編輯:關於Android編程
android 文件存儲分為:internal storage(內部存儲)和 External storage(外部存儲例如sdcard)
internal storage:
1.內部存儲一直存在
2.默認的只能被你自己的應用訪問(當然通過設置 MODE_PRIVATE讓其他應用訪問而且其他應用要知道你的包名因為file存儲的地址在/data/data/packname)下面。
3.當你刪除此應用,這些文件也會被刪除
4.訪問內部存儲不用manifest裡面加權限
5.一般apk安裝的在內部存儲中當然也可以通過在manifest中設置android:installLocation設置apk安裝的目錄
6.內部目錄分為filesDir和cacheDir 可以通過方法getFileDir()、getCacheDir()去獲取他的地址
7.在內部存儲放置的文件不用的要進行刪除,如果一直不刪除超出了系統分給你的大小,系統會在沒有警告的自動刪除你的存儲的文件
8.內部文件的寫入
String filename = "myfile";
String string = "Hello world!";
FileOutputStream outputStream;
try {
outputStream = openFileOutput(filename, Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
outputStream.write(string.getBytes());
outputStream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}9.內部文件臨時文件的寫入
public File getTempFile(Context context, String url) {
File file;
try {
String fileName = Uri.parse(url).getLastPathSegment();
file = File.createTempFile(fileName, null, context.getCacheDir());
catch (IOException e) {
// Error while creating file
}
return file;
}1.外部文件不一定一直都在。
2.外部文件可以通過其他方式讀取
3.當你刪除應用是文件還是會存在
4.如果你向外部文件進行寫入需要在manifest中加入權限:uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE“
如果你要讀取尾外部文件到現在位置的版本是不需要加如權限的但是為了保證向後兼容最好在讀文件時也加入權限:uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"
備注:android:installLocation
Although apps are installed onto the internal storage by default, you can specify theandroid:installLocation attribute in your manifest so your app may be installed on external storage. Users appreciate this option when the APK size is very large
and they have an external storage space that's larger than the internal storage. For more information, see App Install Location.
 android studio基本設置以及常見項目打開出現的問題一
android studio基本設置以及常見項目打開出現的問題一
因為之前工作項目開發都是適應eclipse開發android的。用習慣了,一時半會不是很好適應android studio編譯器。所以把android studio常用設
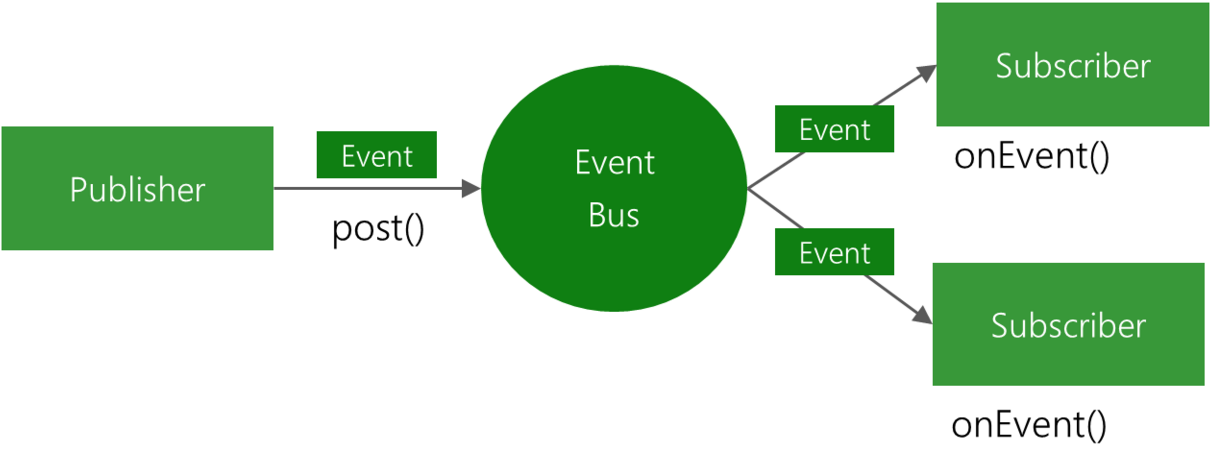 Android EventBus3.0使用及源碼解析
Android EventBus3.0使用及源碼解析
叨了個叨最近因為換工作的一些瑣事搞的我一個頭兩個大,也沒怎麼去學新東西,實在是有些愧疚。新項目用到了EventBus3.0,原來只是聽說EventBus的鼎鼎大名,一直沒
 【自定義View系列】04--談談事件分發
【自定義View系列】04--談談事件分發
引言:這部分會分三個模塊來講,先講View對Touch的處理,再講ViewGroup的事件分發,最後講如何解決滑動沖突。我習慣通過在源碼中添加注釋來理解源碼,以下是我提取
 Android好奇寶寶_05_PopupWindow與懸浮窗
Android好奇寶寶_05_PopupWindow與懸浮窗
之所以把PopupWindow與懸浮窗這兩個放到一起講,是因為這兩個的實現原理基本是一致的,只是有點不同而已。 原理: 使用系統服務(WindowManag