編輯:關於Android編程
小結:
對比項 顯示清晰度 占用內存 支持縮放 支持色相色差調整 支持旋轉 支持透明色 繪制速度 支持像素操作
Bitmap 相同 大 是 是 是 是 慢 是
Drawable 相同 小 是 否 是 是 快 否
Drawable在內存占用和繪制速度這兩個非常關鍵的點上勝過Bitmap
//轉換Bitmap to Drawable
Bitmap bitmap = new Bitmap (...);
Drawable drawable = new BitmapDrawable(bitmap);
//轉換Drawable to Bitmap
Drawable d = ImagesList.get(0);
Bitmap bitmap = ((BitmapDrawable)d).getBitmap();
//1、Drawable → Bitmap
public static Bitmap drawableToBitmap(Drawable drawable) {
Bitmap bitmap = Bitmap
.createBitmap(
drawable.getIntrinsicWidth(),
drawable.getIntrinsicHeight(),
drawable.getOpacity() != PixelFormat.OPAQUE ? Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888
: Bitmap.Config.RGB_565);
Canvas canvas = new Canvas(bitmap);
//canvas.setBitmap(bitmap);
drawable.setBounds(0, 0, drawable.getIntrinsicWidth(), drawable.getIntrinsicHeight());
drawable.draw(canvas);
return bitmap;
}
//2、從資源中獲取Bitmap
Resources res=getResources();
Bitmap bmp=BitmapFactory.decodeResource(res, R.drawable.pic);
//3、Bitmap → byte[]
private byte[] Bitmap2Bytes(Bitmap bm){
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
bm.compress(Bitmap.CompressFormat.PNG, 100, baos);
return baos.toByteArray();
}
//4、 byte[] → Bitmap
private Bitmap Bytes2Bimap(byte[] b){
if(b.length!=0){
return BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(b, 0, b.length);
}
else {
return null;
}
}
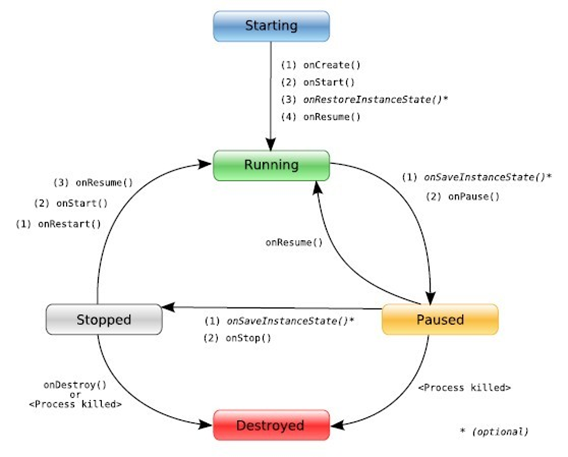 Android學習筆記四之Activity
Android學習筆記四之Activity
1、什麼是ActivityActivity是Android四大組件之一,用於顯示View。Activity是一個應用程序組件,提供一個用戶交互的接口,其本身是沒有界面的,
 qq空間打賞功能是什麼 qq空間打賞紅包有什麼用
qq空間打賞功能是什麼 qq空間打賞紅包有什麼用
qq空間現在也可以打賞紅包啦啦!據了解,QQ空間打賞紅包在上個月QQ6.5版中就有了,現在打賞的最高金額是200元!那麼晚qq空間打賞功能是什麼?qq空間打
 Android adb logcat 命令查看日志詳細介紹
Android adb logcat 命令查看日志詳細介紹
Android 開發的程序員開發程序的時候,一定為log而苦惱過吧。Eclipse老是Log找不到,是不是很讓人不爽,雖然Android Studio的Logcat功能很
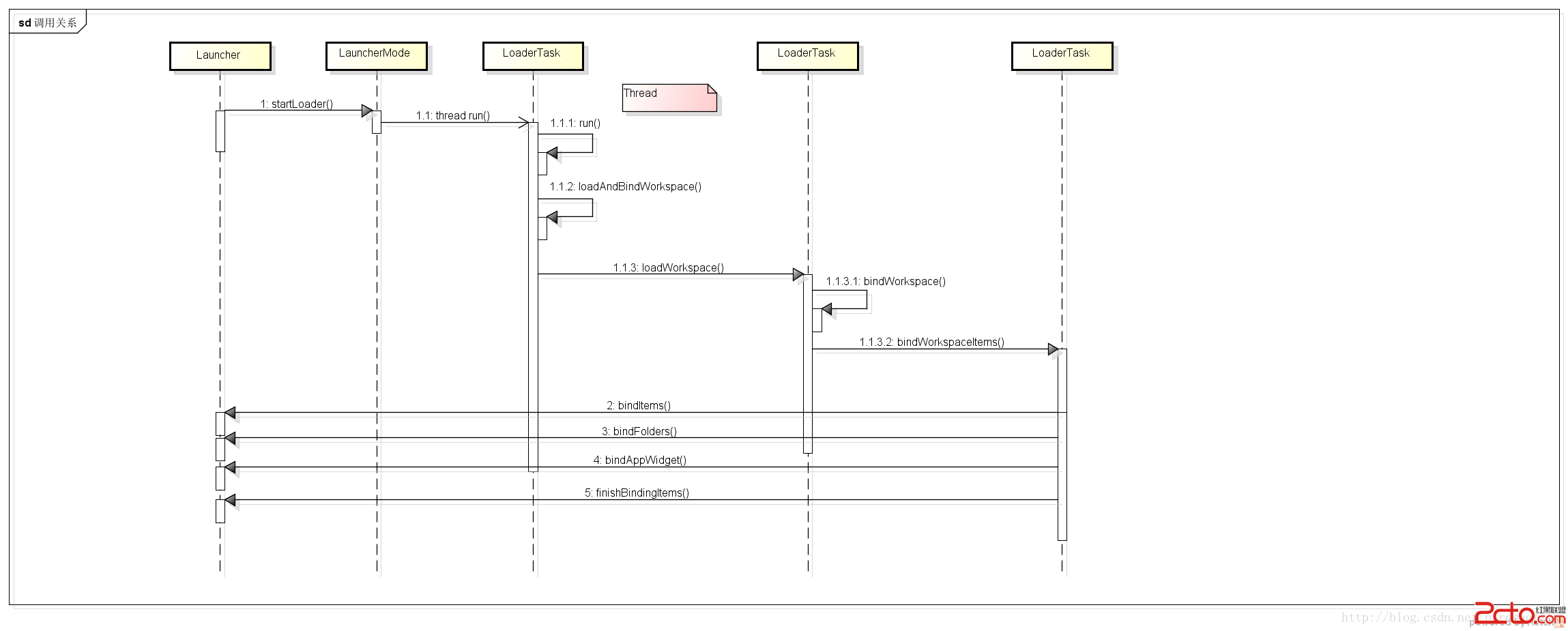 Android Launcher源碼研究(三) 加載app流程2
Android Launcher源碼研究(三) 加載app流程2
接上次的。 首先Launcher實現了LauncherModel.Callbacks接口,APP信息數據加載成功後 ,回調接口把app信息顯示到Launcher的 wor
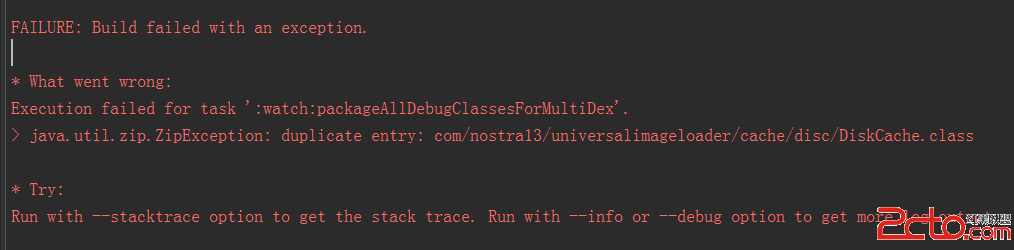 我的Android進階之旅------)Android編譯錯誤java.util.zip.ZipException: duplicate entry的解決方法
我的Android進階之旅------)Android編譯錯誤java.util.zip.ZipException: duplicate entry的解決方法
今天在Android Studio中把另外一個項目引入當前項目,編譯的時