編輯:關於Android編程
package com.hck.test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.json.JSONArray;
import org.json.JSONException;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
private Button button1, button2, button3, button4; //4個按鈕
private TextView textView; //顯示處理結果的textview
private List<UserBean> userBeans; //保存數據的集合
private JSONObject object; //JSONObject對象,處理一個一個的對象
private JSONObject object2;
private JSONArray jsonArray;//JSONObject對象,處理一個一個集合或者數組
private String jsonString; //保存帶集合的json字符串
private String jsonString2;//不帶集合的json字符串
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
initView(); //初始化控件
initDate(); //初始化數據
setListener(); //綁定監事件
}
private void initView() {
button1 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bt1);
button2 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bt2);
button3 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bt3);
button4 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bt4);
textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text);
}
/**
* 初始化2個用戶對象
*/
private void initDate() {
userBeans = new ArrayList<UserBean>();
UserBean userBean = new UserBean();
userBean.setUserId(1);
userBean.setUserName("hck");
userBeans.add(userBean);
UserBean userBean2 = new UserBean();
userBean2.setUserId(2);
userBean2.setUserName("蝌蚪");
userBeans.add(userBean2);
}
private void setListener() {
button1.setOnClickListener(this);
button2.setOnClickListener(this);
button3.setOnClickListener(this);
button4.setOnClickListener(this);
}
private void changeArrayDateToJson() { //把一個集合轉換成json格式的字符串
jsonArray=null;
object=null;
jsonArray = new JSONArray();
object=new JSONObject();
for (int i = 0; i < userBeans.size(); i++) { //遍歷上面初始化的集合數據,把數據加入JSONObject裡面
object2 = new JSONObject();//一個user對象,使用一個JSONObject對象來裝
try {
object2.put("userId", userBeans.get(i).getUserId()); //從集合取出數據,放入JSONObject裡面 JSONObject對象和map差不多用法,以鍵和值形式存儲數據
object2.put("userName", userBeans.get(i).getUserName());
jsonArray.put(object2); //把JSONObject對象裝入jsonArray數組裡面
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
object.put("userDate", jsonArray); //再把JSONArray數據加入JSONObject對象裡面(數組也是對象)
//object.put("time", "2013-11-14"); //這裡還可以加入數據,這樣json型字符串,就既有集合,又有普通數據
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
jsonString=null;
jsonString = object.toString(); //把JSONObject轉換成json格式的字符串
textView.setText(jsonString);
Log.i("hck", "轉換成json字符串: " + jsonString);
}
private void changeNotArrayDateToJson() {
object=null;
object=new JSONObject();
try {
object.put("userId", "1"); //把數據加入JSONObject對象即可,"userid"相當於map裡面的key,1即為value的值。
object.put("userName", "hck");
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
jsonString2=null;
jsonString2 = object.toString();//把JSONObject轉換成json格式的字符串
Log.i("hck", "轉換成json字符串: " + jsonString2);
textView.setText(jsonString2);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.bt1:
changeNotArrayDateToJson(); //點擊第一個按鈕,把集合轉換成json數據格式的string
break;
case R.id.bt2:
changeArrayDateToJson(); //點擊第2個按鈕,把普通數據換成json數據格式的string
break;
case R.id.bt3: //解析不帶集合的json字符串
if (jsonString2==null || "".equals(jsonString2)) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "請先點擊上面第1個按鈕轉把數據換成json字符串", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return;
}
changeJsonToData2();
break;
case R.id.bt4://解析帶集合的json字符串
if (jsonString==null || "".equals(jsonString)) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "請先點擊第2按鈕把數據換成json字符串", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return;
}
changeJsonToData1();
break;
default:
break;
}
}
private void changeJsonToData1()
{
StringBuilder stringBuilder=new StringBuilder(); //用來保存解析出來的額數據,顯示在textview
UserBean userBean;
List<UserBean> bList=new ArrayList<UserBean>();
try {
object=new JSONObject(jsonString); //用json格式的字符串獲取一個JSONObject對象
jsonArray=object.getJSONArray("userDate"); //通過key,獲取JSONObject裡面的一個JSONArray數組
for (int i = 0; i < jsonArray.length(); i++) { //遍歷數據
object=jsonArray.getJSONObject(i); //從JSONArray裡面獲取一個JSONObject對象
userBean=new UserBean();
userBean.setUserId(object.getInt("userId")); //通過key,獲取裡面的數據
userBean.setUserName(object.getString("userName"));
bList.add(userBean);
}
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int i = 0; i < bList.size(); i++) {
stringBuilder.append("用戶id:"+bList.get(i).getUserId()).append(" ").append("用戶名字:"+bList.get(i).getUserName());
}
textView.setText(stringBuilder.toString().replace("null", ""));
}
private void changeJsonToData2()
{
try {
object=new JSONObject(jsonString2);
String userName=object.getString("userName");
String userIdString=object.getString("userId");
textView.setText("用戶id"+userIdString+"用戶名字:"+userName);
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
 Android開發之 SwipeRefreshLayout
Android開發之 SwipeRefreshLayout
SwipeRefreshLayout概述 用戶通過手勢或者點擊某個按鈕實現內容視圖的刷新,布局裡加入SwipeRefreshLayout嵌套一個子視圖如ListView、
 android開發最常用例子整理----(1)自定義按鈕實現
android開發最常用例子整理----(1)自定義按鈕實現
android開發最常用例子整理----(1)自定義按鈕實現 一、Activity MainActivity.java源碼: public class MainA
 Android應用開發中View繪制的一些優化點解析
Android應用開發中View繪制的一些優化點解析
一個通常的錯誤觀念就是使用基本的布局結構(例如:LinearLayout、FrameLayout等)能夠在大多數情況下 產生高效率 的
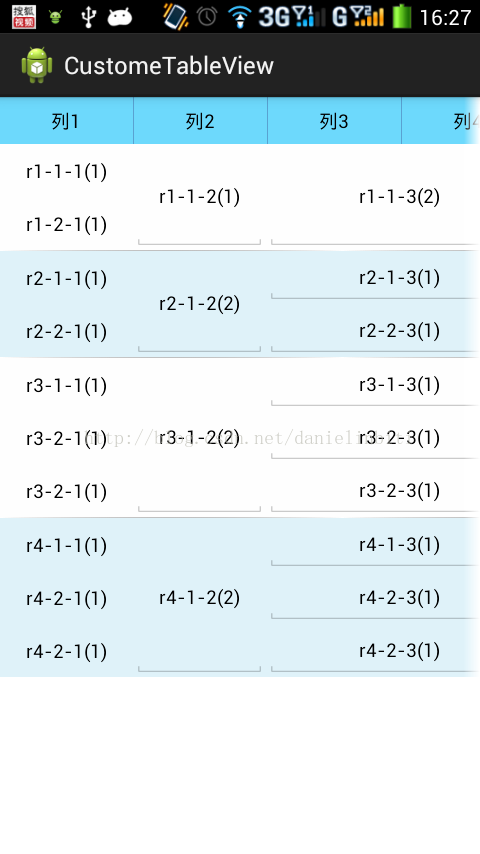 Android中使用ListView繪制自定義表格(3)
Android中使用ListView繪制自定義表格(3)
把自定義表格又改進了一下,可以支持行合並。表格分為簡單和復雜兩種模式 1、簡單模式就是《Android中使用ListView繪制自定義表格(2)》描述的方式。不支持行合並