編輯:關於Android編程
我們知道,android開發時少不了用到數據庫,android系統提供了輕量級的數據庫:SQLite。在你的應用開發中,如果需要用到數據庫就能使用SQLite了。為了使用的SQLite方便,Android提供了SQLite的一個工具類:SQLiteOpenHelper。如果能夠保證更好的用SQLite,你當然你可以不用這個工具類。這裡我們來看看SQLiteOpenHelper的實現。
(1)首先,SQLiteOpenHelper是一個abstract的類,所以,你不能直接用這個工具類,必須以該類為父類寫一個自己的工具類來操作自己需要的數據庫。這裡我們先後介紹兩個我們常用的兩個abstract 方法:
/**
* Called when the database is created for the first time. This is where the
* creation of tables and the initial population of the tables should happen.
*
* @param db The database.
*/
public abstract void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db);從這個方法的原文說明可以知道:onCreate 這個方法是在database第一次創建時候調用的,一般用來為這個數據庫創建我們需要用到的表以及這些表的一些初始化工作。所以,很顯然,調用這個方法時候,這個數據庫文件肯定已經創建好了。一般情況下,這個方法是我們必須要用到的。
/**
* Called when the database needs to be upgraded. The implementation
* should use this method to drop tables, add tables, or do anything else it
* needs to upgrade to the new schema version.
*
*
* The SQLite ALTER TABLE documentation can be found
* here. If you add new columns
* you can use ALTER TABLE to insert them into a live table. If you rename or remove columns
* you can use ALTER TABLE to rename the old table, then create the new table and then
* populate the new table with the contents of the old table.
*
*
* This method executes within a transaction. If an exception is thrown, all changes
* will automatically be rolled back.
*
*
* @param db The database.
* @param oldVersion The old database version.
* @param newVersion The new database version.
*/
public abstract void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion);從上面的英文說明可以知道onUpgrade這個方法主要是用於更新、更改數據庫的,一般主要用於該數據庫中表的修改。比如需要刪除一些表、添加一些表、修改表中某一項等。
(2)來看看database是如何創建的:
首先來看看他的構造方法:
public SQLiteOpenHelper(Context context, String name, CursorFactory factory, int version,
DatabaseErrorHandler errorHandler) {
if (version < 1) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Version must be >= 1, was " + version);
mContext = context;
mName = name;
mFactory = factory;
mNewVersion = version;
mErrorHandler = errorHandler;
}從這個方法可以看出,其實這個方法沒有創建database,只是做了一些信息的保存! 那database是如何創建的呢?
首先,來看看下面兩個常用的方法:
public SQLiteDatabase getReadableDatabase() {
synchronized (this) {
return getDatabaseLocked(false);
}
}
public SQLiteDatabase getWritableDatabase() {
synchronized (this) {
return getDatabaseLocked(true);
}
}這兩個方法都調用的一個方法:getDatabaseLocked(),很明顯這個函數就會返回一個SQLiteDatabase。這個方法代碼量太大,我就不一起貼出來了,其實SQLiteOpenHelper的主要工作就這這個方法裡面。這個方法主要是獲取這個SQLiteDatabase,如果當前還沒有這個SQLiteDatabase實例,就會創建一個新的,此外還同時會檢測這個SQLiteDatabase實例的版本號和當前這個SQLiteOpenHelper所設置的版本號是否相等,否則就會做相應的升級(調用onUpgrade、onDowngrade來實現)。
這裡我們只貼出這個方法裡面創建數據庫的幾行代碼:
if (DEBUG_STRICT_READONLY && !writable) {
final String path = mContext.getDatabasePath(mName).getPath();
db = SQLiteDatabase.openDatabase(path, mFactory,
SQLiteDatabase.OPEN_READONLY, mErrorHandler);
} else {
db = mContext.openOrCreateDatabase(mName, mEnableWriteAheadLogging ?
Context.MODE_ENABLE_WRITE_AHEAD_LOGGING : 0,
mFactory, mErrorHandler);
}這裡我們關注的是mContext,其實創建一數據庫最後是來自這mContext的。這裡的mContext的兩個方法getDatabasePath和openOrCreateDatabase其實都是可能會創建一個數據庫文件的,我們來看看mContext中兩個方法:
@Override
public File getDatabasePath(String name) {
return validateFilePath(name, false);
}
public SQLiteDatabase openOrCreateDatabase(String name, int mode, CursorFactory factory,
DatabaseErrorHandler errorHandler) {
File f = validateFilePath(name, true);
int flags = SQLiteDatabase.CREATE_IF_NECESSARY;
if ((mode & MODE_ENABLE_WRITE_AHEAD_LOGGING) != 0) {
flags |= SQLiteDatabase.ENABLE_WRITE_AHEAD_LOGGING;
}
SQLiteDatabase db = SQLiteDatabase.openDatabase(f.getPath(), factory, flags, errorHandler);
setFilePermissionsFromMode(f.getPath(), mode, 0);
return db;
}看到了嗎?其實都會調用一個函數validateFilePath();
private File validateFilePath(String name, boolean createDirectory) {
File dir;
File f;
if (name.charAt(0) == File.separatorChar) {
String dirPath = name.substring(0, name.lastIndexOf(File.separatorChar));
dir = new File(dirPath);
name = name.substring(name.lastIndexOf(File.separatorChar));
f = new File(dir, name);
} else {
dir = getDatabasesDir();
f = makeFilename(dir, name);
}
if (createDirectory && !dir.isDirectory() && dir.mkdir()) {
FileUtils.setPermissions(dir.getPath(),
FileUtils.S_IRWXU|FileUtils.S_IRWXG|FileUtils.S_IXOTH,
-1, -1);
}
return f;
}看到了嗎?其實就是創建一個數據庫文件new File(base, name)、new File(dirPath)。
(3)我們的關注點來到了Context,在Context裡面還有幾個方法:
@Override
public boolean deleteDatabase(String name) {
try {
File f = validateFilePath(name, false);
return SQLiteDatabase.deleteDatabase(f);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
return false;
}
@Override
public File getDatabasePath(String name) {
return validateFilePath(name, false);
}從上面分析可以知道在android中,實際上數據庫SQLite的起源是Context ,其實也只是創建數據庫、刪除數據庫、已經獲取數據庫文件路徑等。而android提供的工具SQLiteOpenHelper只是方便我們使用! 我們知道Context 其實是app的activity、service的起源,所以一個數據庫實例其實是屬於一個APP的,也是這個APP管理的。
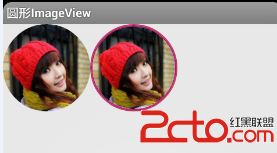 Android圓形圖片--自定義控件
Android圓形圖片--自定義控件
Android圓形圖片控件效果圖如下: 代碼如下: RoundImageView.java package com.dxd.roundimageview; imp
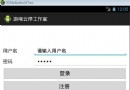 .Net程序員玩轉Android開發---(3)登陸頁面布局
.Net程序員玩轉Android開發---(3)登陸頁面布局
這一節我們來看看登陸頁面怎樣布局,對於剛接觸到Android開發的童鞋來說,Android的布局感覺比較棘手,需要結合各種屬性進行設置,接下來我們由點入面來 了解安卓中頁
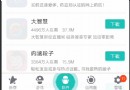 Android實現360手機助手底部的動畫菜單
Android實現360手機助手底部的動畫菜單
首先來看下我們實現的效果和360效果的對比:360手機助手效果演示本庫實現的效果(Icon來自360手機助手,侵刪)xml布局文件注:為了美觀,講每個Button的高度以
 【騰訊TMQ】5小時搞定谷歌原生自動化框架UiAutomator1.0
【騰訊TMQ】5小時搞定谷歌原生自動化框架UiAutomator1.0
前言谷歌對UI測試(UI Tetsting)的概念是:確保用戶在一系列操作過程中(例如鍵盤輸入、點擊菜單、彈出對話框、圖像顯示以及其他UI控件的改變),你的應用程序做出正