編輯:關於Android編程
Android Service
Android Serivce is called by Activity or Context.
Two ways to start it,
1) start service directly
Intent intent = new Intent(ActivityA.this, ServiceA.class); startService(intent);
onCreate -> onStart -> onDestroy
If exit the application and not call the method onStop, the service will run on the backgroud forever.
2) bind service
If the service does not start, onCreate -> onDestory.
If the service starts, the activity will bind the service and do not call onCreate again. When exit the application, it should unbind the service.
public class ServiceA extends Service {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Toast.makeText(this, "Service onCreate", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return new LocalBinder();
}
public class LocalBinder extends Binder {
public ServiceA getService() {
return ServiceA.this;
}
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Received start id " + startId + ": " + intent,
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return START_STICKY;
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Toast.makeText(this, "Service onDestory", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
public void doSomething() {
Toast.makeText(this, "Service do something", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
package com.example.servicetest;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
private Button bindServiceBtn;
private Button unbindServiceBtn;
private boolean mIsBound = false;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initViews();
}
private void initViews() {
bindServiceBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button_bindservice);
bindServiceBtn.setOnClickListener(this);
unbindServiceBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button_unbindservice);
unbindServiceBtn.setOnClickListener(this);
unbindServiceBtn.setEnabled(false);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
int viewId = view.getId();
switch (viewId) {
case R.id.button_bindservice:
doBindService();
break;
case R.id.button_unbindservice:
doUnbindService();
break;
}
}
private ServiceA mBoundService;
private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "This service connected",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
// This is called when the connection with the service has been
// established, giving us the service object we can use to
// interact with the service. Because we have bound to a explicit
// service that we know is running in our own process, we can
// cast its IBinder to a concrete class and directly access it.
mBoundService = ((ServiceA.LocalBinder) service).getService();
if (mBoundService != null) {
mBoundService.doSomething();
}
}
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName className) {
// This is called when the connection with the service has been
// unexpectedly disconnected -- that is, its process crashed.
// Because it is running in our same process, we should never
// see this happen.
mBoundService = null;
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Thi service disconnected unexpectedly",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
unbindServiceBtn.setEnabled(false);
}
};
void doBindService() {
// Establish a connection with the service. We use an explicit
// class name because we want a specific service implementation that
// we know will be running in our own process (and thus won't be
// supporting component replacement by other applications).
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Begin to bind a service.",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
bindService(new Intent(MainActivity.this, ServiceA.class), mConnection,
Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
mIsBound = true;
unbindServiceBtn.setEnabled(true);
}
void doUnbindService() {
if (mIsBound) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Begin to unbind a service.",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
unbindService(mConnection);
mIsBound = false;
unbindServiceBtn.setEnabled(false);
}
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
stopService(new Intent(MainActivity.this, ServiceA.class));
}
}
 無視數量限制 微信傳圖多少隨你而定
無視數量限制 微信傳圖多少隨你而定
雖然QQ的功能更多,但越來越多的用戶都習慣使用微信作為聊天和分享的工具。問題來了,在我們用微信給好友傳圖時總有最多9張的數量限制,如何才能破解這個限制呢?令
 android:ScrollView監視什麼時候滑到底部
android:ScrollView監視什麼時候滑到底部
這是效果主要是onTouchListener監聽事件,監視什麼時候滑到底部同時要理解getMeasuredHeight和getHeight的區別getMeasuredHe
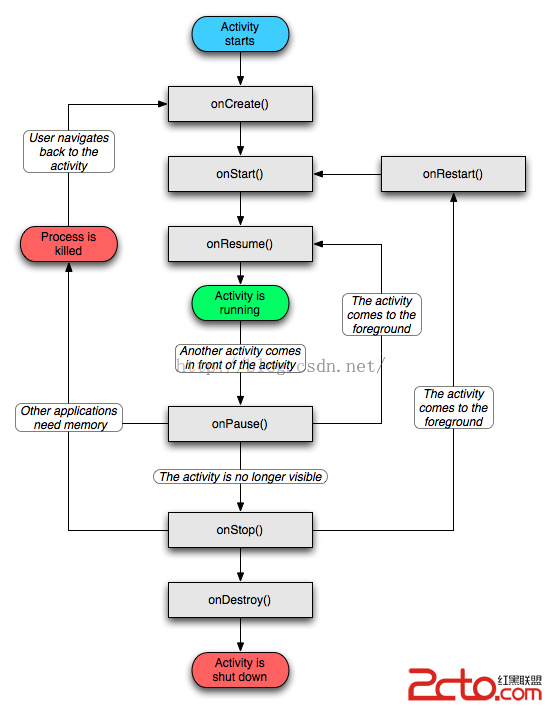 Android的生命周期
Android的生命周期
Activity的生命周期圖2 Android生命周期中涉及到的幾個過程 1.啟動Activity:系統會先調用onCreate方法,然後調用onStart方法,最後
 Android百度地圖應用開發基礎知識
Android百度地圖應用開發基礎知識
一、概述 這一章先來點有意思的百度地圖應用示例,然後再分章詳細介紹用C#開發Android App的各種基本技術。 本章以百度官網2016年1月發布的