編輯:關於Android編程
一、可以利用如下命令
bash -x ndk-build根據調試信息來分析
二、
PROGDIR=`dirname $0`
PROGDIR=`cd $PROGDIR && pwd`
# Check if absolute NDK path contain space
#
case $PROGDIR in
*\ *) echo "ERROR: NDK path cannot contain space"
exit 1
;;
esac
# If NDK_LOG is set to 1 or true in the environment, or the command-line
# then enable log messages below
# Also normalize NDK_HOST_32BIT and NDK_ANALYZE to 1 or 0
if [ -z "$NDK_LOG" ]; then
NDK_LOG=0
fi
if [ -z "$NDK_HOST_32BIT" ]; then
NDK_HOST_32BIT=0
fi
if [ -z "$NDK_ANALYZE" ]; then
NDK_ANALYZE=0
fiPROGDIR為/home/jltxgcy/android-ndk-r8e
然後檢查這個目錄是否有空格
如果下面的變量長度為0,則都賦值為0
PROJECT_PATH=
PROJECT_PATH_NEXT=
for opt; do
if [ -z "$PROJECT_PATH" -a "$PROJECT_PATH_NEXT" = "yes" ] ; then
PROJECT_PATH=$opt
PROJECT_PATH_NEXT=
else
case $opt in
NDK_LOG=1|NDK_LOG=true)
NDK_LOG=1
;;
NDK_LOG=*)
NDK_LOG=0
;;
NDK_HOST_32BIT=1|NDK_HOST_32BIT=true)
NDK_HOST_32BIT=1
;;
NDK_HOST_32BIT=*)
NDK_HOST_32BIT=0
;;
NDK_ANALYZE=1|NDK_ANALYZE=true)
NDK_ANALYZE=1
;;
NDK_ANALYZE=*)
NDK_ANALYZE=0
;;
NDK_TOOLCHAIN_VERSION=*)
NDK_TOOLCHAIN_VERSION=${opt#NDK_TOOLCHAIN_VERSION=}
;;
APP_ABI=*)
APP_ABI=${opt#APP_ABI=}
;;
-C)
PROJECT_PATH_NEXT="yes"
;;
esac
fi
done此段代碼沒有執行,暫不分析
if [ "$NDK_LOG" = "true" ]; then
NDK_LOG=1
fi
if [ "$NDK_HOST_32BIT" = "true" ]; then
NDK_HOST_32BIT=1
fi
if [ "$NDK_ANALYZE" = "true" ]; then
NDK_ANALYZE=1
fi
if [ "$NDK_LOG" = "1" ]; then
log () {
echo "$@"
}
else
log () {
: # nothing
}
fi此段代碼均為假,不執行
# Detect host operating system and architecture
# The 64-bit / 32-bit distinction gets tricky on Linux and Darwin because
# uname -m returns the kernel's bit size, and it's possible to run with
# a 64-bit kernel and a 32-bit userland.
#
HOST_OS=$(uname -s)
case $HOST_OS in
Darwin) HOST_OS=darwin;;
Linux) HOST_OS=linux;;
FreeBsd) HOST_OS=freebsd;;
CYGWIN*|*_NT-*) HOST_OS=cygwin;;
*) echo "ERROR: Unknown host operating system: $HOST_OS"
exit 1
esac
log "HOST_OS=$HOST_OS"
HOST_OS為Linux,所以HOST_OS為linux
HOST_ARCH=$(uname -m)
case $HOST_ARCH in
i?86) HOST_ARCH=x86;;
x86_64|amd64) HOST_ARCH=x86_64;;
*) echo "ERROR: Unknown host CPU architecture: $HOST_ARCH"
exit 1
esac
log "HOST_ARCH=$HOST_ARCH"
HOST_ARCH為x86_64
# Detect 32-bit userland on 64-bit kernels
HOST_TAG="$HOST_OS-$HOST_ARCH"
case $HOST_TAG in
linux-x86_64|darwin-x86_64)
# we look for x86_64 or x86-64 in the output of 'file' for our shell
# the -L flag is used to dereference symlinks, just in case.
file -L "$SHELL" | grep -q "x86[_-]64"
if [ $? != 0 ]; then
HOST_ARCH=x86
log "HOST_ARCH=$HOST_ARCH (32-bit userland detected)"
fi
;;
esac
# Check that we have 64-bit binaries on 64-bit system, otherwise fallback
# on 32-bit ones. This gives us more freedom in packaging the NDK.
LOG_MESSAGE=
if [ $HOST_ARCH = x86_64 ]; then
if [ ! -d $PROGDIR/prebuilt/$HOST_TAG ]; then
HOST_ARCH=x86
LOG_MESSAGE="(no 64-bit prebuilt binaries detected)"
fi
if [ "$NDK_HOST_32BIT" = "1" ]; then
HOST_ARCH=x86
LOG_MESSAGE="(force 32-bit host toolchain)"
fi
fi
# If GNUMAKE is defined, check that it points to a valid file
if [ -n "$GNUMAKE" ] ; then
ABS_GNUMAKE=`which $GNUMAKE 2> /dev/null`
if [ $? != 0 ] ; then
echo "ERROR: Your GNUMAKE variable is defined to an invalid name: $GNUMAKE"
echo "Please fix it to point to a valid make executable (e.g. /usr/bin/make)"
exit 1
fi
GNUMAKE="$ABS_GNUMAKE"
log "GNUMAKE=$GNUMAKE (from environment variable)"
else
# Otherwise use the prebuilt version for our host tag, if it exists
# Note: we intentionally do not provide prebuilt make binaries for Cygwin
# or MSys.
GNUMAKE=$PROGDIR/prebuilt/$HOST_TAG/bin/make
if [ ! -f "$GNUMAKE" ]; then
# Otherwise, use 'make' and check that it is available
GNUMAKE=`which make 2> /dev/null`
if [ $? != 0 ] ; then
echo "ERROR: Cannot find 'make' program. Please install Cygwin make package"
echo "or define the GNUMAKE variable to point to it."
exit 1
fi
log "GNUMAKE=$GNUMAKE (system path)"
else
log "GNUMAKE=$GNUMAKE (NDK prebuilt)"
fi
fi
# On Windows, when running under cygwin, check that we are
# invoking a cygwin-compatible GNU Make binary. It is unfortunately
# common for app developers to have another non cygwin-compatible
# 'make' program in their PATH.
#
if [ "$OSTYPE" = "cygwin" ] ; then
GNUMAKE=`cygpath -u $GNUMAKE`
PROGDIR_MIXED=`cygpath -m $PROGDIR`
CYGWIN_GNUMAKE=`$GNUMAKE -f "$PROGDIR_MIXED/build/core/check-cygwin-make.mk" 2>&1`
if [ $? != 0 ] ; then
echo "ERROR: You are using a non-Cygwin compatible Make program."
echo "Currently using: `cygpath -m $GNUMAKE`"
echo ""
echo "To solve the issue, follow these steps:"
echo ""
echo "1. Ensure that the Cygwin 'make' package is installed."
echo " NOTE: You will need GNU Make 3.81 or later!"
echo ""
echo "2. Define the GNUMAKE environment variable to point to it, as in:"
echo ""
echo " export GNUMAKE=/usr/bin/make"
echo ""
echo "3. Call 'ndk-build' again."
echo ""
exit 1
fi
log "Cygwin-compatible GNU make detected"
fi
if [ "$NDK_ANALYZE" = 1 ]; then
. $PROGDIR/build/tools/dev-defaults.sh # for DEFAULT_LLVM_VERSION
# Find perl. If HOST_PERL is defined, check that it points to a valid file
HOST_PERL_LIB=
if [ -n "$HOST_PERL" ] ; then
ABS_PERL=`which $HOST_PERL 2> /dev/null`
if [ $? != 0 ] ; then
echo "ERROR: Your HOST_PERL variable is defined to an invalid name: $HOST_PERL"
echo "Please fix it to point to a valid perl executable (e.g. /usr/bin/perl)"
exit 1
fi
HOST_PERL="$ABS_PERL"
log "HOST_PERL=$HOST_PERL (from environment variable)"
else
# Otherwise use the prebuilt version for our host tag
HOST_PERL="$PROGDIR/prebuilt/$HOST_TAG/bin/perl"
if [ ! -f "$HOST_PERL" ]; then
# Otherwise, use 'perl' and check that it is available
HOST_PERL=`which perl 2> /dev/null`
if [ $? != 0 ] ; then
echo "ERROR: Cannot find 'perl' program. Please install perl package"
echo "or define the HOST_PERL variable to point to it."
exit 1
fi
log "HOST_PERL=$HOST_PERL (system path)"
else
HOST_PERL_LIB="$PROGDIR/prebuilt/$HOST_TAG/lib/perl5"
log "HOST_PERL=$HOST_PERL (NDK prebuilt)"
fi
fi
# Return flags send in env. or command line which are enough to retrive APP_ABI and TOOLCHAIN_PREFIX later
gen_flags ()
{
local FLAGS=
if [ -n "$PROJECT_PATH" ] ; then
FLAGS=$FLAGS" -C $PROJECT_PATH"
fi
if [ -n "$APP_ABI" ] ; then
FLAGS=$FLAGS" APP_ABI=$APP_ABI"
fi
if [ -n "$NDK_HOST_32BIT" ] ; then
FLAGS=$FLAGS" NDK_HOST_32BIT=$NDK_HOST_32BIT"
fi
if [ -n "$NDK_TOOLCHAIN_VERSION" ] ; then
FLAGS=$FLAGS" NDK_TOOLCHAIN_VERSION=$NDK_TOOLCHAIN_VERSION"
fi
echo "$FLAGS"
}
get_build_var ()
{
local VAR=$1
local FLAGS=`gen_flags`
$GNUMAKE --no-print-dir -f $PROGDIR/build/core/build-local.mk $FLAGS DUMP_${VAR} | tail -1
}
get_build_var_for_abi ()
{
local VAR=$1
local ABI=$2
local FLAGS=`gen_flags`
$GNUMAKE --no-print-dir -f $PROGDIR/build/core/build-local.mk $FLAGS DUMP_${VAR} APP_ABI=${ABI} | tail -1
}
APP_ABIS=`get_build_var APP_ABI`
for ABI in $APP_ABIS; do
TOOLCHAIN_PREFIX=`get_build_var_for_abi TOOLCHAIN_PREFIX $ABI`
PERL5LIB="$HOST_PERL_LIB" "$HOST_PERL" $PROGDIR/prebuilt/common/scan-build/scan-build \
--use-analyzer $PROGDIR/toolchains/llvm-${DEFAULT_LLVM_VERSION}/prebuilt/$HOST_TAG/bin/${ABI}/analyzer \
--use-cc ${TOOLCHAIN_PREFIX}gcc \
--use-c++ ${TOOLCHAIN_PREFIX}g++ \
--status-bugs -v -v \
$GNUMAKE -f $PROGDIR/build/core/build-local.mk "$@" APP_ABI=$ABI
done
else
$GNUMAKE -f $PROGDIR/build/core/build-local.mk "$@"
fi
 Android應用中繪制圓形頭像的方法解析
Android應用中繪制圓形頭像的方法解析
要畫這種圓形帶陰影的頭像,個人分解成三個圖層1,先畫頭像邊緣的漸變RadialGradient gradient = new RadialGradient(j/2,k/2
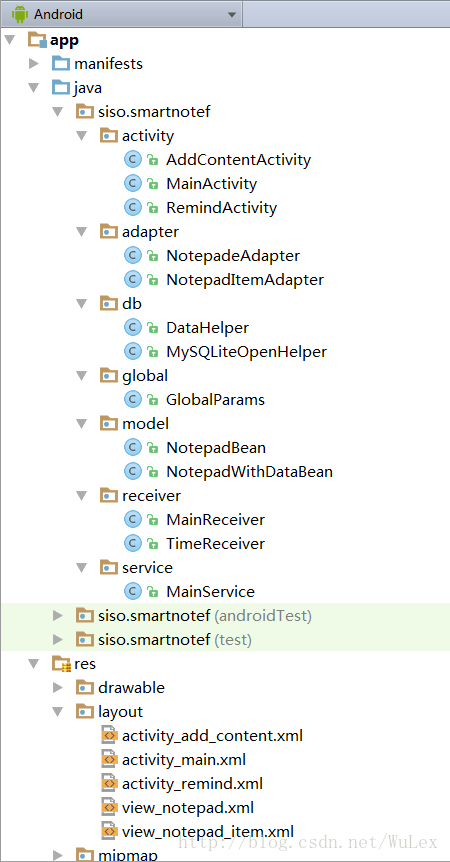 Android實現記事本功能(26)
Android實現記事本功能(26)
本文實例為大家分享了Android實現記事本功能的具體代碼,供大家參考,具體內容如下MainActivity.java代碼:package siso.smartnotef
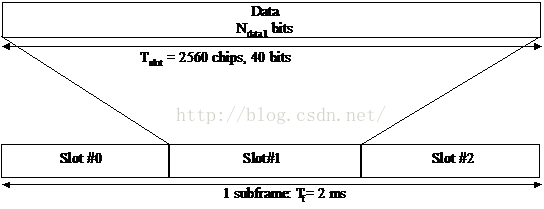 HSDPA學習小結
HSDPA學習小結
1 HSDPA 簡介HSDPA中引入的HS-DSCH棄用了R99中的功率控制技術、軟切換技術和可變擴頻增益技術。同時引入了一系列關鍵技術:1) 更短的無線幀結構;(2ms
 Android實現圖片多點觸控自由伸縮
Android實現圖片多點觸控自由伸縮
簡介作為Android開發者,我們經常需要自定義控件,比如下面我們說的實現圖片的多點觸控和伸縮釋放,這也是由於用戶已經有這樣的常識了,那就是看見有圖片的地方就可以點擊查看