編輯:關於Android編程
項目中有這麼一個bug,即在切換語言後輸入法沒有實現國際化,只有重啟設備輸入法中的語言才會變過來即為正確的語言,後來經過下面的分析發現只要自己重啟輸入發服務就ok了,那麼為什麼會ok呢?下面已經說明
先看我們怎麼實現所有Activity展示的國際化,正常我們不會在原生態的setting中去實現,因為多數現在都是定制,我們也是,下面是我們自己的設置應用的語言切換實現功能代碼:
try {
Class activityManagerNative = Class.forName("android.app.ActivityManagerNative");
Object am = activityManagerNative.getMethod("getDefault").invoke(activityManagerNative);
Object config = am.getClass().getMethod("getConfiguration").invoke(am);
config.getClass().getDeclaredField("locale").set(config, language);
config.getClass().getDeclaredField("userSetLocale").setBoolean(config, true);
am.getClass().getMethod("updateConfiguration", android.content.res.Configuration.class).invoke(am, config);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
IActivityManager am = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
Configuration config = am.getConfiguration();
config.locale = locale;
config.userSetLocale = true;
am.updateConfiguration(config);我們先獲取到ActivityManagerNative的getDefault()對象,跟蹤下這個代碼
/**
* Retrieve the system's default/global activity manager.
*/
static public IActivityManager getDefault() {
return gDefault.get();
}private static final SingletongDefault = new Singleton () { protected IActivityManager create() { IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService("activity"); if (false) { Log.v("ActivityManager", "default service binder = " + b); } IActivityManager am = asInterface(b); if (false) { Log.v("ActivityManager", "default service = " + am); } return am; } };
public static void setSystemProcess() {
try {
ActivityManagerService m = mSelf;
ServiceManager.addService("activity", m);
public void updateConfiguration(Configuration values) {
enforceCallingPermission(android.Manifest.permission.CHANGE_CONFIGURATION,
"updateConfiguration()");
synchronized(this) {
if (values == null && mWindowManager != null) {
// sentinel: fetch the current configuration from the window manager
values = mWindowManager.computeNewConfiguration();
}
if (mWindowManager != null) {
mProcessList.applyDisplaySize(mWindowManager);
}
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
if (values != null) {
Settings.System.clearConfiguration(values);
}
updateConfigurationLocked(values, null, false, false);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}上面的enforceCallingPermission方法進行權限驗證,重點看updateConfigurationLocked(values, null, false, false);
/**
* Do either or both things: (1) change the current configuration, and (2)
* make sure the given activity is running with the (now) current
* configuration. Returns true if the activity has been left running, or
* false if starting is being destroyed to match the new
* configuration.
* @param persistent TODO
*/
public boolean updateConfigurationLocked(Configuration values,
ActivityRecord starting, boolean persistent, boolean initLocale) {
int changes = 0;
boolean kept = true;
if (values != null) {
Configuration newConfig = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
changes = newConfig.updateFrom(values);
if (changes != 0) {
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Updating configuration to: " + values);
}
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.CONFIGURATION_CHANGED, changes);
if (values.locale != null && !initLocale) {
saveLocaleLocked(values.locale,
!values.locale.equals(mConfiguration.locale),
values.userSetLocale);
}
mConfigurationSeq++;
if (mConfigurationSeq <= 0) {
mConfigurationSeq = 1;
}
newConfig.seq = mConfigurationSeq;
mConfiguration = newConfig;
Slog.i(TAG, "Config changed: " + newConfig);
final Configuration configCopy = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
AttributeCache ac = AttributeCache.instance();
if (ac != null) {
ac.updateConfiguration(configCopy);
}
// Make sure all resources in our process are updated
// right now, so that anyone who is going to retrieve
// resource values after we return will be sure to get
// the new ones. This is especially important during
// boot, where the first config change needs to guarantee
// all resources have that config before following boot
// code is executed.
mSystemThread.applyConfigurationToResources(configCopy);
if (persistent && Settings.System.hasInterestingConfigurationChanges(changes)) {
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(UPDATE_CONFIGURATION_MSG);
msg.obj = new Configuration(configCopy);
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
for (int i=mLruProcesses.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
ProcessRecord app = mLruProcesses.get(i);
try {
if (app.thread != null) {
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Sending to proc "
+ app.processName + " new config " + mConfiguration);
app.thread.scheduleConfigurationChanged(configCopy);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_CONFIGURATION_CHANGED);
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REGISTERED_ONLY
| Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REPLACE_PENDING);
broadcastIntentLocked(null, null, intent, null, null, 0, null, null,
null, false, false, MY_PID, Process.SYSTEM_UID);
if ((changes&ActivityInfo.CONFIG_LOCALE) != 0) {
broadcastIntentLocked(null, null,
new Intent(Intent.ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED),
null, null, 0, null, null,
null, false, false, MY_PID, Process.SYSTEM_UID);
}
}
}
if (changes != 0 && starting == null) {
// If the configuration changed, and the caller is not already
// in the process of starting an activity, then find the top
// activity to check if its configuration needs to change.
starting = mMainStack.topRunningActivityLocked(null);
}
if (starting != null) {
kept = mMainStack.ensureActivityConfigurationLocked(starting, changes);
// And we need to make sure at this point that all other activities
// are made visible with the correct configuration.
mMainStack.ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(starting, changes);
}
if (values != null && mWindowManager != null) {
mWindowManager.setNewConfiguration(mConfiguration);
}
return kept;
}(1)更改當前配置,通俗講就是讓改變的configuration更新到當前configuration
(2)確保所有正在運行的activity都能更新改變後的configuration
注釋還是比較清晰的,我們重點看下面這個方法
for (int i=mLruProcesses.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
ProcessRecord app = mLruProcesses.get(i);
try {
if (app.thread != null) {
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v("PateoConfig", "Sending to proc "
+ app.processName + " new config " + mConfiguration);
app.thread.scheduleConfigurationChanged(configCopy);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}
} /**
* List of running applications, sorted by recent usage.
* The first entry in the list is the least recently used.
* It contains ApplicationRecord objects. This list does NOT include
* any persistent application records (since we never want to exit them).
*/
final ArrayList mLruProcesses
= new ArrayList();
IApplicationThread thread;
public abstract class ApplicationThreadNative extends Binder
implements IApplicationThread { public final void scheduleConfigurationChanged(Configuration config)
throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IApplicationThread.descriptor);
config.writeToParcel(data, 0);
mRemote.transact(SCHEDULE_CONFIGURATION_CHANGED_TRANSACTION, data, null,
IBinder.FLAG_ONEWAY);
data.recycle();
}
看看這個msg消息的處理
case SCHEDULE_CONFIGURATION_CHANGED_TRANSACTION:
{
data.enforceInterface(IApplicationThread.descriptor);
Configuration config = Configuration.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
scheduleConfigurationChanged(config);
return true;
}void scheduleConfigurationChanged(Configuration config) throws RemoteException;找到它的實現:
private class ApplicationThread extends ApplicationThreadNative {
......
public void scheduleConfigurationChanged(Configuration config) {
updatePendingConfiguration(config);
queueOrSendMessage(H.CONFIGURATION_CHANGED, config);
}
......
} case CONFIGURATION_CHANGED:
handleConfigurationChanged((Configuration)msg.obj, null);
break; final void handleConfigurationChanged(Configuration config, CompatibilityInfo compat) {
ArrayList callbacks = null;
synchronized (mPackages) {
if (mPendingConfiguration != null) {
if (!mPendingConfiguration.isOtherSeqNewer(config)) {
config = mPendingConfiguration;
}
mPendingConfiguration = null;
}
if (config == null) {
return;
}
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Handle configuration changed: "
+ config);
applyConfigurationToResourcesLocked(config, compat);
if (mConfiguration == null) {
mConfiguration = new Configuration();
}
if (!mConfiguration.isOtherSeqNewer(config) && compat == null) {
return;
}
mConfiguration.updateFrom(config);
config = applyCompatConfiguration();
callbacks = collectComponentCallbacksLocked(false, config);
}
// Cleanup hardware accelerated stuff
WindowManagerImpl.getDefault().trimLocalMemory();
if (callbacks != null) {
final int N = callbacks.size();
for (int i=0; i
我們先來看applyConfigurationToResourcesLocked(config, compat);
final boolean applyConfigurationToResourcesLocked(Configuration config,
CompatibilityInfo compat) {
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v("PateoConfig","ActivityThread class ,applyConfigurationToResourcesLocked coming");
if (mResConfiguration == null) {
mResConfiguration = new Configuration();
}
if (!mResConfiguration.isOtherSeqNewer(config) && compat == null) {
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Skipping new config: curSeq="
+ mResConfiguration.seq + ", newSeq=" + config.seq);
return false;
}
int changes = mResConfiguration.updateFrom(config);
DisplayMetrics dm = getDisplayMetricsLocked(null, true);
if (compat != null && (mResCompatibilityInfo == null ||
!mResCompatibilityInfo.equals(compat))) {
mResCompatibilityInfo = compat;
changes |= ActivityInfo.CONFIG_SCREEN_LAYOUT
| ActivityInfo.CONFIG_SCREEN_SIZE
| ActivityInfo.CONFIG_SMALLEST_SCREEN_SIZE;
}
// set it for java, this also affects newly created Resources
if (config.locale != null) {
Locale.setDefault(config.locale);
}
Resources.updateSystemConfiguration(config, dm, compat);
ApplicationPackageManager.configurationChanged();
//Slog.i(TAG, "Configuration changed in " + currentPackageName());
Iterator> it =
mActiveResources.values().iterator();
//Iterator>> it =
// mActiveResources.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
WeakReference v = it.next();
Resources r = v.get();
if (r != null) {
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v("PateoConfig", "ActivityThread class ,Changing resources "
+ r + " config to: " + config);
r.updateConfiguration(config, dm, compat);
//Slog.i(TAG, "Updated app resources " + v.getKey()
// + " " + r + ": " + r.getConfiguration());
} else {
//Slog.i(TAG, "Removing old resources " + v.getKey());
it.remove();
}
}
return changes != 0;
}
Resources.updateSystemConfiguration()清除一部分系統資源, 並且將config更新到Resources, 而Resources包含了一個AssetManager對象, 該對象的核心實現是在AssetManager.cpp中完成的. 然後循環清空mActivityResources資源. 再回到handleConfigurationChanged()函數,執行下面的方法
callbacks = collectComponentCallbacksLocked(false, config);
ArrayList collectComponentCallbacksLocked(
boolean allActivities, Configuration newConfig) {
ArrayList callbacks
= new ArrayList();
if (mActivities.size() > 0) {
Iterator it = mActivities.values().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
ActivityClientRecord ar = it.next();
Activity a = ar.activity;
if (a != null) {
Configuration thisConfig = applyConfigCompatMainThread(newConfig,
ar.packageInfo.mCompatibilityInfo.getIfNeeded());
if (!ar.activity.mFinished && (allActivities ||
(a != null && !ar.paused))) {
// If the activity is currently resumed, its configuration
// needs to change right now.
callbacks.add(a);
} else if (thisConfig != null) {
// Otherwise, we will tell it about the change
// the next time it is resumed or shown. Note that
// the activity manager may, before then, decide the
// activity needs to be destroyed to handle its new
// configuration.
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Setting activity "
+ ar.activityInfo.name + " newConfig=" + thisConfig);
ar.newConfig = thisConfig;
}
}
}
}
if (mServices.size() > 0) {
Iterator it = mServices.values().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
callbacks.add(it.next());
}
}
synchronized (mProviderMap) {
if (mLocalProviders.size() > 0) {
Iterator it = mLocalProviders.values().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
callbacks.add(it.next().mLocalProvider);
}
}
}
final int N = mAllApplications.size();
for (int i=0; i
從上來看callbacks是Activity等被作為參數傳入
if (callbacks != null) {
final int N = callbacks.size();
for (int i=0; i
進入performConfigurationChanged方法
private final void performConfigurationChanged(
ComponentCallbacks2 cb, Configuration config) {
// Only for Activity objects, check that they actually call up to their
// superclass implementation. ComponentCallbacks2 is an interface, so
// we check the runtime type and act accordingly.
Activity activity = (cb instanceof Activity) ? (Activity) cb : null;
if (activity != null) {
activity.mCalled = false;
}
boolean shouldChangeConfig = false;
if ((activity == null) || (activity.mCurrentConfig == null)) {
shouldChangeConfig = true;
} else {
// If the new config is the same as the config this Activity
// is already running with then don't bother calling
// onConfigurationChanged
int diff = activity.mCurrentConfig.diff(config);
if (diff != 0) {
// If this activity doesn't handle any of the config changes
// then don't bother calling onConfigurationChanged as we're
// going to destroy it.
if ((~activity.mActivityInfo.getRealConfigChanged() & diff) == 0) {
shouldChangeConfig = true;
}
}
}
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Config callback " + cb
+ ": shouldChangeConfig=" + shouldChangeConfig);
if (shouldChangeConfig) {
cb.onConfigurationChanged(config);
if (activity != null) {
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + activity.getLocalClassName() +
" did not call through to super.onConfigurationChanged()");
}
activity.mConfigChangeFlags = 0;
activity.mCurrentConfig = new Configuration(config);
}
}
}上面判斷configuration是否改變, 如果改變那麼shouldChangeConfig為true. 然後調用activity的onConfigurationChange(config);
/**
* Called by the system when the device configuration changes while your
* activity is running. Note that this will only be called if
* you have selected configurations you would like to handle with the
* {@link android.R.attr#configChanges} attribute in your manifest. If
* any configuration change occurs that is not selected to be reported
* by that attribute, then instead of reporting it the system will stop
* and restart the activity (to have it launched with the new
* configuration).
*
* At the time that this function has been called, your Resources
* object will have been updated to return resource values matching the
* new configuration.
*
* @param newConfig The new device configuration.
*/
public void onConfigurationChanged(Configuration newConfig) {
mCalled = true;
mFragments.dispatchConfigurationChanged(newConfig);
if (mWindow != null) {
// Pass the configuration changed event to the window
mWindow.onConfigurationChanged(newConfig);
}
if (mActionBar != null) {
// Do this last; the action bar will need to access
// view changes from above.
mActionBar.onConfigurationChanged(newConfig);
}
}
看上面的注釋意思:如果你的activity運行 , 設備信息有改變(即configuration改變)時由系統調用. 如果你在manifest.xml中配置了configChnages屬性則表示有你自己來處理configuration change. 否則就重啟當前這個activity. 而重啟之前, 舊的resources已經被清空,
那麼就會裝載新的資源, 整個過程就完成了語言切換後 , 能夠讓所有app使用新的語言.
那麼我們要問真正實現重啟Activity的代碼在哪呢,我們回到ActivityManagerService的updateConfigurationLocked方法,在我們分析完app.thread.scheduleConfigurationChanged(configCopy);的代碼後,其實在app.thread.scheduleConfigurationChanged(configCopy);該代碼下面即在updateConfigurationLocked方法內,有這麼一行代碼
if (changes != 0 && starting == null) {
// If the configuration changed, and the caller is not already
// in the process of starting an activity, then find the top
// activity to check if its configuration needs to change.
starting = mMainStack.topRunningActivityLocked(null);
}
if (starting != null) {
kept = mMainStack.ensureActivityConfigurationLocked(starting, changes);
主要是 kept = mMainStack.ensureActivityConfigurationLocked(starting, changes);
我們進入該方法
/**
* Make sure the given activity matches the current configuration. Returns
* false if the activity had to be destroyed. Returns true if the
* configuration is the same, or the activity will remain running as-is
* for whatever reason. Ensures the HistoryRecord is updated with the
* correct configuration and all other bookkeeping is handled.
*/
final boolean ensureActivityConfigurationLocked(ActivityRecord r,
int globalChanges) {
if (mConfigWillChange) {
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG,
"Skipping config check (will change): " + r);
return true;
}
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG,
"Ensuring correct configuration: " + r);
// Short circuit: if the two configurations are the exact same
// object (the common case), then there is nothing to do.
Configuration newConfig = mService.mConfiguration;
if (r.configuration == newConfig && !r.forceNewConfig) {
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG,
"Configuration unchanged in " + r);
return true;
}
// We don't worry about activities that are finishing.
if (r.finishing) {
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG,
"Configuration doesn't matter in finishing " + r);
r.stopFreezingScreenLocked(false);
return true;
}
// Okay we now are going to make this activity have the new config.
// But then we need to figure out how it needs to deal with that.
Configuration oldConfig = r.configuration;
r.configuration = newConfig;
// Determine what has changed. May be nothing, if this is a config
// that has come back from the app after going idle. In that case
// we just want to leave the official config object now in the
// activity and do nothing else.
final int changes = oldConfig.diff(newConfig);
if (changes == 0 && !r.forceNewConfig) {
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG,
"Configuration no differences in " + r);
return true;
}
// If the activity isn't currently running, just leave the new
// configuration and it will pick that up next time it starts.
if (r.app == null || r.app.thread == null) {
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG,
"Configuration doesn't matter not running " + r);
r.stopFreezingScreenLocked(false);
r.forceNewConfig = false;
return true;
}
// Figure out how to handle the changes between the configurations.
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) {
Slog.v(TAG, "Checking to restart " + r.info.name + ": changed=0x"
+ Integer.toHexString(changes) + ", handles=0x"
+ Integer.toHexString(r.info.getRealConfigChanged())
+ ", newConfig=" + newConfig);
}
if ((changes&(~r.info.getRealConfigChanged())) != 0 || r.forceNewConfig) {
// Aha, the activity isn't handling the change, so DIE DIE DIE.
r.configChangeFlags |= changes;
r.startFreezingScreenLocked(r.app, globalChanges);
r.forceNewConfig = false;
if (r.app == null || r.app.thread == null) {
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG,
"Switch is destroying non-running " + r);
destroyActivityLocked(r, true, false, "config");
} else if (r.state == ActivityState.PAUSING) {
// A little annoying: we are waiting for this activity to
// finish pausing. Let's not do anything now, but just
// flag that it needs to be restarted when done pausing.
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG,
"Switch is skipping already pausing " + r);
r.configDestroy = true;
return true;
} else if (r.state == ActivityState.RESUMED) {
// Try to optimize this case: the configuration is changing
// and we need to restart the top, resumed activity.
// Instead of doing the normal handshaking, just say
// "restart!".
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG,
"Switch is restarting resumed " + r);
relaunchActivityLocked(r, r.configChangeFlags, true);
r.configChangeFlags = 0;
} else {
if (DEBUG_SWITCH || DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG,
"Switch is restarting non-resumed " + r);
relaunchActivityLocked(r, r.configChangeFlags, false);
r.configChangeFlags = 0;
}
// All done... tell the caller we weren't able to keep this
// activity around.
return false;
}
// Default case: the activity can handle this new configuration, so
// hand it over. Note that we don't need to give it the new
// configuration, since we always send configuration changes to all
// process when they happen so it can just use whatever configuration
// it last got.
if (r.app != null && r.app.thread != null) {
try {
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Sending new config to " + r);
r.app.thread.scheduleActivityConfigurationChanged(r.appToken);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// If process died, whatever.
}
}
r.stopFreezingScreenLocked(false);
return true;
}
我們會發現上面的代碼有日志輸出
V/ActivityManager( 1265): Switch is restarting resumed ActivityRecord{41ad1e90 com.pateo.as.settings/.activity.SettingActivity}
V/ActivityManager( 1265): Relaunching: ActivityRecord{41ad1e90 com.pateo.as.settings/.activity.SettingActivity} with results=null newIntents=null andResume=true
I/ActivityManager( 1265): Switch is restarting resumed ActivityRecord{41ad1e90 com.pateo.as.settings/.activity.SettingActivity}
根據輸出日志我們來看下,是走入了下面這個方法:
relaunchActivityLocked(r, r.configChangeFlags, true);
private final boolean relaunchActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r,
int changes, boolean andResume) {
List results = null;
List newIntents = null;
if (andResume) {
results = r.results;
newIntents = r.newIntents;
}
if (DEBUG_SWITCH) Slog.v(TAG, "Relaunching: " + r
+ " with results=" + results + " newIntents=" + newIntents
+ " andResume=" + andResume);
EventLog.writeEvent(andResume ? EventLogTags.AM_RELAUNCH_RESUME_ACTIVITY
: EventLogTags.AM_RELAUNCH_ACTIVITY, System.identityHashCode(r),
r.task.taskId, r.shortComponentName);
r.startFreezingScreenLocked(r.app, 0);
try {
if (DEBUG_SWITCH) Slog.i(TAG, "Switch is restarting resumed " + r);
r.forceNewConfig = false;
r.app.thread.scheduleRelaunchActivity(r.appToken, results, newIntents,
changes, !andResume, new Configuration(mService.mConfiguration));
// Note: don't need to call pauseIfSleepingLocked() here, because
// the caller will only pass in 'andResume' if this activity is
// currently resumed, which implies we aren't sleeping.
} catch (RemoteException e) {
return false;
}
if (andResume) {
r.results = null;
r.newIntents = null;
if (mMainStack) {
mService.reportResumedActivityLocked(r);
}
}
return true;
}
上面主要的調用了
r.app.thread.scheduleRelaunchActivity(r.appToken, results, newIntents,
changes, !andResume, new Configuration(mService.mConfiguration));
我們來看看這個scheduleRelaunchActivity方法,是public interface IApplicationThread類中,其實現在ActivityThread中
public final void scheduleRelaunchActivity(IBinder token,
List pendingResults, List pendingNewIntents,
int configChanges, boolean notResumed, Configuration config) {
requestRelaunchActivity(token, pendingResults, pendingNewIntents,
configChanges, notResumed, config, true);
}
public final void requestRelaunchActivity(IBinder token,
List pendingResults, List pendingNewIntents,
int configChanges, boolean notResumed, Configuration config,
boolean fromServer) {
ActivityClientRecord target = null;
synchronized (mPackages) {
for (int i=0; i
接著看下消息的處理
case RELAUNCH_ACTIVITY: {
ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord)msg.obj;
handleRelaunchActivity(r);
} break;
private void handleRelaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord tmp) {
// If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well
// we are back active so skip it.
unscheduleGcIdler();
Configuration changedConfig = null;
int configChanges = 0;
// First: make sure we have the most recent configuration and most
// recent version of the activity, or skip it if some previous call
// had taken a more recent version.
synchronized (mPackages) {
int N = mRelaunchingActivities.size();
IBinder token = tmp.token;
tmp = null;
for (int i=0; i
上面我們梳理下,調用了如下重要的三個方法
1、performPauseActivity(r.token, false, r.isPreHoneycomb());
2、handleDestroyActivity(r.token, false, configChanges, true);
3、handleLaunchActivity(r, currentIntent);
先來看第一個方法performPauseActivity
final Bundle performPauseActivity(IBinder token, boolean finished,
boolean saveState) {
ActivityClientRecord r = mActivities.get(token);
return r != null ? performPauseActivity(r, finished, saveState) : null;
}
final Bundle performPauseActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, boolean finished,
boolean saveState) {
if (r.paused) {
if (r.activity.mFinished) {
// If we are finishing, we won't call onResume() in certain cases.
// So here we likewise don't want to call onPause() if the activity
// isn't resumed.
return null;
}
RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(
"Performing pause of activity that is not resumed: "
+ r.intent.getComponent().toShortString());
Slog.e(TAG, e.getMessage(), e);
}
Bundle state = null;
if (finished) {
r.activity.mFinished = true;
}
try {
// Next have the activity save its current state and managed dialogs...
if (!r.activity.mFinished && saveState) {
state = new Bundle();
state.setAllowFds(false);
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnSaveInstanceState(r.activity, state);
r.state = state;
}
// Now we are idle.
r.activity.mCalled = false;
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPause(r.activity);
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_ON_PAUSE_CALLED, r.activity.getComponentName().getClassName());
if (!r.activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onPause()");
}
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(r.activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to pause activity "
+ r.intent.getComponent().toShortString()
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
r.paused = true;
// Notify any outstanding on paused listeners
ArrayList listeners;
synchronized (mOnPauseListeners) {
listeners = mOnPauseListeners.remove(r.activity);
}
int size = (listeners != null ? listeners.size() : 0);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
listeners.get(i).onPaused(r.activity);
}
return state;
}
上面最重要的是調用了如下:
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPause(r.activity);
進入該方法
/**
* Perform calling of an activity's {@link Activity#onPause} method. The
* default implementation simply calls through to that method.
*
* @param activity The activity being paused.
*/
public void callActivityOnPause(Activity activity) {
activity.performPause();
} final void performPause() {
mFragments.dispatchPause();
mCalled = false;
onPause();
mResumed = false;
if (!mCalled && getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion
>= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.GINGERBREAD) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + mComponent.toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onPause()");
}
mResumed = false;
}
從上面來看最終調用了生命周期中的onPause方法
我們再來看第二個方法 handleDestroyActivity(r.token, false, configChanges, true);
private void handleDestroyActivity(IBinder token, boolean finishing,
int configChanges, boolean getNonConfigInstance) {
ActivityClientRecord r = performDestroyActivity(token, finishing,
configChanges, getNonConfigInstance);
if (r != null) {
cleanUpPendingRemoveWindows(r);
WindowManager wm = r.activity.getWindowManager();
View v = r.activity.mDecor;
if (v != null) {
if (r.activity.mVisibleFromServer) {
mNumVisibleActivities--;
}
IBinder wtoken = v.getWindowToken();
if (r.activity.mWindowAdded) {
if (r.onlyLocalRequest) {
// Hold off on removing this until the new activity's
// window is being added.
r.mPendingRemoveWindow = v;
r.mPendingRemoveWindowManager = wm;
} else {
wm.removeViewImmediate(v);
}
}
if (wtoken != null && r.mPendingRemoveWindow == null) {
WindowManagerImpl.getDefault().closeAll(wtoken,
r.activity.getClass().getName(), "Activity");
}
r.activity.mDecor = null;
}
if (r.mPendingRemoveWindow == null) {
// If we are delaying the removal of the activity window, then
// we can't clean up all windows here. Note that we can't do
// so later either, which means any windows that aren't closed
// by the app will leak. Well we try to warning them a lot
// about leaking windows, because that is a bug, so if they are
// using this recreate facility then they get to live with leaks.
WindowManagerImpl.getDefault().closeAll(token,
r.activity.getClass().getName(), "Activity");
}
// Mocked out contexts won't be participating in the normal
// process lifecycle, but if we're running with a proper
// ApplicationContext we need to have it tear down things
// cleanly.
Context c = r.activity.getBaseContext();
if (c instanceof ContextImpl) {
((ContextImpl) c).scheduleFinalCleanup(
r.activity.getClass().getName(), "Activity");
}
}
if (finishing) {
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().activityDestroyed(token);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// If the system process has died, it's game over for everyone.
}
}
}
ActivityClientRecord r = performDestroyActivity(token, finishing,
configChanges, getNonConfigInstance);
public final ActivityClientRecord performDestroyActivity(IBinder token, boolean finishing) {
return performDestroyActivity(token, finishing, 0, false);
}
private ActivityClientRecord performDestroyActivity(IBinder token, boolean finishing,
int configChanges, boolean getNonConfigInstance) {
ActivityClientRecord r = mActivities.get(token);
Class activityClass = null;
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Performing finish of " + r);
if (r != null) {
activityClass = r.activity.getClass();
r.activity.mConfigChangeFlags |= configChanges;
if (finishing) {
r.activity.mFinished = true;
}
if (!r.paused) {
try {
r.activity.mCalled = false;
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPause(r.activity);
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_ON_PAUSE_CALLED,
r.activity.getComponentName().getClassName());
if (!r.activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + safeToComponentShortString(r.intent)
+ " did not call through to super.onPause()");
}
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(r.activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to pause activity "
+ safeToComponentShortString(r.intent)
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
r.paused = true;
}
if (!r.stopped) {
try {
r.activity.performStop();
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(r.activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to stop activity "
+ safeToComponentShortString(r.intent)
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
r.stopped = true;
}
if (getNonConfigInstance) {
try {
r.lastNonConfigurationInstances
= r.activity.retainNonConfigurationInstances();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(r.activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to retain activity "
+ r.intent.getComponent().toShortString()
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
try {
r.activity.mCalled = false;
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnDestroy(r.activity);
if (!r.activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + safeToComponentShortString(r.intent) +
" did not call through to super.onDestroy()");
}
if (r.window != null) {
r.window.closeAllPanels();
}
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(r.activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to destroy activity " + safeToComponentShortString(r.intent)
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
mActivities.remove(token);
StrictMode.decrementExpectedActivityCount(activityClass);
return r;
}
上面代碼重要的調用了如下:
r.activity.performStop();和 mInstrumentation.callActivityOnDestroy(r.activity);
這兩個方法重點的是stop當前的Activity並且destroy Activity
我們回到第三個方法handleLaunchActivity
private void handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
// If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well
// we are back active so skip it.
unscheduleGcIdler();
if (r.profileFd != null) {
mProfiler.setProfiler(r.profileFile, r.profileFd);
mProfiler.startProfiling();
mProfiler.autoStopProfiler = r.autoStopProfiler;
}
// Make sure we are running with the most recent config.
handleConfigurationChanged(null, null);
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
TAG, "Handling launch of " + r);
Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);
if (a != null) {
r.createdConfig = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
Bundle oldState = r.state;
handleResumeActivity(r.token, false, r.isForward);
if (!r.activity.mFinished && r.startsNotResumed) {
// The activity manager actually wants this one to start out
// paused, because it needs to be visible but isn't in the
// foreground. We accomplish this by going through the
// normal startup (because activities expect to go through
// onResume() the first time they run, before their window
// is displayed), and then pausing it. However, in this case
// we do -not- need to do the full pause cycle (of freezing
// and such) because the activity manager assumes it can just
// retain the current state it has.
try {
r.activity.mCalled = false;
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPause(r.activity);
// We need to keep around the original state, in case
// we need to be created again.
r.state = oldState;
if (!r.activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onPause()");
}
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(r.activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to pause activity "
+ r.intent.getComponent().toShortString()
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
r.paused = true;
}
} else {
// If there was an error, for any reason, tell the activity
// manager to stop us.
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()
.finishActivity(r.token, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// Ignore
}
}
}
假設,我們把handleLaunchActivity方法注釋掉,則我們應該會看到當前界面銷毀,而又沒有起Activity,則會黑屏,呵呵
上面重要的兩個方法如下:
1、 Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);
2、 handleResumeActivity(r.token, false, r.isForward);
先來看performLaunchActivity方法
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
// System.out.println("##### [" + System.currentTimeMillis() + "] ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity(" + r + ")");
ActivityInfo aInfo = r.activityInfo;
if (r.packageInfo == null) {
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfo(aInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo,
Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE);
}
ComponentName component = r.intent.getComponent();
if (component == null) {
component = r.intent.resolveActivity(
mInitialApplication.getPackageManager());
r.intent.setComponent(component);
}
if (r.activityInfo.targetActivity != null) {
component = new ComponentName(r.activityInfo.packageName,
r.activityInfo.targetActivity);
}
Activity activity = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = r.packageInfo.getClassLoader();
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
StrictMode.incrementExpectedActivityCount(activity.getClass());
r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
if (r.state != null) {
r.state.setClassLoader(cl);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Performing launch of " + r);
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
TAG, r + ": app=" + app
+ ", appName=" + app.getPackageName()
+ ", pkg=" + r.packageInfo.getPackageName()
+ ", comp=" + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString()
+ ", dir=" + r.packageInfo.getAppDir());
if (activity != null) {
ContextImpl appContext = new ContextImpl();
appContext.init(r.packageInfo, r.token, this);
appContext.setOuterContext(activity);
CharSequence title = r.activityInfo.loadLabel(appContext.getPackageManager());
Configuration config = new Configuration(mCompatConfiguration);
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Launching activity "
+ r.activityInfo.name + " with config " + config);
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config);
if (customIntent != null) {
activity.mIntent = customIntent;
}
r.lastNonConfigurationInstances = null;
activity.mStartedActivity = false;
int theme = r.activityInfo.getThemeResource();
if (theme != 0) {
activity.setTheme(theme);
}
activity.mCalled = false;
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onCreate()");
}
r.activity = activity;
r.stopped = true;
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
activity.performStart();
r.stopped = false;
}
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
if (r.state != null) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state);
}
}
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
activity.mCalled = false;
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnPostCreate(activity, r.state);
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onPostCreate()");
}
}
}
r.paused = true;
mActivities.put(r.token, r);
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to start activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
return activity;
}
上面重要的一句代碼:
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);
public void callActivityOnCreate(Activity activity, Bundle icicle) {
if (mWaitingActivities != null) {
synchronized (mSync) {
final int N = mWaitingActivities.size();
for (int i=0; i
進入方法performCreate
final void performCreate(Bundle icicle) {
onCreate(icicle);
mVisibleFromClient = !mWindow.getWindowStyle().getBoolean(
com.android.internal.R.styleable.Window_windowNoDisplay, false);
mFragments.dispatchActivityCreated();
}
我們看到了調用了onCreate啟動了
再回到第二個方法handleResumeActivity,同上面一步步跟蹤下去調用了Resume
從上面來看,我們有幾點需要總結下:
說明:輸入法的國際化在cb中有Activity也有service,而輸入法是服務,在InputMethodService的繼承類中加入了onConfigurationChanged方法,所以會回調onConfigurationChanged方法,而我在這個方法裡面做了kill動作,類似於上面的代碼的Activity的重啟
cb.onConfigurationChanged(config);
public void KillPinyin(){
android.os.Process.killProcess(android.os.Process.myPid());
final ActivityManager am = (ActivityManager)getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
am.restartPackage(getPackageName());
}
現在有個疑問,即如果我不去重新覆蓋 onConfigurationChanged方法會怎麼樣?呵呵,按規矩不去覆蓋該方法應該像其他應用一樣會自動實現國家化,會嗎?它是不會的,不信你試試,為什麼呢?這又是另一個課題了,呵呵,我也很想有人和我交流這個,即為什麼不去覆蓋此方法也不行呢?我現在沒有時間寫博客了,要做項目了
 Android中AIDL實現進程通信
Android中AIDL實現進程通信
AIDL概述但用Messenger實現的IPC存在一點不足:Service內部維護著一個Messenger,Messenger內部又維護著一個Hanlder,當多個cli
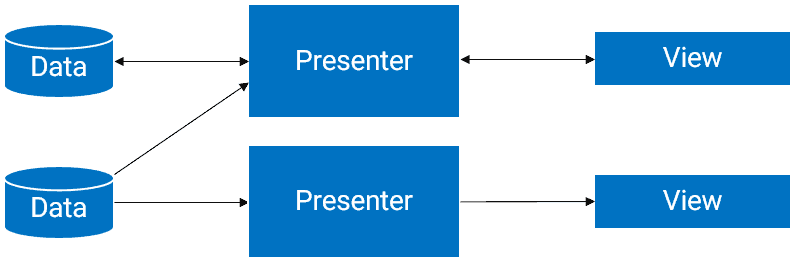 Android中MVP的初步認識與簡單用法
Android中MVP的初步認識與簡單用法
概述認識MVP模式MVP 模式實際上指的是 Model-View-Presenter 主要的目的是為了劃分各個模塊的負責區域,分工明確,使代碼清晰了很多。也是為了減少 A
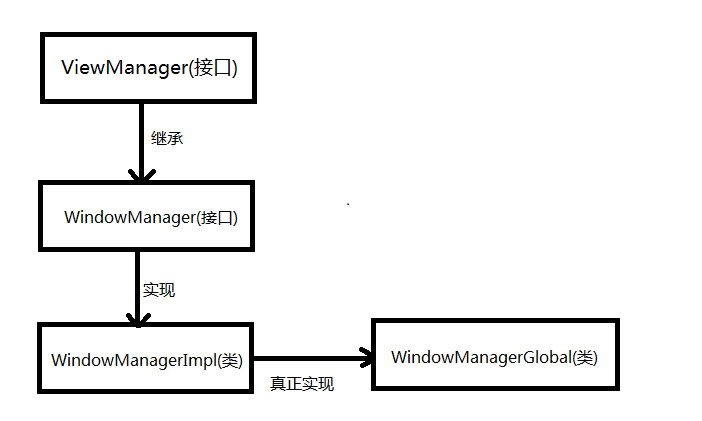 我眼中的Window創建/添加/刪除/更新過程
我眼中的Window創建/添加/刪除/更新過程
在Android中和我們打交道最多的就是Activity,因為我們會頻繁的與界面進行交互,而Activity內部關於界面方面的操作都是由Window來實現的,因此我們有必
 使用RoundedBitmapDrawable生成圓角圖片的方法
使用RoundedBitmapDrawable生成圓角圖片的方法
Bitmap src = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), imageId); //獲取Bitmap圖片Round