編輯:關於Android編程
/**
*
*/
package com.kince.progressrectangle;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.RectF;
import android.graphics.Paint.Style;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
/**
* @author kince
* @category 仿solo桌面內存清理效果
* @since 2014.7.30
* @version 1.0.0
* {@link }
*
*/
public class ProgressRectangle extends View {
// Sizes (with defaults)
private int layout_height = 0;
private int layout_width = 0;
// Colors (with defaults)
private int bgColor = Color.TRANSPARENT;
private int progressColor = 0xFF339933;
// Paints
private Paint progressPaint = new Paint();
private Paint bgPaint = new Paint();
private Paint titlePaint = new Paint();
private Paint usePaint = new Paint();
// Rectangles
private RectF rectBgBounds = new RectF();
private RectF rectProgressBounds = new RectF();
int progress = 100;
boolean isProgress;
private Handler spinHandler = new Handler() {
/**
* This is the code that will increment the progress variable and so
* spin the wheel
*/
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
invalidate();
// super.handleMessage(msg);
}
};
/**
* @param context
*/
public ProgressRectangle(Context context) {
super(context);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
/**
* @param context
* @param attrs
*/
public ProgressRectangle(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
/**
* @param context
* @param attrs
* @param defStyleAttr
*/
public ProgressRectangle(Context context, AttributeSet attrs,
int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
// Share the dimensions
layout_width = w;
Log.i(layout_width, layout_width + );
layout_height = h;
Log.i(layout_height, layout_height + );
setupBounds();
setupPaints();
invalidate();
}
private void setupPaints() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
bgPaint.setColor(bgColor);
bgPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
bgPaint.setStyle(Style.FILL);
progressPaint.setColor(progressColor);
progressPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
progressPaint.setStyle(Style.FILL);
titlePaint.setColor(Color.WHITE);
titlePaint.setTextSize(20);
titlePaint.setAntiAlias(true);
titlePaint.setStyle(Style.FILL);
usePaint.setColor(Color.WHITE);
usePaint.setAntiAlias(true);
usePaint.setTextSize(30);
usePaint.setStyle(Style.FILL);
}
private void setupBounds() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int width = getWidth(); // this.getLayoutParams().width;
Log.i(width, width + );
int height = getHeight(); // this.getLayoutParams().height;
Log.i(height, height + );
rectBgBounds = new RectF(0, 0, width, height);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDraw(canvas);
canvas.drawRect(rectBgBounds, bgPaint);
Log.i(progress, progress + );
rectProgressBounds = new RectF(0, 0, progress, layout_height);
canvas.drawRect(rectProgressBounds, progressPaint);
canvas.drawText(使用內存, 25, 25, titlePaint);
canvas.drawText(progress + M + /1024M, 25, 60, usePaint);
}
/**
* Increment the progress by 1 (of 100)
*/
public void incrementProgress() {
isProgress = true;
progress++;
if (progress > 200)
progress = 100;
// setText(Math.round(((float) progress / 360) * 100) + %);
spinHandler.sendEmptyMessage(0);
}
/**
* Increment the progress by 1 (of 100)
*/
public void unIncrementProgress() {
isProgress = true;
progress--;
if (progress < 1)
progress = 100;
// setText(Math.round(((float) progress / 360) * 100) + %);
spinHandler.sendEmptyMessage(0);
}
/**
* Set the progress to a specific value
*/
public void setProgress(int i) {
progress = i;
spinHandler.sendEmptyMessage(0);
}
}
實現思路也是很簡單的,就是在onDraw()方法裡面繪制進度條的背景以及進度,進度的參數是傳遞進來的數值。Activity的代碼如下:
package com.kince.progressrectangle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class RecActivity extends Activity {
boolean running;
int progress = 0;
ProgressRectangle progressRectangle;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_rec);
progressRectangle=(ProgressRectangle) findViewById(R.id.progressBar);
final Runnable r = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
running = true;
while(progress<100) {
progressRectangle.incrementProgress();
progress++;
try {
Thread.sleep(15);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
while(progress>0) {
progressRectangle.unIncrementProgress();
progress--;
try {
Thread.sleep(15);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
running = false;
}
};
Button increment = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_increment);
increment.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
if(!running) {
progress = 0;
Thread s = new Thread(r);
s.start();
}
}
});
}
}
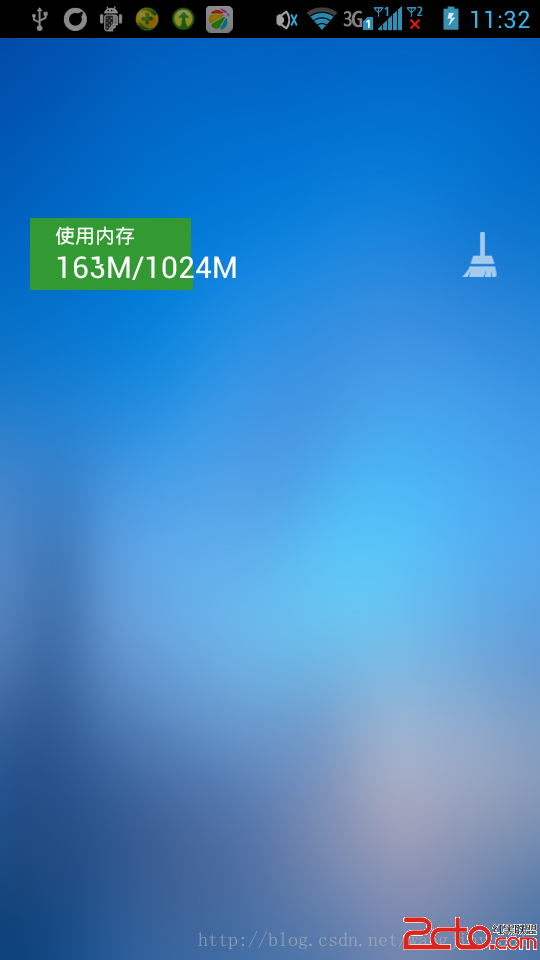
效果如下: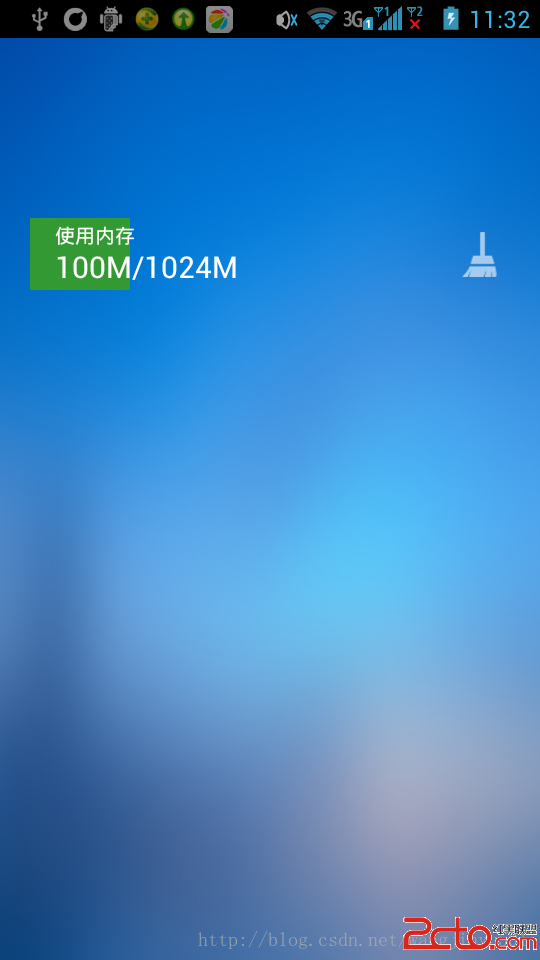
 Android XML數據的三種解析方式
Android XML數據的三種解析方式
本篇文章包含以下內容: XML數據的Dom解析 XML數據的Sax解析&n
 必須懂的Intent Filter匹配規則
必須懂的Intent Filter匹配規則
Intent簡介Android中提供了Intent機制來協助應用間的交互與通訊,Intent負責對應用中一次操作的動作、動作涉及數據、附加數據進行描述,Android則根
 Android屏幕適配全攻略
Android屏幕適配全攻略
Android屏幕適配出現的原因在我們學習如何進行屏幕適配之前,我們需要先了解下為什麼Android需要進行屏幕適配。由於Android系統的開放性,任何用戶、開發者、O
 android圖片處理之讓圖片一直勻速旋轉
android圖片處理之讓圖片一直勻速旋轉
本文是在我的文章android圖片處理,讓圖片變成圓形 的基礎上繼續寫的,可以去看看,直接看也沒關系,也能看懂 1、首先在res文件夾下創建一個名字為anim的