編輯:關於Android編程
ListView是一種可以顯示一系列項目並能進行滾動顯示的View。在每行裡,既可以是簡單的文本,也可以是復雜的結構。一般情況下,你都需要保證ListView運行得很好(即:渲染更快,滾動流暢)。在接下來的內容裡,我將就ListView的使用,向大家提供幾種解決不同性能問題的解決方案。
如果你想使用ListView,你就不得不使用ListAdapter來顯示內容。SDK中,已經有了幾種簡單實現的Adapter:
· ArrayAdapter
· SimpleAdapter (顯示Maps列表)
· SimpleCursorAdapter(顯示通過Cursor從DB中獲取的信息)
這些實現對於顯示簡單的列表來說,非常棒!一旦你的列表比較復雜,你就不得不書寫自己的ListAdapter實現。在多數情況下,直接從ArrayAdapter擴展就能很好地處理一組對象。此時,你需要處理的工作只是告訴系統如何處理列表中的對象。通過重寫getView(int, View, ViewGroup)方法即可達到。
在這裡,舉一個你需要自定義ListAdapter的例子:顯示一組圖片,圖片的旁邊有文字挨著。
圖片需要實時從internet上下載下來。讓我們先創建一個Class來代表列表中的項目:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29public
class ImageAndText {
private
String imageUrl;
private
String text;
public
ImageAndText(String imageUrl, String text) {
this.imageUrl
= imageUrl;
this.text
= text;
}
public
String getImageUrl() {
return
imageUrl;
}
public
String getText() {
return
text;
}
}
現在,我們要實現一個ListAdapter,來顯示ImageAndText列表。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71public
class ImageAndTextListAdapter extends ArrayAdapter {
public
ImageAndTextListAdapter(Activity activity, List imageAndTexts) {
super(activity,
0, imageAndTexts);
}
@Override
public
View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
Activity
activity = (Activity) getContext();
LayoutInflater
inflater = activity.getLayoutInflater();
//
Inflate the views from XML
View
rowView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.image_and_text_row, null);
ImageAndText
imageAndText = getItem(position);
//
Load the image and set it on the ImageView
ImageView
imageView = (ImageView) rowView.findViewById(R.id.image);
imageView.setImageDrawable(loadImageFromUrl(imageAndText.getImageUrl()));
//
Set the text on the TextView
TextView
textView = (TextView) rowView.findViewById(R.id.text);
textView.setText(imageAndText.getText());
return
rowView;
}
public
static Drawable loadImageFromUrl(String url) {
InputStream
inputStream;
try
{
inputStream
= new
URL(url).openStream();
}
catch
(IOException e) {
throw
new
RuntimeException(e);
}
return
Drawable.createFromStream(inputStream, "src");
}
}
這些View都是從“image_and_text_row.xml”XML文件中inflate的:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31"1.0"
encoding="utf-8"?>
"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
"@+id/image"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/default_image"/>
"@+id/text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
這個ListAdapter實現正如你所期望的那樣,能在ListView中加載ImageAndText。但是,它唯一可用的場合是那些擁有很少項目、無需滾動即可看到全部的列表。如果ImageAndText列表內容很多的時候,你會看到,滾動起來不是那麼的平滑(事實上,遠遠不是)。
性能改善
上面例子最大的瓶頸是圖片需要從internet上下載。因為我們的代碼都在UI線程中執行,所以,每當一張圖片從網絡上下載時,UI就會變得停滯。如果你用3G網絡代替WiFi的話,性能情況會變得更糟。
為了避免這種情況,我們想讓圖片的下載處於單獨的線程裡,這樣就不會過多地占用UI線程。為了達到這一目的,我們可能需要使用為這種情況特意設計的AsyncTask。實際情況中,你將注意到AsyncTask被限制在10個以內。這個數量是在Android SDK中硬編碼的,所以我們無法改變。這對我們來說是一個制限事項,因為常常有超過10個圖片同時在下載。
AsyncImageLoader
一個變通的做法是手動的為每個圖片創建一個線程。另外,我們還應該使用Handler來將下載的圖片invoke到UI線程。我們這樣做的原因是我們只能在UI線程中修改UI。我創建了一個AsyncImageLoader類,利用線程和Handler來負責圖片的下載。此外,它還緩存了圖片,防止單個圖片被下載多次。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
public
class AsyncImageLoader {
private
HashMap> imageCache;
public
AsyncImageLoader() {
imageCache
= new
HashMap>();
}
public
Drawable loadDrawable(final String imageUrl, final ImageCallback imageCallback) {
if
(imageCache.containsKey(imageUrl)) {
SoftReference
softReference = imageCache.get(imageUrl);
Drawable
drawable = softReference.get();
if
(drawable != null)
{
return
drawable;
}
}
final
Handler handler = new
Handler() {
@Override
public
void handleMessage(Message message) {
imageCallback.imageLoaded((Drawable)
message.obj, imageUrl);
}
};
new
Thread() {
@Override
public
void run() {
Drawable
drawable = loadImageFromUrl(imageUrl);
imageCache.put(imageUrl,
new
SoftReference(drawable));
Message
message = handler.obtainMessage(0, drawable);
handler.sendMessage(message);
}
}.start();
return
null;
}
public
static Drawable loadImageFromUrl(String url) {
//
...
}
public
interface ImageCallback {
public
void imageLoaded(Drawable imageDrawable, String imageUrl);
}
}
注意:我使用了SoftReference來緩存圖片,允許GC在需要的時候可以對緩存中的圖片進行清理。它這樣工作:
· 調用loadDrawable(ImageUrl, imageCallback),傳入一個匿名實現的ImageCallback接口
· 如果圖片在緩存中不存在的話,圖片將從單一的線程中下載並在下載結束時通過ImageCallback回調
· 如果圖片確實存在於緩存中,就會馬上返回,不會回調ImageCallback
在你的程序中,只能存在一個AsyncImageLoader實例,否則,緩存不能正常工作。在ImageAndTextListAdapter類中,我們可以這樣替換:
1
2
3
ImageView
imageView = (ImageView) rowView.findViewById(R.id.image);
imageView.setImageDrawable(loadImageFromUrl(imageAndText.getImageUrl()));
換成
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
final
ImageView imageView = (ImageView) rowView.findViewById(R.id.image);
Drawable
cachedImage = asyncImageLoader.loadDrawable(imageAndText.getImageUrl(), new
ImageCallback() {
public
void imageLoaded(Drawable imageDrawable, String imageUrl) {
imageView.setImageDrawable(imageDrawable);
}
});
imageView.setImageDrawable(cachedImage);
使用這個方法,ListView執行得很好了,並且感覺滑動更平滑了,因為UI線程再也不會被圖片加載所阻塞。
更好的性能改善
如果你嘗試了上面的解決方案,你將注意到ListView也不是100%的平滑,仍然會有些東西阻滯著它的平滑性。這裡,還有兩個地方可以進行改善:
· findViewById()的昂貴調用
· 每次都inflate XML
因此,修改代碼如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
public
class ImageAndTextListAdapter extends ArrayAdapter {
private
ListView listView;
private
AsyncImageLoader asyncImageLoader;
public
ImageAndTextListAdapter(Activity activity, List imageAndTexts, ListView listView) {
super(activity,
0, imageAndTexts);
this.listView
= listView;
asyncImageLoader
= new
AsyncImageLoader();
}
@Override
public
View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
Activity
activity = (Activity) getContext();
//
Inflate the views from XML
View
rowView = convertView;
ViewCache
viewCache;
if
(rowView == null)
{
LayoutInflater
inflater = activity.getLayoutInflater();
rowView
= inflater.inflate(R.layout.image_and_text_row, null);
viewCache
= new
ViewCache(rowView);
rowView.setTag(viewCache);
}
else
{
viewCache
= (ViewCache) rowView.getTag();
}
ImageAndText
imageAndText = getItem(position);
//
Load the image and set it on the ImageView
String
imageUrl = imageAndText.getImageUrl();
ImageView
imageView = viewCache.getImageView();
imageView.setTag(imageUrl);
Drawable
cachedImage = asyncImageLoader.loadDrawable(imageUrl, new
ImageCallback() {
public
void imageLoaded(Drawable imageDrawable, String imageUrl) {
ImageView
imageViewByTag = (ImageView) listView.findViewWithTag(imageUrl);
if
(imageViewByTag != null)
{
imageViewByTag.setImageDrawable(imageDrawable);
}
}
});
imageView.setImageDrawable(cachedImage);
//
Set the text on the TextView
TextView
textView = viewCache.getTextView();
textView.setText(imageAndText.getText());
return
rowView;
}
}
這裡有兩點需要注意:第一點是drawable不再是加載完畢後直接設定到ImageView上。正確的ImageView是通過tag查找的,這是因為我們現在重用了View,並且圖片有可能出現在錯誤的行上。我們需要擁有一個ListView的引用來通過tag查找ImageView。
另外一點是,實現中我們使用了一個叫ViewCache的對象。它這樣定義:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
public
class ViewCache {
private
View baseView;
private
TextView textView;
private
ImageView imageView;
public
ViewCache(View baseView) {
this.baseView
= baseView;
}
public
TextView getTextView() {
if
(textView == null)
{
textView
= (TextView) baseView.findViewById(R.id.text);
}
return
titleView;
}
public
ImageView getImageView() {
if
(imageView == null)
{
imageView
= (ImageView) baseView.findViewById(R.id.image);
}
return
imageView;
}
}
有了ViewCache對象,我們就不需要使用findViewById()來多次查詢View對象了。
總結
我已經向大家演示了3種改進ListView性能的方法:
· 在單一線程裡加載圖片
· 重用列表中行
· 緩存行中的View
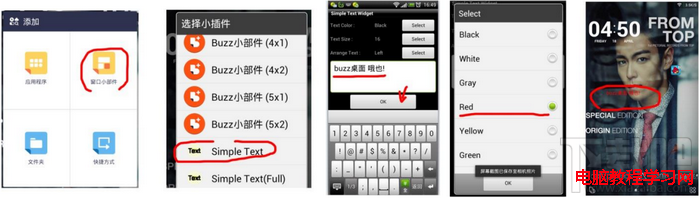 Buzz桌面教程-添加文字到桌面
Buzz桌面教程-添加文字到桌面
有些童鞋想在Buzz桌面上弄點小浪漫、小驚喜、小文藝啥的,添加文字到桌面上是必不可少的,Buzzz桌面就能很方便的在桌面上添加文字,比如“Hon
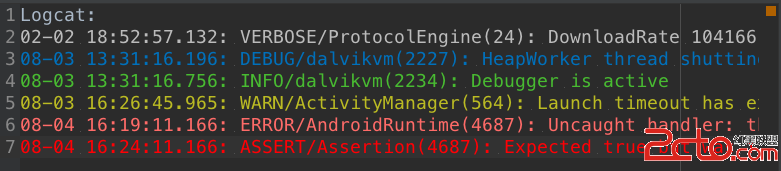 Android Studio -修改LogCat的顏色*美爆了*
Android Studio -修改LogCat的顏色*美爆了*
一、 先看效果二、設置 File->Settings 或Ctrl + Alt +S 找到 Editor -> Colors &Fonts ->
 學會編寫Android Studio插件
學會編寫Android Studio插件
一、概述相信大家在使用Android Studio的時候,或多或少的會使用一些插件,適當的配合插件可以幫助我們提升一定的開發效率,更加快樂。例如:https://gith
 android之SharedPreferences
android之SharedPreferences
簡介 將數據存儲到SharedPreferences中 獲取SharedPreferences對象 Context類中的getSharedPreferences方法 文件