編輯:關於Android編程
今天是2013年的最後一天了,這裡首先提前祝大家新年快樂!同時,本篇文章也是我今年的最後一篇文章了,因此我想要讓它盡量有點特殊性,比起平時的文章要多一些特色。記得在今年年初的時候,我寫的第一篇文章是模仿360手機衛士的桌面懸浮窗效果,那麼為了能夠首尾呼應,今年的最後一篇文章就同樣還是來實現桌面懸浮窗的效果吧,當然效果將會更加高級。
相信用過QQ手機管家的朋友們都會知道它有一個小火箭加速的功能,將小火箭拖動到火箭發射台上發射就會出現一個火箭升空的動畫,那麼今天我們就來模仿著實現一下這個效果吧。
這次我們將代碼的重點放在火箭升空的效果上,因此簡單起見,就直接在模仿360手機衛士懸浮窗的那份代碼的基礎上繼續開發了,如果你還沒有看過那篇文章的話,建議先去閱讀 Android桌面懸浮窗效果實現,仿360手機衛士懸浮窗效果 。
比起普通的桌面懸浮窗,現在我們需要在拖動懸浮窗的時候將懸浮窗變成一個小火箭,並且在屏幕的底部添加一個火箭發射台。那麼我們就從火箭發射台開始編寫吧,首先創建launcher.xml作為火箭發射台的布局文件,如下所示:
可以看到,這裡的ImageView是用於顯示當前火箭發射台狀態的。我事先准備好了兩張圖片,一張是當小火箭未拖動到火箭發射台時顯示的,一張是當小火箭拖動到火箭發射台上時顯示的。
接下來創建RocketLauncher類,作為火箭發射台的View,代碼如下所示:
public class RocketLauncher extends LinearLayout {
/**
* 記錄火箭發射台的寬度
*/
public static int width;
/**
* 記錄火箭發射台的高度
*/
public static int height;
/**
* 火箭發射台的背景圖片
*/
private ImageView launcherImg;
public RocketLauncher(Context context) {
super(context);
LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.launcher, this);
launcherImg = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.launcher_img);
width = launcherImg.getLayoutParams().width;
height = launcherImg.getLayoutParams().height;
}
/**
* 更新火箭發射台的顯示狀態。如果小火箭被拖到火箭發射台上,就顯示發射。
*/
public void updateLauncherStatus(boolean isReadyToLaunch) {
if (isReadyToLaunch) {
launcherImg.setImageResource(R.drawable.launcher_bg_fire);
} else {
launcherImg.setImageResource(R.drawable.launcher_bg_hold);
}
}
}
RocketLauncher中的代碼還是非常簡單的,在構建方法中調用了LayoutInflater的inflate()方法來將launcher.xml這個布局文件加載進來,並獲取到了當前View的寬度和高度。在updateLauncherStatus()方法中會進行判斷,如果傳入的參數是true,就顯示小火箭即將發射的圖片,如果傳入的是false,就顯示將小火箭拖動到發射台的圖片。
新增的文件只有這兩個,剩下的就是要修改之前的代碼了。首先修改MyWindowManager中的代碼,如下所示:
public class MyWindowManager {
/**
* 小懸浮窗View的實例
*/
private static FloatWindowSmallView smallWindow;
/**
* 大懸浮窗View的實例
*/
private static FloatWindowBigView bigWindow;
/**
* 火箭發射台的實例
*/
private static RocketLauncher rocketLauncher;
/**
* 小懸浮窗View的參數
*/
private static LayoutParams smallWindowParams;
/**
* 大懸浮窗View的參數
*/
private static LayoutParams bigWindowParams;
/**
* 火箭發射台的參數
*/
private static LayoutParams launcherParams;
/**
* 用於控制在屏幕上添加或移除懸浮窗
*/
private static WindowManager mWindowManager;
/**
* 用於獲取手機可用內存
*/
private static ActivityManager mActivityManager;
/**
* 創建一個小懸浮窗。初始位置為屏幕的右部中間位置。
*/
public static void createSmallWindow(Context context) {
WindowManager windowManager = getWindowManager(context);
int screenWidth = windowManager.getDefaultDisplay().getWidth();
int screenHeight = windowManager.getDefaultDisplay().getHeight();
if (smallWindow == null) {
smallWindow = new FloatWindowSmallView(context);
if (smallWindowParams == null) {
smallWindowParams = new LayoutParams();
smallWindowParams.type = LayoutParams.TYPE_SYSTEM_ALERT;
smallWindowParams.format = PixelFormat.RGBA_8888;
smallWindowParams.flags = LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL
| LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE;
smallWindowParams.gravity = Gravity.LEFT | Gravity.TOP;
smallWindowParams.width = FloatWindowSmallView.windowViewWidth;
smallWindowParams.height = FloatWindowSmallView.windowViewHeight;
smallWindowParams.x = screenWidth;
smallWindowParams.y = screenHeight / 2;
}
smallWindow.setParams(smallWindowParams);
windowManager.addView(smallWindow, smallWindowParams);
}
}
/**
* 將小懸浮窗從屏幕上移除。
*/
public static void removeSmallWindow(Context context) {
if (smallWindow != null) {
WindowManager windowManager = getWindowManager(context);
windowManager.removeView(smallWindow);
smallWindow = null;
}
}
/**
* 創建一個大懸浮窗。位置為屏幕正中間。
*/
public static void createBigWindow(Context context) {
WindowManager windowManager = getWindowManager(context);
int screenWidth = windowManager.getDefaultDisplay().getWidth();
int screenHeight = windowManager.getDefaultDisplay().getHeight();
if (bigWindow == null) {
bigWindow = new FloatWindowBigView(context);
if (bigWindowParams == null) {
bigWindowParams = new LayoutParams();
bigWindowParams.x = screenWidth / 2
- FloatWindowBigView.viewWidth / 2;
bigWindowParams.y = screenHeight / 2
- FloatWindowBigView.viewHeight / 2;
bigWindowParams.type = LayoutParams.TYPE_PHONE;
bigWindowParams.format = PixelFormat.RGBA_8888;
bigWindowParams.gravity = Gravity.LEFT | Gravity.TOP;
bigWindowParams.width = FloatWindowBigView.viewWidth;
bigWindowParams.height = FloatWindowBigView.viewHeight;
}
windowManager.addView(bigWindow, bigWindowParams);
}
}
/**
* 將大懸浮窗從屏幕上移除。
*/
public static void removeBigWindow(Context context) {
if (bigWindow != null) {
WindowManager windowManager = getWindowManager(context);
windowManager.removeView(bigWindow);
bigWindow = null;
}
}
/**
* 創建一個火箭發射台,位置為屏幕底部。
*/
public static void createLauncher(Context context) {
WindowManager windowManager = getWindowManager(context);
int screenWidth = windowManager.getDefaultDisplay().getWidth();
int screenHeight = windowManager.getDefaultDisplay().getHeight();
if (rocketLauncher == null) {
rocketLauncher = new RocketLauncher(context);
if (launcherParams == null) {
launcherParams = new LayoutParams();
launcherParams.x = screenWidth / 2 - RocketLauncher.width / 2;
launcherParams.y = screenHeight - RocketLauncher.height;
launcherParams.type = LayoutParams.TYPE_PHONE;
launcherParams.format = PixelFormat.RGBA_8888;
launcherParams.gravity = Gravity.LEFT | Gravity.TOP;
launcherParams.width = RocketLauncher.width;
launcherParams.height = RocketLauncher.height;
}
windowManager.addView(rocketLauncher, launcherParams);
}
}
/**
* 將火箭發射台從屏幕上移除。
*/
public static void removeLauncher(Context context) {
if (rocketLauncher != null) {
WindowManager windowManager = getWindowManager(context);
windowManager.removeView(rocketLauncher);
rocketLauncher = null;
}
}
/**
* 更新火箭發射台的顯示狀態。
*/
public static void updateLauncher() {
if (rocketLauncher != null) {
rocketLauncher.updateLauncherStatus(isReadyToLaunch());
}
}
/**
* 更新小懸浮窗的TextView上的數據,顯示內存使用的百分比。
*
* @param context
* 可傳入應用程序上下文。
*/
public static void updateUsedPercent(Context context) {
if (smallWindow != null) {
TextView percentView = (TextView) smallWindow
.findViewById(R.id.percent);
percentView.setText(getUsedPercentValue(context));
}
}
/**
* 是否有懸浮窗(包括小懸浮窗和大懸浮窗)顯示在屏幕上。
*
* @return 有懸浮窗顯示在桌面上返回true,沒有的話返回false。
*/
public static boolean isWindowShowing() {
return smallWindow != null || bigWindow != null;
}
/**
* 判斷小火箭是否准備好發射了。
*
* @return 當火箭被發到發射台上返回true,否則返回false。
*/
public static boolean isReadyToLaunch() {
if ((smallWindowParams.x > launcherParams.x && smallWindowParams.x
+ smallWindowParams.width < launcherParams.x
+ launcherParams.width)
&& (smallWindowParams.y + smallWindowParams.height > launcherParams.y)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 如果WindowManager還未創建,則創建一個新的WindowManager返回。否則返回當前已創建的WindowManager。
*
* @param context
* 必須為應用程序的Context.
* @return WindowManager的實例,用於控制在屏幕上添加或移除懸浮窗。
*/
private static WindowManager getWindowManager(Context context) {
if (mWindowManager == null) {
mWindowManager = (WindowManager) context
.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
}
return mWindowManager;
}
/**
* 如果ActivityManager還未創建,則創建一個新的ActivityManager返回。否則返回當前已創建的ActivityManager。
*
* @param context
* 可傳入應用程序上下文。
* @return ActivityManager的實例,用於獲取手機可用內存。
*/
private static ActivityManager getActivityManager(Context context) {
if (mActivityManager == null) {
mActivityManager = (ActivityManager) context
.getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
}
return mActivityManager;
}
/**
* 計算已使用內存的百分比,並返回。
*
* @param context
* 可傳入應用程序上下文。
* @return 已使用內存的百分比,以字符串形式返回。
*/
public static String getUsedPercentValue(Context context) {
String dir = /proc/meminfo;
try {
FileReader fr = new FileReader(dir);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr, 2048);
String memoryLine = br.readLine();
String subMemoryLine = memoryLine.substring(memoryLine
.indexOf(MemTotal:));
br.close();
long totalMemorySize = Integer.parseInt(subMemoryLine.replaceAll(
\D+, ));
long availableSize = getAvailableMemory(context) / 1024;
int percent = (int) ((totalMemorySize - availableSize)
/ (float) totalMemorySize * 100);
return percent + %;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 懸浮窗;
}
/**
* 獲取當前可用內存,返回數據以字節為單位。
*
* @param context
* 可傳入應用程序上下文。
* @return 當前可用內存。
*/
private static long getAvailableMemory(Context context) {
ActivityManager.MemoryInfo mi = new ActivityManager.MemoryInfo();
getActivityManager(context).getMemoryInfo(mi);
return mi.availMem;
}
}
MyWindowManager是所有桌面懸浮窗的管理器,這裡我們主要添加了createLauncher()、removeLauncher()和updateLauncher()這幾個方法,分別用於創建、移除、以及更新火箭發射台懸浮窗。另外還添加了isReadyToLaunch()這個方法,它是用於判斷小火箭是否已經拖動到火箭發射台上了。判斷的方式當然也很簡單,只需要對小火箭的邊界和火箭發射台的邊界進行檢測,判斷它們是否相交就行了。
接下來還需要修改FloatWindowSmallView中的代碼,當手指拖動懸浮窗的時候要將它變成小火箭,如下所示:
public class FloatWindowSmallView extends LinearLayout {
/**
* 記錄小懸浮窗的寬度
*/
public static int windowViewWidth;
/**
* 記錄小懸浮窗的高度
*/
public static int windowViewHeight;
/**
* 記錄系統狀態欄的高度
*/
private static int statusBarHeight;
/**
* 用於更新小懸浮窗的位置
*/
private WindowManager windowManager;
/**
* 小懸浮窗的布局
*/
private LinearLayout smallWindowLayout;
/**
* 小火箭控件
*/
private ImageView rocketImg;
/**
* 小懸浮窗的參數
*/
private WindowManager.LayoutParams mParams;
/**
* 記錄當前手指位置在屏幕上的橫坐標值
*/
private float xInScreen;
/**
* 記錄當前手指位置在屏幕上的縱坐標值
*/
private float yInScreen;
/**
* 記錄手指按下時在屏幕上的橫坐標的值
*/
private float xDownInScreen;
/**
* 記錄手指按下時在屏幕上的縱坐標的值
*/
private float yDownInScreen;
/**
* 記錄手指按下時在小懸浮窗的View上的橫坐標的值
*/
private float xInView;
/**
* 記錄手指按下時在小懸浮窗的View上的縱坐標的值
*/
private float yInView;
/**
* 記錄小火箭的寬度
*/
private int rocketWidth;
/**
* 記錄小火箭的高度
*/
private int rocketHeight;
/**
* 記錄當前手指是否按下
*/
private boolean isPressed;
public FloatWindowSmallView(Context context) {
super(context);
windowManager = (WindowManager) context
.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.float_window_small, this);
smallWindowLayout = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.small_window_layout);
windowViewWidth = smallWindowLayout.getLayoutParams().width;
windowViewHeight = smallWindowLayout.getLayoutParams().height;
rocketImg = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.rocket_img);
rocketWidth = rocketImg.getLayoutParams().width;
rocketHeight = rocketImg.getLayoutParams().height;
TextView percentView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.percent);
percentView.setText(MyWindowManager.getUsedPercentValue(context));
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
isPressed = true;
// 手指按下時記錄必要數據,縱坐標的值都需要減去狀態欄高度
xInView = event.getX();
yInView = event.getY();
xDownInScreen = event.getRawX();
yDownInScreen = event.getRawY() - getStatusBarHeight();
xInScreen = event.getRawX();
yInScreen = event.getRawY() - getStatusBarHeight();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
xInScreen = event.getRawX();
yInScreen = event.getRawY() - getStatusBarHeight();
// 手指移動的時候更新小懸浮窗的狀態和位置
updateViewStatus();
updateViewPosition();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
isPressed = false;
if (MyWindowManager.isReadyToLaunch()) {
launchRocket();
} else {
updateViewStatus();
// 如果手指離開屏幕時,xDownInScreen和xInScreen相等,且yDownInScreen和yInScreen相等,則視為觸發了單擊事件。
if (xDownInScreen == xInScreen && yDownInScreen == yInScreen) {
openBigWindow();
}
}
break;
default:
break;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 將小懸浮窗的參數傳入,用於更新小懸浮窗的位置。
*
* @param params
* 小懸浮窗的參數
*/
public void setParams(WindowManager.LayoutParams params) {
mParams = params;
}
/**
* 用於發射小火箭。
*/
private void launchRocket() {
MyWindowManager.removeLauncher(getContext());
new LaunchTask().execute();
}
/**
* 更新小懸浮窗在屏幕中的位置。
*/
private void updateViewPosition() {
mParams.x = (int) (xInScreen - xInView);
mParams.y = (int) (yInScreen - yInView);
windowManager.updateViewLayout(this, mParams);
MyWindowManager.updateLauncher();
}
/**
* 更新View的顯示狀態,判斷是顯示懸浮窗還是小火箭。
*/
private void updateViewStatus() {
if (isPressed && rocketImg.getVisibility() != View.VISIBLE) {
mParams.width = rocketWidth;
mParams.height = rocketHeight;
windowManager.updateViewLayout(this, mParams);
smallWindowLayout.setVisibility(View.GONE);
rocketImg.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
MyWindowManager.createLauncher(getContext());
} else if (!isPressed) {
mParams.width = windowViewWidth;
mParams.height = windowViewHeight;
windowManager.updateViewLayout(this, mParams);
smallWindowLayout.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
rocketImg.setVisibility(View.GONE);
MyWindowManager.removeLauncher(getContext());
}
}
/**
* 打開大懸浮窗,同時關閉小懸浮窗。
*/
private void openBigWindow() {
MyWindowManager.createBigWindow(getContext());
MyWindowManager.removeSmallWindow(getContext());
}
/**
* 用於獲取狀態欄的高度。
*
* @return 返回狀態欄高度的像素值。
*/
private int getStatusBarHeight() {
if (statusBarHeight == 0) {
try {
Class c = Class.forName(com.android.internal.R$dimen);
Object o = c.newInstance();
Field field = c.getField(status_bar_height);
int x = (Integer) field.get(o);
statusBarHeight = getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(x);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return statusBarHeight;
}
/**
* 開始執行發射小火箭的任務。
*
* @author guolin
*/
class LaunchTask extends AsyncTask {
@Override
protected Void doInBackground(Void... params) {
// 在這裡對小火箭的位置進行改變,從而產生火箭升空的效果
while (mParams.y > 0) {
mParams.y = mParams.y - 10;
publishProgress();
try {
Thread.sleep(8);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
protected void onProgressUpdate(Void... values) {
windowManager.updateViewLayout(FloatWindowSmallView.this, mParams);
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(Void result) {
// 火箭升空結束後,回歸到懸浮窗狀態
updateViewStatus();
mParams.x = (int) (xDownInScreen - xInView);
mParams.y = (int) (yDownInScreen - yInView);
windowManager.updateViewLayout(FloatWindowSmallView.this, mParams);
}
}
}
這裡在代碼中添加了一個isPressed標識位,用於判斷用戶是否正在拖動懸浮窗。當拖動的時候就調用updateViewStatus()方法來更新懸浮窗的顯示狀態,這時懸浮窗就會變成一個小火箭。然後當手指離開屏幕的時候,也會調用updateViewStatus()方法,這時發現isPressed為false,就會將懸浮窗重新顯示出來。
同時,當手指離開屏幕的時候,還會調用MyWindowManager的isReadyToLaunch()方法來判斷小火箭是否被拖動到火箭發射台上了,如果為true,就會觸發火箭升空的動畫效果。火箭升空的動畫實現是寫在LaunchTask這個任務裡的,可以看到,這裡會在doInBackground()方法中執行耗時邏輯,將小火箭的縱坐標不斷減小,以讓它實現上升的效果。當縱坐標減小到0的時候,火箭升空的動畫就結束了,然後在onPostExecute()方法中重新將懸浮窗顯示出來。
另外,在AndroidManifest.xml文件中記得要聲明兩個權限,如下所示:
代碼就只有這麼多,接下來我們運行一下看看效果吧。在主界面點擊Start Float Window按鈕可以開啟懸浮窗並回到桌面,然後拖動懸浮窗後就會變成小火箭的狀態,將它拖動到屏幕底部火箭發射台上,然後放手,小火箭就會騰空而起了,如下圖所示:

好了,今天的講解就到這裡,伴隨著小火箭的起飛,我今年的最後一篇文章也結束了。
新的一年即將來臨,祝願大家在未來的一年裡,無論是工作還是學習,都能像這個小火箭一樣,騰飛起來,達到一個新的高度!2014年,我們繼續共同努力!
 Android canvas drawBitmap方法詳解及實例
Android canvas drawBitmap方法詳解及實例
Android canvas drawBitmap方法詳解及實例之前自己在自定義view,用到canvas.drawBitmap(Bitmap, SrcRec
 詳解Android中fragment和viewpager的那點事兒
詳解Android中fragment和viewpager的那點事兒
在之前的博文《Android 中使用 ViewPager實現屏幕頁面切換和頁面輪播效果》和《詳解Android中Fragment的兩種創建方式》以及《Android中fr
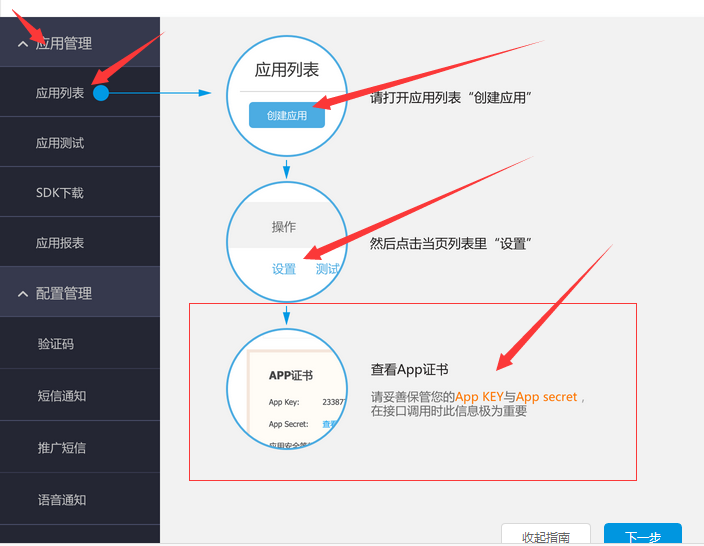 利用阿裡大於平台進行發送手機驗證碼
利用阿裡大於平台進行發送手機驗證碼
短信驗證(注冊或改密碼等)首先去登錄阿裡大於: http://www.alidayu.com/沒有號的就注冊一個!用淘寶就可以登錄了,相信一般人都是不需要注冊的。阿裡大於
 Android 6.0 Reboot 流程源代碼分析
Android 6.0 Reboot 流程源代碼分析
Shutdown 跟 reboot流程很類似,所以這裡以reboot分析:reboot的類型:1、手動長按power鍵選擇reboot;2、adb reboot;3、手動