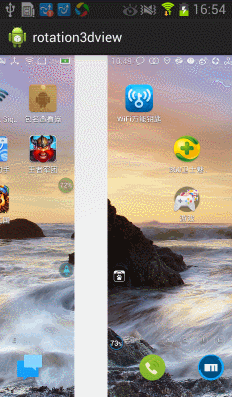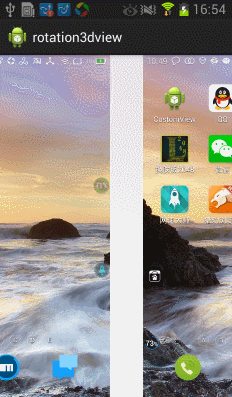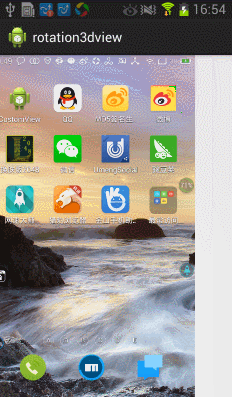 上面的滑動還不太流暢,我們在手勢抬起的時候進行判斷並處理,代碼如下:
上面的滑動還不太流暢,我們在手勢抬起的時候進行判斷並處理,代碼如下:
package com.example.rotation3dview;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Camera;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Matrix;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.VelocityTracker;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewDebug.HierarchyTraceType;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.Scroller;
public class Rote3DView extends ViewGroup{
private int mCurScreen = 1;
// 滑動的速度
private static final int SNAP_VELOCITY = 500;
private VelocityTracker mVelocityTracker;
private int mWidth;
private Scroller mScroller;
private Camera mCamera;
private Matrix mMatrix;
// 旋轉的角度,可以進行修改來觀察效果
private float angle = 90;
public Rote3DView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
mScroller = new Scroller(context);
mCamera = new Camera();
mMatrix = new Matrix();
initScreens();
}
public void initScreens(){
ViewGroup.LayoutParams p = new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
this.addView(new ImageView(this.getContext()), i, p);
}
((ImageView)this.getChildAt(0)).setImageResource(R.drawable.page1);
((ImageView)this.getChildAt(1)).setImageResource(R.drawable.page2);
((ImageView)this.getChildAt(2)).setImageResource(R.drawable.page3);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int childLeft = 0;
final int childCount = getChildCount();
for(int i = 0; i< childCount; i++){
final View childView = getChildAt(i);
if(childView.getVisibility() != View.GONE){
final int childWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth();
childView.layout(childLeft, 0, childLeft + childWidth, childView.getMeasuredHeight());
childLeft += childWidth;
}
}
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
final int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
final int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
if(widthMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){
throw new IllegalStateException(僅支持精確尺寸);
}
final int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
if(heightMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY){
throw new IllegalStateException(僅支持精確尺寸);
}
final int count = getChildCount();
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++){
getChildAt(i).measure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
scrollTo(mCurScreen * width, 0);
}
private float mDownX;
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
if(mVelocityTracker == null){
mVelocityTracker = VelocityTracker.obtain();
}
//將當前的觸摸事件傳遞給VelocityTracker對象
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(event);
float x = event.getX();
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
if(!mScroller.isFinished()){
mScroller.abortAnimation();
}
mDownX = x;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
int disX = (int)(mDownX - x);
mDownX = x;
scrollBy(disX, 0);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
final VelocityTracker velocityTracker = mVelocityTracker;
velocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000);
int velocityX = (int) velocityTracker.getXVelocity();
if(velocityX > SNAP_VELOCITY && mCurScreen > 0){
snapToScreen(mCurScreen - 1);
}else if(velocityX < -SNAP_VELOCITY && mCurScreen < getChildCount() - 1){
snapToScreen(mCurScreen + 1);
}else{
snapToDestination();
}
if(mVelocityTracker != null){
mVelocityTracker.recycle();
mVelocityTracker = null;
}
break;
}
return true;
}
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
if (mScroller.computeScrollOffset()) {
scrollTo(mScroller.getCurrX(), mScroller.getCurrY());
postInvalidate();
}
}
public void snapToDestination(){
setMWidth();
final int destScreen = (getScrollX() + mWidth / 2) / mWidth;
snapToScreen(destScreen);
}
public void snapToScreen(int whichScreen){
whichScreen = Math.max(0, Math.min(whichScreen, getChildCount() - 1));
setMWidth();
int scrollX = getScrollX();
int startWidth = whichScreen * mWidth;
if(scrollX != startWidth){
int delta = 0;
int startX = 0;
if(whichScreen > mCurScreen){
setPre();
delta = startWidth - scrollX;
startX = mWidth - startWidth + scrollX;
}else if(whichScreen < mCurScreen){
setNext();
delta = -scrollX;
startX = scrollX + mWidth;
}else{
startX = scrollX;
delta = startWidth - scrollX;
}
mScroller.startScroll(startX, 0, delta, 0, Math.abs(delta) * 2);
invalidate();
}
}
private void setNext(){
int count = this.getChildCount();
View view = getChildAt(count - 1);
removeViewAt(count - 1);
addView(view, 0);
}
private void setPre(){
int count = this.getChildCount();
View view = getChildAt(0);
removeViewAt(0);
addView(view, count - 1);
}
private void setMWidth(){
if(mWidth == 0){
mWidth = getWidth();
}
}
}
/*
* 當進行View滑動時,會導致當前的View無效,該函數的作用是對View進行重新繪制 調用drawScreen函數
*/
@Override
protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) {
final long drawingTime = getDrawingTime();
final int count = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
drawScreen(canvas, i, drawingTime);
}
}
public void drawScreen(Canvas canvas, int screen, long drawingTime) {
// 得到當前子View的寬度
final int width = getWidth();
final int scrollWidth = screen * width;
final int scrollX = this.getScrollX();
// 偏移量不足的時
if (scrollWidth > scrollX + width || scrollWidth + width < scrollX) {
return;
}
final View child = getChildAt(screen);
final int faceIndex = screen;
final float currentDegree = getScrollX() * (angle / getMeasuredWidth());
final float faceDegree = currentDegree - faceIndex * angle;
if (faceDegree > 90 || faceDegree < -90) {
return;
}
final float centerX = (scrollWidth < scrollX) ? scrollWidth + width
: scrollWidth;
final float centerY = getHeight() / 2;
final Camera camera = mCamera;
final Matrix matrix = mMatrix;
canvas.save();
camera.save();
camera.rotateY(-faceDegree);
camera.getMatrix(matrix);
camera.restore();
matrix.preTranslate(-centerX, -centerY);
matrix.postTranslate(centerX, centerY);
canvas.concat(matrix);
drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime);
canvas.restore();
}
 Android Loader 技術的簡單實用
Android Loader 技術的簡單實用
從Android3.0開始,Android SDK提供了Loader技術,使用Loader技術可以很容易進行數據的異步加載。Loader技術為我們提供的核心類有:
 Android官方開發文檔之Android Studio(Meet Android Studio)篇
Android官方開發文檔之Android Studio(Meet Android Studio)篇
1、前言Android Studio是基於IntelliJ IDEA下官方整和的一個Android應用程序開發環境。在IntelliJ強大的代碼編輯器和開發工具基礎之上,
 Android動畫總結系列(6)——矢量圖形與矢量動畫
Android動畫總結系列(6)——矢量圖形與矢量動畫
按照我一開始的打算,上面一篇文章應該是“Android動畫總結系列(5)——屬性動畫源碼分析”,不過屬性動畫源碼分析寫起來
 Android高仿京東垂直循環滾動新聞欄
Android高仿京東垂直循環滾動新聞欄
實現思路其實很簡單,就是一個自定義的LinearLayout,並且textView能夠循環垂直滾動,而且條目可以點擊,顯示區域最多顯示2個條目,並且還有交替的屬性垂直移動