這個課程向你展示如何實現一個Runnalbe類,它在一個單獨的線程中運行它的Runnable.run()方法中的代碼。你也能傳遞一個Runnable給其它的對象,然後將它連接到一個線程並且運行它。一個或者多個執行一個特殊操作的Runnable對象在某些時候被稱之為一個任務。
Thread和Runnabl都是基礎類,憑借它們自己,只有有限的能力。相反,它們是強大的Android類的基礎,如HandlerThread,AsyncTask,和IntentService.Thread和Runnable也是ThreadPollExecutor類的基礎。這節類自動管理線程和任務隊列,也可以並行運行多個線程。
定義一個實現Runnable的類
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
實現一個實現了Runnalbe的類是簡單的。例如:
[java]
public class PhotoDecodeRunnable implements Runnable {
...
@Override
public void run() {
/*
* Code you want to run on the thread goes here
*/
...
}
...
}
實現run()方法
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
在這個類中,Runnable.run()方法包含被執行的代碼。通常,任何事情都被允許在一個Runnable中。記住,這個Runnable沒有運行在這個UI線程中,所以它不能直接修改UI線程對象,如View對象。為了和UI線程通信,你必須使用在Communicate with the UI Thread課程中被描述的技術。
在run()方法的開始,通過使用THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND調用Process.setThreadPriority()方法來設置線程使用的後台優先級。這個方式降低了在Runnable對象的線程和UI線程之間的資源競爭。
你也應該在這個Runnable自己中保存一個Runnable對象的線程的引用,通過調用Thead.currentThread()方法。
下面的代碼片段展示了如何設置這個run()方法:
[java]
class PhotoDecodeRunnable implements Runnable {
...
/*
* Defines the code to run for this task.
*/
@Override
public void run() {
// Moves the current Thread into the background
android.os.Process.setThreadPriority(android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
...
/*
* Stores the current Thread in the the PhotoTask instance,
* so that the instance
* can interrupt the Thread.
*/
mPhotoTask.setImageDecodeThread(Thread.currentThread());
...
}
...
}
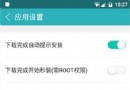 Android靜默安裝實現方案 仿360手機助手秒裝和智能安裝功能
Android靜默安裝實現方案 仿360手機助手秒裝和智能安裝功能
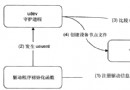 Android中的ueventd
Android中的ueventd
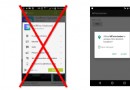 Android6.0權限系統
Android6.0權限系統
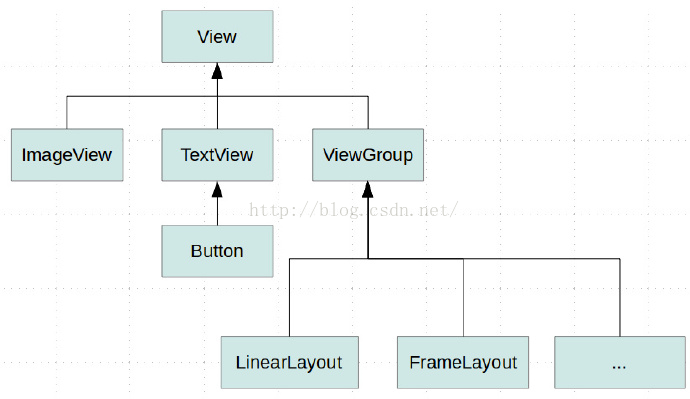 Android View的工作原理
Android View的工作原理