編輯:關於Android編程
在我們平時使用的手機應用都可以實現只需要登陸一次賬號後,第二次進入應用直接跳轉到效果界面的效果,還有QQ的登陸框是如何記憶我們的隱身登陸,保存賬號選項的呢,這些都是通過使用SharedPreferences共享參數效果實現的,而無須使用數據庫來存儲。以下我們直接看詳細代碼分析。
package com.example.account.login;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import com.android.dao.MySQLiteOpenHelper;
import com.example.account.MainActivity;
import com.example.account.R;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class LoginActivity extends Activity {
private EditText e1, e2;
private SQLiteOpenHelper helper;
private boolean flag, flag2, flag3;
private HashMap map;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.login);
TextView textView = (TextView) this.findViewById(R.id.textView1);
e1 = (EditText) this.findViewById(R.id.editText1);
e2 = (EditText) this.findViewById(R.id.editText2);
//從共享參數獲取數據
map = (HashMap) getMsg("login");
if (map != null && !map.isEmpty()) {
if ((Boolean) map.get("login2")) {
//若值為true,用戶無需輸入密碼,直接跳轉進入操作界面
Intent intent = new Intent(LoginActivity.this,
MainActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
}
helper = new MySQLiteOpenHelper(this);
textView.setText("登錄界面");
Button button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button2);
button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (!e1.getText().toString().isEmpty()
&& !e2.getText().toString().isEmpty()) {
//從數據庫獲取賬號信息
SQLiteDatabase database = helper.getReadableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = database.query("user", new String[] {
"username", "password" }, null, null, null, null,
null);
while (cursor.moveToNext()) {
flag = e1
.getText()
.toString()
.equals(cursor.getString(cursor
.getColumnIndex("username")));
flag2 = e2
.getText()
.toString()
.equals(cursor.getString(cursor
.getColumnIndex("password")));
if (flag && flag2) {
Intent intent = new Intent(LoginActivity.this,
MainActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
//登陸跳轉動畫
overridePendingTransition(R.anim.zoomin,
R.anim.zoomout);
Toast.makeText(LoginActivity.this, "登錄成功",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
flag3 = true;
//登陸成功後將flag設置為ture存入共享參數中
HashMap map = new HashMap();
map.put("login2", flag3);
saveMsg("login", map);
}
}
if (!flag3) {
Toast.makeText(LoginActivity.this, "您輸入的帳號或密碼有誤",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
} else {
Toast.makeText(LoginActivity.this, "請正確輸入您的帳號密碼",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
});
Button button2 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1);
button2.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent(LoginActivity.this,
RegisterActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
//將數據存儲進入共享參數
public boolean saveMsg(String fileName, Map map) {
boolean flag = false;
// 一般Mode都使用private,比較安全
SharedPreferences preferences = getSharedPreferences(fileName,
Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = preferences.edit();
// Map類提供了一個稱為entrySet()的方法,這個方法返回一個Map.Entry實例化後的對象集。
// 接著,Map.Entry類提供了一個getKey()方法和一個getValue()方法,
// 因此,上面的代碼可以被組織得更符合邏輯
for (Map.Entry entry : map.entrySet()) {
String key = entry.getKey();
Object object = entry.getValue();
// 根據值得不同類型,添加
if (object instanceof Boolean) {
Boolean new_name = (Boolean) object;
editor.putBoolean(key, new_name);
} else if (object instanceof Integer) {
Integer integer = (Integer) object;
editor.putInt(key, integer);
} else if (object instanceof Float) {
Float f = (Float) object;
editor.putFloat(key, f);
} else if (object instanceof Long) {
Long l = (Long) object;
editor.putLong(key, l);
} else if (object instanceof String) {
String s = (String) object;
editor.putString(key, s);
}
}
flag = editor.commit();
return flag;
}
// 讀取數據
public Map getMsg(String fileName) {
Map map = null;
// 讀取數據用不到edit
SharedPreferences preferences = getSharedPreferences(fileName,
Context.MODE_APPEND);
//Context.MODE_APPEND可以對已存在的值進行修改
map = preferences.getAll();
return map;
}
}
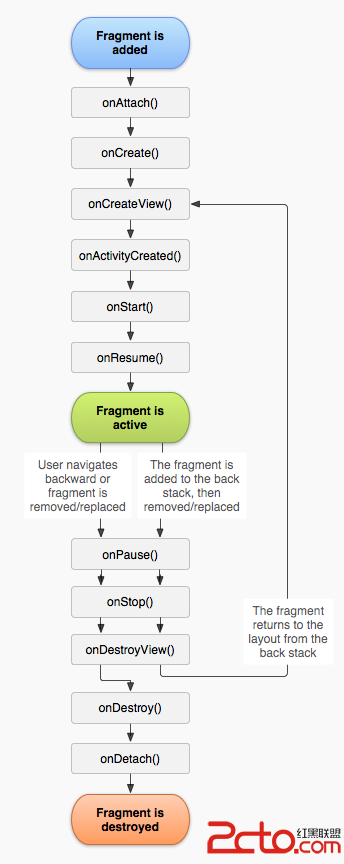 Android Fragment 簡單實例
Android Fragment 簡單實例
Android上的界面展示都是通過Activity實現的,Activity實在是太常用了,我相信大家都已經非常熟悉了,這裡就不再贅述。 但是Activity也有它的局限性
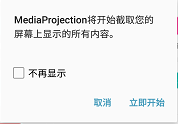 Android中利用5.0系統屏幕錄制UI漏洞騙取應用錄制屏幕授權
Android中利用5.0系統屏幕錄制UI漏洞騙取應用錄制屏幕授權
一、漏洞分析今天我們來看一下Android中的屏幕錄制功能帶來的一個漏洞問題,在之前的一篇文章中介紹了關於Android5.0新增的Api來進行錄制屏幕視頻,不了解的同學
 魅族pro6與mx6有什麼區別 魅族MX6配置詳細介紹
魅族pro6與mx6有什麼區別 魅族MX6配置詳細介紹
魅族MX6正式發布上線開賣了,很多買家都在猶豫買魅族pro6還是魅族MX6?那魅族pro6與mx6有什麼區別呢?魅族MX6配置怎麼樣呢?有什麼機身尺寸呢?正
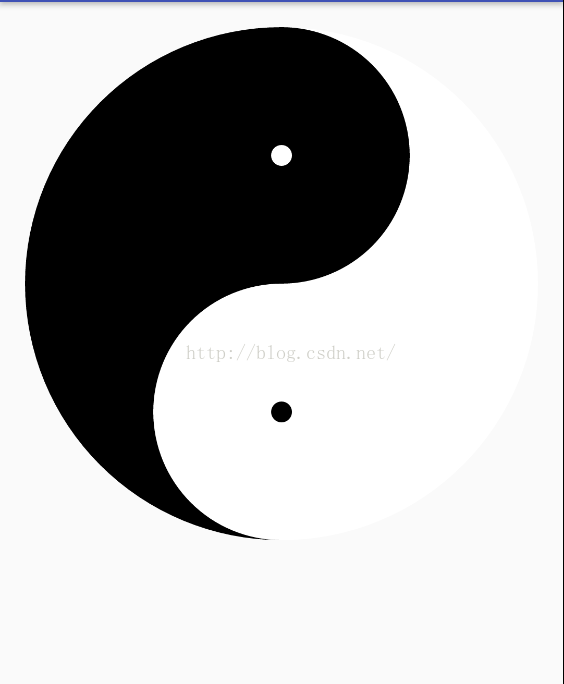 Android 繪制太極圖實例詳解
Android 繪制太極圖實例詳解
Android 繪制太極圖繪制一個太極圖實現代碼:package com.jackie.taijicircle; import android.content.Cont