編輯:關於Android編程
android.hardware.Camera
The Camera class is used to set image capture settings, start/stop preview, snap pictures, and retrieve frames for encoding for video. This class is a client for the Camera service, which manages the actual camera hardware.
權限AndroidManifest.xml:
下面寫上:
如果涉及到存儲,則還應當添加:
To take pictures with this class, use the following steps:
獲取個Camera實例open(int).獲取已經存在(默認)的設置 getParameters().如果必要,可以修改返回的 Camera.Parameters 對象 and 調用setParameters(Camera.Parameters).如果需要,也可以調用 setDisplayOrientation(int).重要: 傳遞一個完全初始化後的 SurfaceHolder 到setPreviewDisplay(SurfaceHolder). Without a surface, the camera will be unable to start the preview.重要: 調用startPreview() 更新預覽界面,預覽必須在你拍照之前啟動。 當你想要的時候,調用takePicture(Camera.ShutterCallback, Camera.PictureCallback, Camera.PictureCallback, Camera.PictureCallback) 來捕獲一張照片.等待 回調函數提供實際的圖像數據。 照完之後,預覽顯示將會停止。如果想照更多的照片,請再次調用 startPreview() .調用 stopPreview() 來通知更新預覽界面。重要: 調用release() 來釋放相機,讓其他應用程序使用. 應用程序應該用onPause() (and re-open() it inonResume())來立即釋放相機.
To quickly switch to video recording mode, use these steps:
Obtain and initialize a Camera and start preview as described above. Callunlock() to allow the media process to access the camera.Pass the camera to setCamera(Camera). SeeMediaRecorder information about video recording.When finished recording, call reconnect() to re-acquire and re-lock the camera.If desired, restart preview and take more photos or videos. Call stopPreview() andrelease() as described above.
This class is not thread-safe, and is meant for use from one event thread. Most long-running operations (preview, focus, photo capture, etc) happen asynchronously and invoke callbacks as necessary. Callbacks will be invoked on the event thread open(int) was called from. This class's methods must never be called from multiple threads at once.
這個類不是線程安全的,並且是供一個事件線程使用。最長時間運行的操作(預覽,對焦,照片拍攝等)發生 異步調用的回調是必要的。回調將在事件線程open(int)被調用後被調用。這個類的方法,絕不能從多個線程立即調用。
Caution: Different Android-powered devices may have different hardware specifications, such as megapixel ratings and auto-focus capabilities. In order for your application to be compatible with more devices, you should not make assumptions about the device camera specifications.
注意:不同版本的Android手機可能有不同的硬件規格,如像素的分級和自動對焦功能。為了讓您的應用程序能與更多的設備兼容,你不應該做出有關該設備的攝像頭規格的假設。
Enable or disable the default shutter sound when taking a picture.拍攝時啟用或禁用默認的快門聲。
Installs a callback to be invoked for the next preview frame in addition to displaying it on the screen.
Installs a callback to be invoked for every preview frame in addition to displaying them on the screen.
Installs a callback to be invoked for every preview frame, using buffers supplied with addCallbackBuffer(byte[]), in addition to displaying them on the screen.
Surface to be used for live preview.
SurfaceTexture to be used for live preview.
startPreview().
Broadcast Action: A new picture is taken by the camera, and the entry of the picture has been added to the media store. getData() is URI of the picture.
Broadcast Action: A new video is recorded by the camera, and the entry of the video has been added to the media store. getData() is URI of the video.
Media server died. In this case, the application must release the Camera object and instantiate a new one.
Camera.ErrorCallback Constant Value: 100 (0x00000064)
Unspecified camera error.
Camera.ErrorCallback Constant Value: 1 (0x00000001)
Adds a pre-allocated buffer to the preview callback buffer queue. Applications can add one or more buffers to the queue. When a preview frame arrives and there is still at least one available buffer, the buffer will be used and removed from the queue. Then preview callback is invoked with the buffer. If a frame arrives and there is no buffer left, the frame is discarded. Applications should add buffers back when they finish processing the data in them.
For formats besides YV12, the size of the buffer is determined by multiplying the preview image width, height, and bytes per pixel. The width and height can be read from getPreviewSize(). Bytes per pixel can be computed from getBitsPerPixel(int) / 8, using the image format from getPreviewFormat().
If using the YV12 format, the size can be calculated using the equations listed in setPreviewFormat(int).
This method is only necessary when setPreviewCallbackWithBuffer(PreviewCallback) is used. When setPreviewCallback(PreviewCallback) or setOneShotPreviewCallback(PreviewCallback) are used, buffers are automatically allocated. When a supplied buffer is too small to hold the preview frame data, preview callback will return null and the buffer will be removed from the buffer queue.
setPreviewCallbackWithBuffer(PreviewCallback)
Starts camera auto-focus and registers a callback function to run when the camera is focused. This method is only valid when preview is active (between startPreview() and before stopPreview()).
Callers should check getFocusMode() to determine if this method should be called. If the camera does not support auto-focus, it is a no-op and onAutoFocus(boolean, Camera) callback will be called immediately.
If your application should not be installed on devices without auto-focus, you must declare that your application uses auto-focus with the
If the current flash mode is not FLASH_MODE_OFF, flash may be fired during auto-focus, depending on the driver and camera hardware.
Auto-exposure lock getAutoExposureLock() and auto-white balance locks getAutoWhiteBalanceLock() do not change during and after autofocus. But auto-focus routine may stop auto-exposure and auto-white balance transiently during focusing.
Stopping preview with stopPreview(), or triggering still image capture with takePicture(Camera.ShutterCallback, Camera.PictureCallback, Camera.PictureCallback), will not change the the focus position. Applications must call cancelAutoFocus to reset the focus.
If autofocus is successful, consider using MediaActionSound to properly play back an autofocus success sound to the user.
cancelAutoFocus()setAutoExposureLock(boolean)setAutoWhiteBalanceLock(boolean)MediaActionSound
Cancels any auto-focus function in progress. Whether or not auto-focus is currently in progress, this function will return the focus position to the default. If the camera does not support auto-focus, this is a no-op.
autoFocus(Camera.AutoFocusCallback)
Enable or disable the default shutter sound when taking a picture.
By default, the camera plays the system-defined camera shutter sound when takePicture(Camera.ShutterCallback, Camera.PictureCallback, Camera.PictureCallback) is called. Using this method, the shutter sound can be disabled. It is strongly recommended that an alternative shutter sound is played in the Camera.ShutterCallback when the system shutter sound is disabled.
Note that devices may not always allow disabling the camera shutter sound. If the shutter sound state cannot be set to the desired value, this method will return false. canDisableShutterSound can be used to determine whether the device will allow the shutter sound to be disabled.
takePicture is called.
true if the shutter sound state was successfully changed. false if the shutter sound state could not be changed. true is also returned if shutter sound playback is already set to the requested state.
takePicture(Camera.ShutterCallback, Camera.PictureCallback, Camera.PictureCallback)canDisableShutterSoundCamera.ShutterCallback
Returns the information about a particular camera. If getNumberOfCameras() returns N, the valid id is 0 to N-1.
Returns the number of physical cameras available on this device.
Returns the current settings for this Camera service. If modifications are made to the returned Parameters, they must be passed to setParameters(Camera.Parameters) to take effect.
setParameters(Camera.Parameters)
Re-locks the camera to prevent other processes from accessing it. Camera objects are locked by default unless unlock() is called. Normally reconnect() is used instead.
Since API level 14, camera is automatically locked for applications in start(). Applications can use the camera (ex: zoom) after recording starts. There is no need to call this after recording starts or stops.
If you are not recording video, you probably do not need this method.
Creates a new Camera object to access a particular hardware camera. If the same camera is opened by other applications, this will throw a RuntimeException.
You must call release() when you are done using the camera, otherwise it will remain locked and be unavailable to other applications.
Your application should only have one Camera object active at a time for a particular hardware camera.
Callbacks from other methods are delivered to the event loop of the thread which called open(). If this thread has no event loop, then callbacks are delivered to the main application event loop. If there is no main application event loop, callbacks are not delivered.
Caution: On some devices, this method may take a long time to complete. It is best to call this method from a worker thread (possibly using AsyncTask) to avoid blocking the main application UI thread.
getNumberOfCameras()-1.
getCameraDisabled(android.content.ComponentName)
Creates a new Camera object to access the first back-facing camera on the device. If the device does not have a back-facing camera, this returns null.
open(int)
Reconnects to the camera service after another process used it. After unlock() is called, another process may use the camera; when the process is done, you must reconnect to the camera, which will re-acquire the lock and allow you to continue using the camera.
Since API level 14, camera is automatically locked for applications in start(). Applications can use the camera (ex: zoom) after recording starts. There is no need to call this after recording starts or stops.
If you are not recording video, you probably do not need this method.
Disconnects and releases the Camera object resources.
You must call this as soon as you're done with the Camera object.
Sets camera auto-focus move callback.
Set the clockwise rotation of preview display in degrees. This affects the preview frames and the picture displayed after snapshot. This method is useful for portrait mode applications. Note that preview display of front-facing cameras is flipped horizontally before the rotation, that is, the image is reflected along the central vertical axis of the camera sensor. So the users can see themselves as looking into a mirror.
This does not affect the order of byte array passed in onPreviewFrame(byte[], Camera), JPEG pictures, or recorded videos. This method is not allowed to be called during preview.
If you want to make the camera image show in the same orientation as the display, you can use the following code.
public static void setCameraDisplayOrientation(Activity activity,
int cameraId, android.hardware.Camera camera) {
android.hardware.Camera.CameraInfo info =
new android.hardware.Camera.CameraInfo();
android.hardware.Camera.getCameraInfo(cameraId, info);
int rotation = activity.getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay()
.getRotation();
int degrees = 0;
switch (rotation) {
case Surface.ROTATION_0: degrees = 0; break;
case Surface.ROTATION_90: degrees = 90; break;
case Surface.ROTATION_180: degrees = 180; break;
case Surface.ROTATION_270: degrees = 270; break;
}
int result;
if (info.facing == Camera.CameraInfo.CAMERA_FACING_FRONT) {
result = (info.orientation + degrees) % 360;
result = (360 - result) % 360; // compensate the mirror
} else { // back-facing
result = (info.orientation - degrees + 360) % 360;
}
camera.setDisplayOrientation(result);
}
Starting from API level 14, this method can be called when preview is active.
setPreviewDisplay(SurfaceHolder)
Registers a callback to be invoked when an error occurs.
Registers a listener to be notified about the faces detected in the preview frame.
startFaceDetection()
Installs a callback to be invoked for the next preview frame in addition to displaying it on the screen. After one invocation, the callback is cleared. This method can be called any time, even when preview is live. Any other preview callbacks are overridden.
If you are using the preview data to create video or still images, strongly consider using MediaActionSound to properly indicate image capture or recording start/stop to the user.
MediaActionSound
Changes the settings for this Camera service.
getParameters()
Installs a callback to be invoked for every preview frame in addition to displaying them on the screen. The callback will be repeatedly called for as long as preview is active. This method can be called at any time, even while preview is live. Any other preview callbacks are overridden.
If you are using the preview data to create video or still images, strongly consider using MediaActionSound to properly indicate image capture or recording start/stop to the user.
MediaActionSound
Installs a callback to be invoked for every preview frame, using buffers supplied with addCallbackBuffer(byte[]), in addition to displaying them on the screen. The callback will be repeatedly called for as long as preview is active and buffers are available. Any other preview callbacks are overridden.
The purpose of this method is to improve preview efficiency and frame rate by allowing preview frame memory reuse. You must call addCallbackBuffer(byte[]) at some point -- before or after calling this method -- or no callbacks will received.
The buffer queue will be cleared if this method is called with a null callback, setPreviewCallback(Camera.PreviewCallback) is called, or setOneShotPreviewCallback(Camera.PreviewCallback) is called.
If you are using the preview data to create video or still images, strongly consider using MediaActionSound to properly indicate image capture or recording start/stop to the user.
addCallbackBuffer(byte[])MediaActionSound
Sets the Surface to be used for live preview. Either a surface or surface texture is necessary for preview, and preview is necessary to take pictures. The same surface can be re-set without harm. Setting a preview surface will un-set any preview surface texture that was set via setPreviewTexture(SurfaceTexture).
The SurfaceHolder must already contain a surface when this method is called. If you are using SurfaceView, you will need to register a SurfaceHolder.Callback with addCallback(SurfaceHolder.Callback) and wait for surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder) before calling setPreviewDisplay() or starting preview.
This method must be called before startPreview(). The one exception is that if the preview surface is not set (or set to null) before startPreview() is called, then this method may be called once with a non-null parameter to set the preview surface. (This allows camera setup and surface creation to happen in parallel, saving time.) The preview surface may not otherwise change while preview is running.
Sets the SurfaceTexture to be used for live preview. Either a surface or surface texture is necessary for preview, and preview is necessary to take pictures. The same surface texture can be re-set without harm. Setting a preview surface texture will un-set any preview surface that was set via setPreviewDisplay(SurfaceHolder).
This method must be called before startPreview(). The one exception is that if the preview surface texture is not set (or set to null) before startPreview() is called, then this method may be called once with a non-null parameter to set the preview surface. (This allows camera setup and surface creation to happen in parallel, saving time.) The preview surface texture may not otherwise change while preview is running.
The timestamps provided by getTimestamp() for a SurfaceTexture set as the preview texture have an unspecified zero point, and cannot be directly compared between different cameras or different instances of the same camera, or across multiple runs of the same program.
If you are using the preview data to create video or still images, strongly consider using MediaActionSound to properly indicate image capture or recording start/stop to the user.
SurfaceTexture to which the preview images are to be sent or null to remove the current preview surface texture
MediaActionSoundSurfaceTextureTextureView
Registers a listener to be notified when the zoom value is updated by the camera driver during smooth zoom.
startSmoothZoom(int)
Starts the face detection. This should be called after preview is started. The camera will notify Camera.FaceDetectionListener of the detected faces in the preview frame. The detected faces may be the same as the previous ones. Applications should call stopFaceDetection() to stop the face detection. This method is supported if getMaxNumDetectedFaces() returns a number larger than 0. If the face detection has started, apps should not call this again.
When the face detection is running, setWhiteBalance(String), setFocusAreas(List), and setMeteringAreas(List) have no effect. The camera uses the detected faces to do auto-white balance, auto exposure, and autofocus.
If the apps call autoFocus(AutoFocusCallback), the camera will stop sending face callbacks. The last face callback indicates the areas used to do autofocus. After focus completes, face detection will resume sending face callbacks. If the apps call cancelAutoFocus(), the face callbacks will also resume.
After calling takePicture(Camera.ShutterCallback, Camera.PictureCallback, Camera.PictureCallback) or stopPreview(), and then resuming preview with startPreview(), the apps should call this method again to resume face detection.
Camera.FaceDetectionListenerstopFaceDetection()getMaxNumDetectedFaces()
Starts capturing and drawing preview frames to the screen. Preview will not actually start until a surface is supplied with setPreviewDisplay(SurfaceHolder) or setPreviewTexture(SurfaceTexture).
If setPreviewCallback(Camera.PreviewCallback), setOneShotPreviewCallback(Camera.PreviewCallback), or setPreviewCallbackWithBuffer(Camera.PreviewCallback) were called, onPreviewFrame(byte[], Camera) will be called when preview data becomes available.
Zooms to the requested value smoothly. The driver will notify Camera.OnZoomChangeListener of the zoom value and whether zoom is stopped at the time. For example, suppose the current zoom is 0 and startSmoothZoom is called with value 3. The onZoomChange(int, boolean, Camera) method will be called three times with zoom values 1, 2, and 3. Applications can call stopSmoothZoom() to stop the zoom earlier. Applications should not call startSmoothZoom again or change the zoom value before zoom stops. If the supplied zoom value equals to the current zoom value, no zoom callback will be generated. This method is supported if isSmoothZoomSupported() returns true.
getMaxZoom().
setZoomChangeListener(OnZoomChangeListener)
Stops the face detection.
startFaceDetection()
Stops capturing and drawing preview frames to the surface, and resets the camera for a future call to startPreview().
Stops the smooth zoom. Applications should wait for the Camera.OnZoomChangeListener to know when the zoom is actually stopped. This method is supported if isSmoothZoomSupported() is true.
Equivalent to takePicture(shutter, raw, null, jpeg).
takePicture(ShutterCallback, PictureCallback, PictureCallback, PictureCallback)
Triggers an asynchronous image capture. The camera service will initiate a series of callbacks to the application as the image capture progresses. The shutter callback occurs after the image is captured. This can be used to trigger a sound to let the user know that image has been captured. The raw callback occurs when the raw image data is available (NOTE: the data will be null if there is no raw image callback buffer available or the raw image callback buffer is not large enough to hold the raw image). The postview callback occurs when a scaled, fully processed postview image is available (NOTE: not all hardware supports this). The jpeg callback occurs when the compressed image is available. If the application does not need a particular callback, a null can be passed instead of a callback method.
This method is only valid when preview is active (after startPreview()). Preview will be stopped after the image is taken; callers must call startPreview() again if they want to re-start preview or take more pictures. This should not be called between start() and stop().
After calling this method, you must not call startPreview() or take another picture until the JPEG callback has returned.
Unlocks the camera to allow another process to access it. Normally, the camera is locked to the process with an active Camera object until release() is called. To allow rapid handoff between processes, you can call this method to release the camera temporarily for another process to use; once the other process is done you can call reconnect() to reclaim the camera.
This must be done before calling setCamera(Camera). This cannot be called after recording starts.
If you are not recording video, you probably do not need this method.
Invoked when the garbage collector has detected that this instance is no longer reachable. The default implementation does nothing, but this method can be overridden to free resources.
Note that objects that override finalize are significantly more expensive than objects that don't. Finalizers may be run a long time after the object is no longer reachable, depending on memory pressure, so it's a bad idea to rely on them for cleanup. Note also that finalizers are run on a single VM-wide finalizer thread, so doing blocking work in a finalizer is a bad idea. A finalizer is usually only necessary for a class that has a native peer and needs to call a native method to destroy that peer. Even then, it's better to provide an explicit close method (and implement Closeable), and insist that callers manually dispose of instances. This works well for something like files, but less well for something like a BigInteger where typical calling code would have to deal with lots of temporaries. Unfortunately, code that creates lots of temporaries is the worst kind of code from the point of view of the single finalizer thread.
If you must use finalizers, consider at least providing your own ReferenceQueue and having your own thread process that queue.
Unlike constructors, finalizers are not automatically chained. You are responsible for calling super.finalize() yourself.
Uncaught exceptions thrown by finalizers are ignored and do not terminate the finalizer thread. See Effective Java Item 7, Avoid finalizers for more.
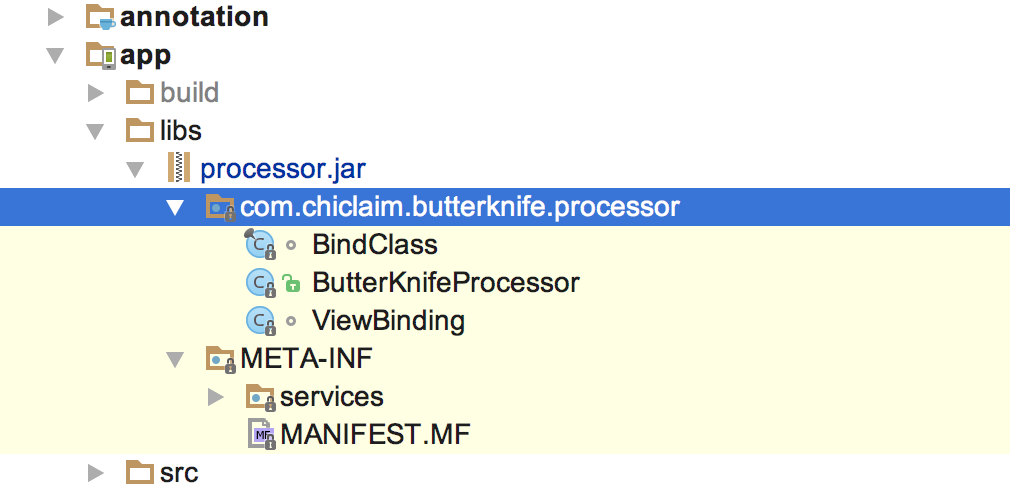 Android開發之手把手教你寫ButterKnife框架(二)
Android開發之手把手教你寫ButterKnife框架(二)
一、新建個項目, 然後創建一個module名叫processor新建module的時候一定要選擇 Java Library 否則在後面會找不到AbstractProces
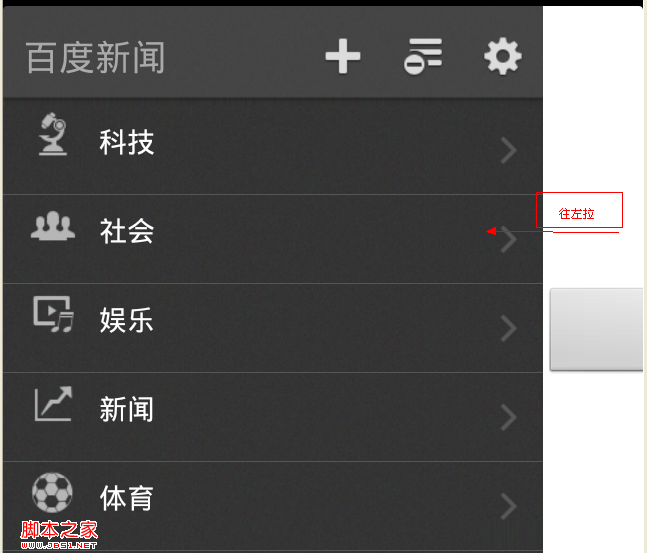 Android界面設計(APP設計趨勢 左側隱藏菜單右邊顯示content)
Android界面設計(APP設計趨勢 左側隱藏菜單右邊顯示content)
相關文章android popwindow實現左側彈出菜單層http://www.jb51.net/article/33533.htm移動App設計的13大精髓http:
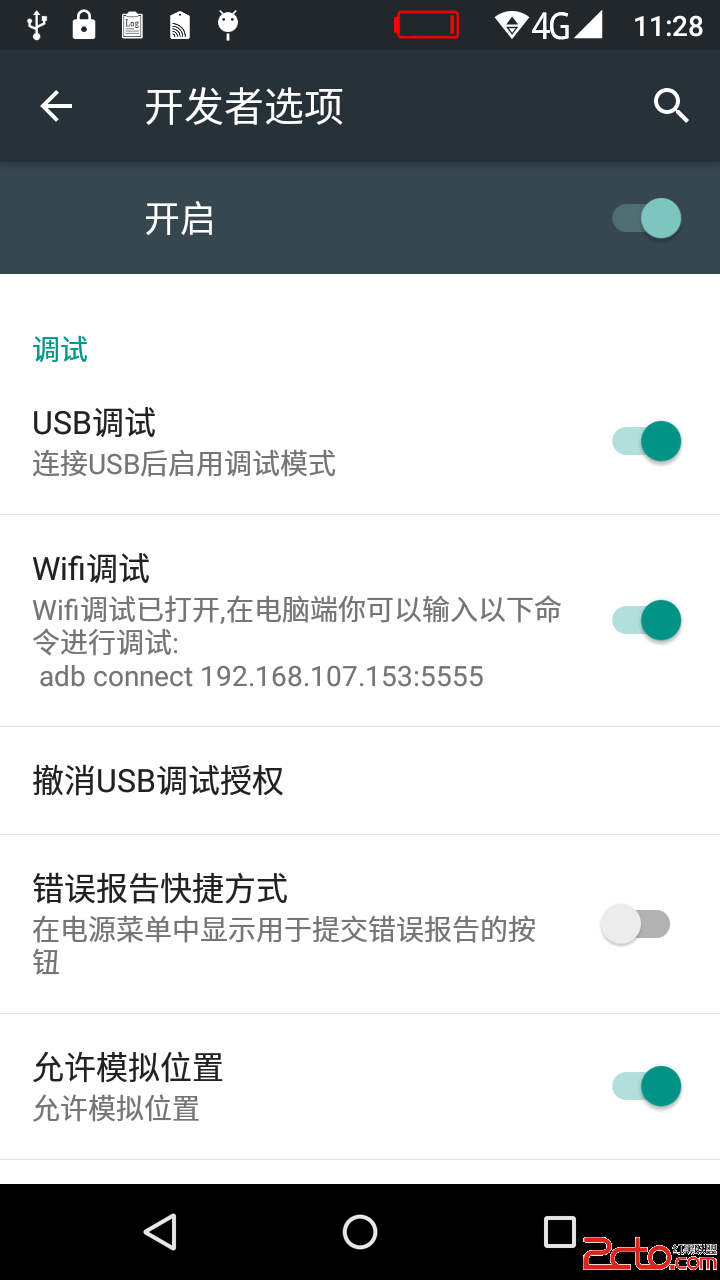 Android系統移植與調試之-------)如何添加一個adb wifi無線調試的功能【開發者選項】-【Wifi調試】
Android系統移植與調試之-------)如何添加一個adb wifi無線調試的功能【開發者選項】-【Wifi調試】
首先弄懂怎麼設置adb wifi無線調試的功能,如下所示。1. 手機端開啟adb tcp連接端口:/$setprop service.adb.tcp.port 5555:
 Android高手進階教程(二十六)之---Android超仿Path菜單的功能實現!
Android高手進階教程(二十六)之---Android超仿Path菜單的功能實現!
Hi~大家好,出來創業快3個月了,一切還不錯,前一段時間用了業余時間搞了個問答類網站YQMA.想做中國的stackoverflow,哈哈,只是YY下,希望大家多多支持!好