編輯:關於Android編程
在ListView中加載圖片是非常常見的場景,圖片的加載要滿足下面的幾個要求:
(1)不管圖片是位於網絡還是本地,加載都不應該是同步的,而是應該異步去加載,比如用AsyncTask。
(2)為了避免重復下載圖片和頁面展示的速度,一般要做緩存,比如最常見的LruCache。
(3)為了提高Listview的性能,我們一般會用holder來重用Listview的item。
代碼大概就是這樣的:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private ImageLoader imageLoader;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
imageLoader = new ImageLoader(new ImageDownloader(){
@Override
public Bitmap download(String path, int width, int height) {
return HttpUtil.download(path);
}
});
final ListView listview = (ListView)this.findViewById(R.id.listview);
Button btn = (Button)this.findViewById(R.id.btn);
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
List dataList = getDataList();
listview.setAdapter(new ListViewAdapter(MainActivity.this, dataList));
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
imageLoader.destory();
}
private class ListViewAdapter extends BaseAdapter{
private Context context;
private List dataList;
public ListViewAdapter(Context context, List dataList){
this.context = context;
this.dataList = dataList;
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return dataList.size();
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return dataList.get(position);
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return position;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
Holder holder = null;
if(convertView == null){
holder = new Holder();
convertView = new ItemView(context);
holder.itemView = (ItemView)convertView;
convertView.setTag(holder);
}else{
holder = (Holder)convertView.getTag();
}
ItemView itemView = holder.itemView;
ImageView itemImageView = itemView.getImageView();
ItemBean item = dataList.get(position);
// 先設置一個默認的圖片
// 假如不設置,當頁面滑到了某個正在加載的item上,恰好這個item是復用的前面的已經顯示的item
// 那麼這個item首先會顯示前一個item的圖片,等自己的下載完成以後,再替換掉這個圖片,
// 假如下載時間很長,會讓用戶感覺圖片錯亂了!
itemImageView.setImageResource(R.drawable.ic_launcher);
//隨後下載實際的圖片
imageLoader.loadImage(item.getImagePath(), 50, 50, itemImageView);
return itemView;
}
class Holder{
ItemView itemView;
}
}
現在問題就出現了,考慮下面的場景:
下載一幅圖片的時間很長,比如說10s,每一頁顯示3個item。
用戶第一次打開頁面,第一頁應該展示item0,item1,item2。在item0還沒下載完的時候,用戶滑到了第3頁,第3頁應該展示的是item6,item7,item8。那麼這一頁的item肯定是重用的第一頁的那些item。此時,用戶等待頁面加載。假如,item6重用的是item0,item7重用的是item1,item8重用的是item2,當item0下載完成以後,item6上展示的是item0上的圖片,這就混亂了!只有當item6自己的圖片下載完以後,item6展示的才是正確的圖片!如果在加載的過程中,用戶不停的滑動,那麼用戶看到的頁面就是完全錯亂的!
本文的圖片加載器就可以避免這個問題,是一個同事寫的,感覺很不錯,就直接拿過來了,看下代碼:
public class ImageLoader {
private static final String TAG = "ImageLoader";
private ImageCache cache;
private HashSet cacheKeys = new HashSet();
private ImageDownloader downloader;
// 保存filepath和ImageView的關系,因為ImageView會復用,所以只有這個關系才是正確的關系
// 一個imageView只能對應一個filepath,一個filepath對應一個物理文件
private WeakHashMap imageView2FileMap = new WeakHashMap();
// 一個filepath可能對應多個imageView,因為有可能會有多個imageView顯示同一張圖片
private HashMap> file2ImageViewMap = new HashMap>();
// 正在讀的或者已經在列隊裡的filepath,讀完刪除
private HashSet fileInLoadSet = new HashSet();
public ImageLoader(ImageDownloader downloader) {
if(downloader == null){
throw new RuntimeException("ImageDownloader can not be null");
}
this.cache = ImageCache.getInstance();
this.downloader = downloader;
}
/**
* 給imageView設置圖片
*
* @param filePath
* 圖片路徑
* @param width
* 寬
* @param height
* 高
* @param imageView
* @return 緩存中有,直接設置,並返回true,沒有異步讀取,讀完再設置,返回false
*/
public boolean loadImage(String filePath, int width, int height, ImageView imageView) {
String filePathKey = getKeyForFilePath(filePath, width, height);
Bitmap bmp = cache.get(filePathKey);
if (bmp == null) {
ImageViewReference imageViewRef = new ImageViewReference(imageView);
// 更新imageView和filepath的最新的關系
imageView2FileMap.put(imageView, filePathKey);
HashSet imageViewSet = file2ImageViewMap.get(filePathKey);
if (imageViewSet == null) {
imageViewSet = new HashSet();
file2ImageViewMap.put(filePathKey, imageViewSet);
}
imageViewSet.add(imageViewRef);
// 不會重復下載
if (fileInLoadSet.contains(filePathKey)) {
return false;
} else {
fileInLoadSet.add(filePathKey);
}
Holder holder = new Holder();
holder.width = width;
holder.height = height;
holder.filePath = filePath;
holder.filePathKey = filePathKey;
holder.imageViewRef = imageViewRef;
new ImageLoadTask().execute(holder);
return false;
} else {
imageView.setImageBitmap(bmp);
return true;
}
}
private class ImageLoadTask extends AsyncTask {
@Override
protected Holder doInBackground(Holder... params) {
Holder holder = params[0];
int width = holder.width;
int height = holder.height;
String filePath = holder.filePath;
String filePathKey = holder.filePathKey;
// 找到key對應的所有imageView,如果imageView的數量是0說明不用下載了
int count = getCountOfImageViewForKey(filePathKey);
if (count <= 0) {
return null;
}
try {
Random rnd = new Random();
Thread.sleep((int) (1000 * rnd.nextDouble()));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 開始讀取,放入cache
if(downloader != null){
//Bitmap bmp = ImageUtil.compressBitmap(filePath, width, height);
Bitmap bmp = downloader.download(filePath, width, height);
if(bmp != null){
cache.put(filePathKey, bmp);
cacheKeys.add(filePath);
holder.imageData = bmp;
}
}
return holder;
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(Holder holder) {
super.onPostExecute(holder);
// 讀完圖片,把key移除
String filePathKey = holder.filePathKey;
fileInLoadSet.remove(filePathKey);
Bitmap data = holder.imageData;
if(data == null){
return;
}
ArrayList imageViewArrayList = getImageViewListForKey(filePathKey);
if (imageViewArrayList.size() == 0) {
return;
}
// 遍歷imageview列表,通過imageView2FileMap查找該imageView對應的最新的latestFilePathKey是不是剛剛下載好的這個filePathKey
// 只有一直才需要顯示,如果不一致,說明該imageView已經被復用,對應到了新的key
for (ImageView imageView : imageViewArrayList) {
String latestFilePathKey = imageView2FileMap.get(imageView);
if (latestFilePathKey != null && latestFilePathKey.equals(filePathKey)) {
if (imageView != null) {
imageView.setImageBitmap(data);
Log.e(TAG, "設置圖片 ");
/*
* boolean isSet;
* try{
* isSet=(Boolean)
* imageView.getTag();
* }catch(Exception e) {
* isSet=true;
* }
* if(isSet) {
* imageView.setImageBitmap(result);
* Log.e(TAG,"設置圖片 ");
* }
*/
}
// 即使不remove,也會自動回收
imageView2FileMap.remove(imageView);
} else {
}
}
file2ImageViewMap.remove(filePathKey);
}
}
class Holder {
int width,height;
String filePath, filePathKey;
Bitmap imageData;
ImageViewReference imageViewRef;
}
private String getKeyForFilePath(String imagePath, int width, int height) {
return imagePath + "_" + width + "_" + height;
}
/**
* 銷毀ImageLoader
*
* */
public void clear(){
imageView2FileMap.clear();
file2ImageViewMap.clear();
fileInLoadSet.clear();
for(String cacheKey : cacheKeys){
cache.remove(cacheKey);
}
cacheKeys.clear();
imageView2FileMap = null;
file2ImageViewMap = null;
fileInLoadSet = null;
cacheKeys = null;
downloader = null;
cache = null;
}
/**
* 銷毀ImageLoader, 應用退出的時候調用
*
* */
public void destory() {
clear();
ImageCache.destroy();
}
public interface ImageDownloader{
public Bitmap download(String path,int width, int height);
}
/**
* 通過file2ImageViewMap獲取filePath對應的所有imageView列表 同時刪除被回收的imageView,
*
* @param filePathKey
* @return
*/
private ArrayList getImageViewListForKey(String filePathKey) {
ArrayList imageViewArrayList = new ArrayList();
HashSet imageViewReferences = file2ImageViewMap.get(filePathKey);
if(imageViewReferences == null){
return null;
}
Iterator it = imageViewReferences.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
ImageViewReference reference = it.next();
if (reference.get() != null) {
imageViewArrayList.add(reference.get());
} else {
it.remove();
}
}
return imageViewArrayList;
}
/**
* 獲取指定的filePath對應的有效imageView的數量
*
* @param filePathKey
* @return
*/
private int getCountOfImageViewForKey(String filePathKey) {
ArrayList imageViewArrayList = getImageViewListForKey(filePathKey);
if(imageViewArrayList == null){
return 0;
}else{
return imageViewArrayList.size();
}
}
private static class ImageCache extends LruCache {
private static final int cacheSize = 10 * 1024 * 1024;
private static ImageCache instance = new ImageCache(cacheSize);
public static ImageCache getInstance(){
return instance;
}
private ImageCache(int maxSize) {
super(maxSize);
}
@Override
protected int sizeOf(String key, Bitmap value) {
return value.getByteCount();
}
public static void destroy(){
if(instance == null){
return;
}
instance.evictAll();
instance = null;
}
}
private static class ImageViewReference extends WeakReference {
public ImageViewReference(ImageView r) {
super(r);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
ImageViewReference other=(ImageViewReference)o;
return this.get()==other.get();
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
ImageView imageView = this.get();
if(imageView != null){
return imageView.hashCode();
}
return 0;
}
}
}
源碼在這裡:http://download.csdn.net/download/goldenfish1919/7320823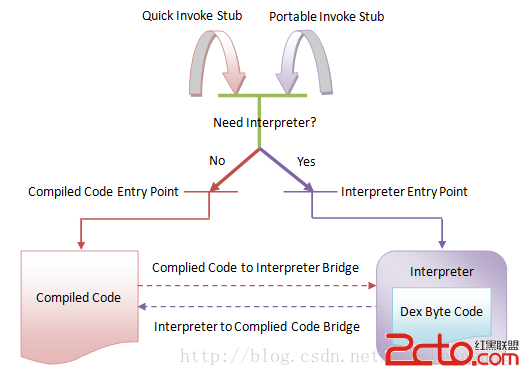 Android Art Hook 技術方案
Android Art Hook 技術方案
0x1 開始Anddroid上的ART從5.0之後變成默認的選擇,可見ART的重要性,目前關於Dalvik Hook方面研究的文章很多,但我在網上
 Android持久化技術之SharedPreferences存儲實例詳解
Android持久化技術之SharedPreferences存儲實例詳解
本文實例講述了Android持久化技術之SharedPreferences存儲。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:1、SharedPreferences存儲在前面一篇文章《
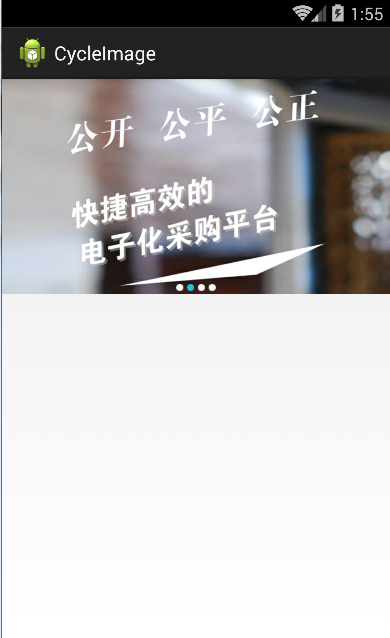 viewpager實現圖片輪番(本地圖片)
viewpager實現圖片輪番(本地圖片)
(項目中需要實現圖片輪番效果,就查資料著重學習,本地圖片實現)原理就是利用定時任務器定時切換ViewPager的頁面,根據圖片個數動態生成下端的圓點。效果圖: 1、獲取本
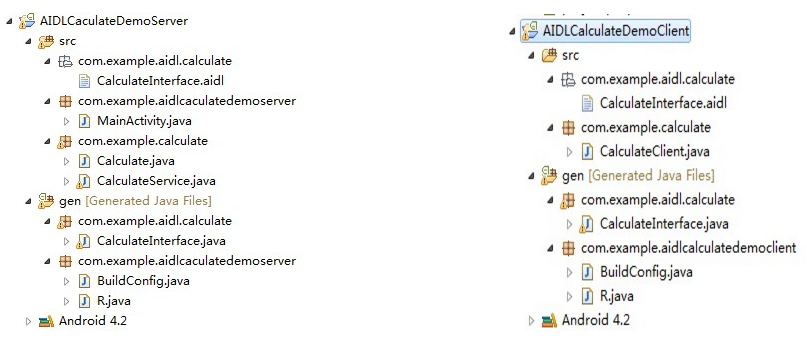 android中的AIDL進程間通信示例
android中的AIDL進程間通信示例
關於IPC應該不用多介紹了,Android系統中的進程之間不能共享內存,那麼如果兩個不同的應用程序之間需要通訊怎麼辦呢?比如公司的一個項目要更新,產品的需求是依附於當前項