編輯:關於Android編程
Android中Linux suspend/resume流程
首先我們從linux kernel 的suspend說起,不管你是使用echo mem > /sys/power/state 或者使用你的開發板已經擁有的power key 都可以實現系統進入suspend的功能,這是suspend的基礎,即控制系統使suspend得到執行的機會,這裡相信大家都可以理解,不再過多說明。
那麼suspend得到了執行的機會又是怎麼一步一步開始往下執行的呢?現在就開始我們的系統的電源管理之旅:
我們就通過echo mem > /sys/power/state這種方式來看,這樣更容易被理解,位於/sys/power下面的這個state,做driver不知道那可說不過去,我們就看看這個state是在哪個地方創建的吧
kernel/kernel/power/suspend.c
[html] view plaincopyprint?
static int __init pm_init(void)
{
int error = pm_start_workqueue();
if (error)
return error;
hibernate_image_size_init();
hibernate_reserved_size_init();
power_kobj = kobject_create_and_add("power", NULL);
if (!power_kobj)
return -ENOMEM;
return sysfs_create_group(power_kobj, &attr_group);
}
core_initcall(pm_init);
static int __init pm_init(void)
{
int error = pm_start_workqueue();
if (error)
return error;
hibernate_image_size_init();
hibernate_reserved_size_init();
power_kobj = kobject_create_and_add("power", NULL);
if (!power_kobj)
return -ENOMEM;
return sysfs_create_group(power_kobj, &attr_group);
}
core_initcall(pm_init);
這段代碼很少卻很重要,我關心的是他確實為我們在sys目錄下先建了一個power目錄,然後,return時創建了很多接口,其中一個就是state,以下是接口定義
[html] view plaincopyprint?
static struct attribute * g[] = {
&state_attr.attr,
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_TRACE
&pm_trace_attr.attr,
&pm_trace_dev_match_attr.attr,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_SLEEP
&pm_async_attr.attr,
&wakeup_count_attr.attr,
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_DEBUG
&pm_test_attr.attr,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_USER_WAKELOCK
&wake_lock_attr.attr,
&wake_unlock_attr.attr,
#endif
#endif
NULL,
};
static struct attribute_group attr_group = {
.attrs = g,
};
static struct attribute * g[] = {
&state_attr.attr,
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_TRACE
&pm_trace_attr.attr,
&pm_trace_dev_match_attr.attr,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_SLEEP
&pm_async_attr.attr,
&wakeup_count_attr.attr,
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_DEBUG
&pm_test_attr.attr,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_USER_WAKELOCK
&wake_lock_attr.attr,
&wake_unlock_attr.attr,
#endif
#endif
NULL,
};
static struct attribute_group attr_group = {
.attrs = g,
};上面你可以看到了這些接口了
我們在echo mem > /sys/power/state,或調用的我們的接口函數state_store,suspend也就才真正開始走出第一步
[html] view plaincopyprint?
static ssize_t state_store(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_attribute *attr,
const char *buf, size_t n)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_SUSPEND
#ifdef CONFIG_EARLYSUSPEND
suspend_state_t state = PM_SUSPEND_ON;
#else
suspend_state_t state = PM_SUSPEND_STANDBY;
#endif
const char * const *s;
#endif
char *p;
int len;
int error = -EINVAL;
p = memchr(buf, '\n', n);
len = p ? p - buf : n;
/* First, check if we are requested to hibernate */
if (len == 4 && !strncmp(buf, "disk", len)) {
error = hibernate();
goto Exit;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_SUSPEND
for (s = &pm_states[state]; state < PM_SUSPEND_MAX; s++, state++) {
if (*s && len == strlen(*s) && !strncmp(buf, *s, len))
break;
}
if (state < PM_SUSPEND_MAX && *s)
#ifdef CONFIG_EARLYSUSPEND
if (state == PM_SUSPEND_ON || valid_state(state)) {
error = 0;
request_suspend_state(state);
}
#else
error = enter_state(state);
#endif
#endif
Exit:
return error ? error : n;
}
static ssize_t state_store(struct kobject *kobj, struct kobj_attribute *attr,
const char *buf, size_t n)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_SUSPEND
#ifdef CONFIG_EARLYSUSPEND
suspend_state_t state = PM_SUSPEND_ON;
#else
suspend_state_t state = PM_SUSPEND_STANDBY;
#endif
const char * const *s;
#endif
char *p;
int len;
int error = -EINVAL;
p = memchr(buf, '\n', n);
len = p ? p - buf : n;
/* First, check if we are requested to hibernate */
if (len == 4 && !strncmp(buf, "disk", len)) {
error = hibernate();
goto Exit;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_SUSPEND
for (s = &pm_states[state]; state < PM_SUSPEND_MAX; s++, state++) {
if (*s && len == strlen(*s) && !strncmp(buf, *s, len))
break;
}
if (state < PM_SUSPEND_MAX && *s)
#ifdef CONFIG_EARLYSUSPEND
if (state == PM_SUSPEND_ON || valid_state(state)) {
error = 0;
request_suspend_state(state);
}
#else
error = enter_state(state);
#endif
#endif
Exit:
return error ? error : n;
}這裡我們echo mem > /sys/power/state, 還有一種echo on > /sys/power/state,接著state_store進入reauest_suspend_state(state),然後如果是on的話進入late_resume_work(在執行late_resume_work之前會向系統申請main_wake_lock),如果是mem進入early_suspend_work。
reauest_suspend_state函數路徑:kernel/kernel/power/earlysuspend.c
[html] view plaincopyprint?
void request_suspend_state(suspend_state_t new_state)
{
unsigned long irqflags;
int old_sleep;
spin_lock_irqsave(&state_lock, irqflags);
old_sleep = state & SUSPEND_REQUESTED;
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_USER_STATE) {
struct timespec ts;
struct rtc_time tm;
getnstimeofday(&ts);
rtc_time_to_tm(ts.tv_sec, &tm);
pr_info("request_suspend_state: %s (%d->%d) at %lld "
"(%d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d.%09lu UTC)\n",
new_state != PM_SUSPEND_ON ? "sleep" : "wakeup",
requested_suspend_state, new_state,
ktime_to_ns(ktime_get()),
tm.tm_year + 1900, tm.tm_mon + 1, tm.tm_mday,
tm.tm_hour, tm.tm_min, tm.tm_sec, ts.tv_nsec);
}
if (!old_sleep && new_state != PM_SUSPEND_ON) {
state |= SUSPEND_REQUESTED;
queue_work(suspend_work_queue, &early_suspend_work);
} else if (old_sleep && new_state == PM_SUSPEND_ON) {
state &= ~SUSPEND_REQUESTED;
wake_lock(&main_wake_lock);
queue_work(suspend_work_queue, &late_resume_work);
}
requested_suspend_state = new_state;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&state_lock, irqflags);
}
void request_suspend_state(suspend_state_t new_state)
{
unsigned long irqflags;
int old_sleep;
spin_lock_irqsave(&state_lock, irqflags);
old_sleep = state & SUSPEND_REQUESTED;
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_USER_STATE) {
struct timespec ts;
struct rtc_time tm;
getnstimeofday(&ts);
rtc_time_to_tm(ts.tv_sec, &tm);
pr_info("request_suspend_state: %s (%d->%d) at %lld "
"(%d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d.%09lu UTC)\n",
new_state != PM_SUSPEND_ON ? "sleep" : "wakeup",
requested_suspend_state, new_state,
ktime_to_ns(ktime_get()),
tm.tm_year + 1900, tm.tm_mon + 1, tm.tm_mday,
tm.tm_hour, tm.tm_min, tm.tm_sec, ts.tv_nsec);
}
if (!old_sleep && new_state != PM_SUSPEND_ON) {
state |= SUSPEND_REQUESTED;
queue_work(suspend_work_queue, &early_suspend_work);
} else if (old_sleep && new_state == PM_SUSPEND_ON) {
state &= ~SUSPEND_REQUESTED;
wake_lock(&main_wake_lock);
queue_work(suspend_work_queue, &late_resume_work);
}
requested_suspend_state = new_state;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&state_lock, irqflags);
}
這裡做的最重要的是就在最下面那兩個分支中,決定了我們執行early_suspend_work,還是late_resume_work。這裡我們走early_suspend_work這個分支接著往下看。先看看early_suspend_work怎麼被調用
queue_work(suspend_work_queue, &early_suspend_work);
這是一個工作隊列的調用方法,找到early_suspend_work的定義
static DECLARE_WORK(early_suspend_work, early_suspend);
這裡有關於工作隊列的方法,不知道就要自己去看看了,所以這裡最終調用的其實是early_suspend這個方法
[html] view plaincopyprint?
static void early_suspend(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct early_suspend *pos;
unsigned long irqflags;
int abort = 0;
mutex_lock(&early_suspend_lock);
spin_lock_irqsave(&state_lock, irqflags);
if (state == SUSPEND_REQUESTED)
state |= SUSPENDED;
else
abort = 1;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&state_lock, irqflags);
if (abort) {
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_SUSPEND)
pr_info("early_suspend: abort, state %d\n", state);
mutex_unlock(&early_suspend_lock);
goto abort;
}
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_SUSPEND)
pr_info("early_suspend: call handlers\n");
list_for_each_entry(pos, &early_suspend_handlers, link) {
if (pos->suspend != NULL) {
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_VERBOSE)
pr_info("early_suspend: calling %pf\n", pos->suspend);
pos->suspend(pos);
}
}
mutex_unlock(&early_suspend_lock);
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_SUSPEND)
pr_info("early_suspend: sync\n");
sys_sync();
abort:
spin_lock_irqsave(&state_lock, irqflags);
if (state == SUSPEND_REQUESTED_AND_SUSPENDED)
wake_unlock(&main_wake_lock);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&state_lock, irqflags);
}
static void early_suspend(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct early_suspend *pos;
unsigned long irqflags;
int abort = 0;
mutex_lock(&early_suspend_lock);
spin_lock_irqsave(&state_lock, irqflags);
if (state == SUSPEND_REQUESTED)
state |= SUSPENDED;
else
abort = 1;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&state_lock, irqflags);
if (abort) {
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_SUSPEND)
pr_info("early_suspend: abort, state %d\n", state);
mutex_unlock(&early_suspend_lock);
goto abort;
}
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_SUSPEND)
pr_info("early_suspend: call handlers\n");
list_for_each_entry(pos, &early_suspend_handlers, link) {
if (pos->suspend != NULL) {
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_VERBOSE)
pr_info("early_suspend: calling %pf\n", pos->suspend);
pos->suspend(pos);
}
}
mutex_unlock(&early_suspend_lock);
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_SUSPEND)
pr_info("early_suspend: sync\n");
sys_sync();
abort:
spin_lock_irqsave(&state_lock, irqflags);
if (state == SUSPEND_REQUESTED_AND_SUSPENDED)
wake_unlock(&main_wake_lock);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&state_lock, irqflags);
}
early_suspend()這個函數裡會遍歷early_suspend_handlers,依次執行裡面的early_suspend函數,執行完所有的early_suspend後,釋放main_wake_lock,進入wake_unlock函數。
wake_unlock(&main_wake_lock);
這裡還是說一下吧,這個main_wake_lock是個什麼東西,路徑:kernel/kernel/power/wakelock.c
struct wake_lock main_wake_lock;
看他的初始化
wake_lock_init(&main_wake_lock, WAKE_LOCK_SUSPEND, "main");
wake_lock(&main_wake_lock);
首先初始化,然後lock,等待unlock
對於一個lock進入wake_unlock,首先會將lock從原鏈表中刪除(active_wake_locks),然後加入inactive_locks鏈表中。
[html] view plaincopyprint?
void wake_unlock(struct wake_lock *lock)
{
int type;
unsigned long irqflags;
spin_lock_irqsave(&list_lock, irqflags);
type = lock->flags & WAKE_LOCK_TYPE_MASK;
#ifdef CONFIG_WAKELOCK_STAT
wake_unlock_stat_locked(lock, 0);
#endif
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_WAKE_LOCK)
pr_info("wake_unlock: %s\n", lock->name);
lock->flags &= ~(WAKE_LOCK_ACTIVE | WAKE_LOCK_AUTO_EXPIRE);
list_del(&lock->link);
list_add(&lock->link, &inactive_locks);
if (type == WAKE_LOCK_SUSPEND) {
long has_lock = has_wake_lock_locked(type);
if (has_lock > 0) {
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_EXPIRE)
pr_info("wake_unlock: %s, start expire timer, "
"%ld\n", lock->name, has_lock);
mod_timer(&expire_timer, jiffies + has_lock);
} else {
if (del_timer(&expire_timer))
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_EXPIRE)
pr_info("wake_unlock: %s, stop expire "
"timer\n", lock->name);
if (has_lock == 0)
queue_work(suspend_work_queue, &suspend_work);
}
if (lock == &main_wake_lock) {
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_SUSPEND)
print_active_locks(WAKE_LOCK_SUSPEND);
#ifdef CONFIG_WAKELOCK_STAT
update_sleep_wait_stats_locked(0);
#endif
}
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&list_lock, irqflags);
}
void wake_unlock(struct wake_lock *lock)
{
int type;
unsigned long irqflags;
spin_lock_irqsave(&list_lock, irqflags);
type = lock->flags & WAKE_LOCK_TYPE_MASK;
#ifdef CONFIG_WAKELOCK_STAT
wake_unlock_stat_locked(lock, 0);
#endif
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_WAKE_LOCK)
pr_info("wake_unlock: %s\n", lock->name);
lock->flags &= ~(WAKE_LOCK_ACTIVE | WAKE_LOCK_AUTO_EXPIRE);
list_del(&lock->link);
list_add(&lock->link, &inactive_locks);
if (type == WAKE_LOCK_SUSPEND) {
long has_lock = has_wake_lock_locked(type);
if (has_lock > 0) {
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_EXPIRE)
pr_info("wake_unlock: %s, start expire timer, "
"%ld\n", lock->name, has_lock);
mod_timer(&expire_timer, jiffies + has_lock);
} else {
if (del_timer(&expire_timer))
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_EXPIRE)
pr_info("wake_unlock: %s, stop expire "
"timer\n", lock->name);
if (has_lock == 0)
queue_work(suspend_work_queue, &suspend_work);
}
if (lock == &main_wake_lock) {
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_SUSPEND)
print_active_locks(WAKE_LOCK_SUSPEND);
#ifdef CONFIG_WAKELOCK_STAT
update_sleep_wait_stats_locked(0);
#endif
}
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&list_lock, irqflags);
}
對於釋放鎖,上面兩個過程就結束了,但是如果這個鎖的類型是WAKE_LOCK_SUSPEND,那麼還需要執行一些操作,判斷是否可以進入睡眠。首先調has_wake_lock_locked(type)去查找是否還有這種類型的鎖,會遍歷active_wake_locks[type]鏈表,如果在這個鏈表中一檢測中有鎖,而且該鎖不是超時鎖,那麼就返回-1。如果是超時鎖,且已經超時了,那就去釋放這個鎖,如果沒超時就得到一個max_timeout,然後返回max_timeout。接著就會回到wake_unlock函數中,調用mod_timer(&expire_timer,jiffies +has_lock);has_lock就是前面返回的max_timeout,這句話的意思就是向系統中再添加定時器,定時時間就是最大的超時時間.expire_timer的操作函數是expire_wake_locks,這裡會去檢測還有沒有鎖,沒有的話就進入suspend_work,執行suspend,進入睡眠流程。上面wake_unlock中如果沒有檢測到鎖,也會執行suspend。在suspend函數中又會通過has_wake_lock去檢測有沒有鎖,有鎖就直接返回。
queue_work(suspend_work_queue, &suspend_work);
又是一個工作隊列,看看他的定義,找到他的處理過程
static DECLARE_WORK(suspend_work, suspend);
所以他真正執行的是suspend這個方法
[html] view plaincopyprint?
static void suspend(struct work_struct *work)
{
int ret;
int entry_event_num;
struct timespec ts_entry, ts_exit;
if (has_wake_lock(WAKE_LOCK_SUSPEND)) {
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_SUSPEND)
pr_info("suspend: abort suspend\n");
return;
}
entry_event_num = current_event_num;
sys_sync();
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_SUSPEND)
pr_info("suspend: enter suspend\n");
getnstimeofday(&ts_entry);
ret = pm_suspend(requested_suspend_state);
getnstimeofday(&ts_exit);
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_EXIT_SUSPEND) {
struct rtc_time tm;
rtc_time_to_tm(ts_exit.tv_sec, &tm);
pr_info("suspend: exit suspend, ret = %d "
"(%d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d.%09lu UTC)\n", ret,
tm.tm_year + 1900, tm.tm_mon + 1, tm.tm_mday,
tm.tm_hour, tm.tm_min, tm.tm_sec, ts_exit.tv_nsec);
}
if (ts_exit.tv_sec - ts_entry.tv_sec <= 1) {
++suspend_short_count;
if (suspend_short_count == SUSPEND_BACKOFF_THRESHOLD) {
suspend_backoff();
suspend_short_count = 0;
}
} else {
suspend_short_count = 0;
}
if (current_event_num == entry_event_num) {
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_SUSPEND)
pr_info("suspend: pm_suspend returned with no event\n");
wake_lock_timeout(&unknown_wakeup, HZ / 2);
}
}
static void suspend(struct work_struct *work)
{
int ret;
int entry_event_num;
struct timespec ts_entry, ts_exit;
if (has_wake_lock(WAKE_LOCK_SUSPEND)) {
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_SUSPEND)
pr_info("suspend: abort suspend\n");
return;
}
entry_event_num = current_event_num;
sys_sync();
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_SUSPEND)
pr_info("suspend: enter suspend\n");
getnstimeofday(&ts_entry);
ret = pm_suspend(requested_suspend_state);
getnstimeofday(&ts_exit);
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_EXIT_SUSPEND) {
struct rtc_time tm;
rtc_time_to_tm(ts_exit.tv_sec, &tm);
pr_info("suspend: exit suspend, ret = %d "
"(%d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d.%09lu UTC)\n", ret,
tm.tm_year + 1900, tm.tm_mon + 1, tm.tm_mday,
tm.tm_hour, tm.tm_min, tm.tm_sec, ts_exit.tv_nsec);
}
if (ts_exit.tv_sec - ts_entry.tv_sec <= 1) {
++suspend_short_count;
if (suspend_short_count == SUSPEND_BACKOFF_THRESHOLD) {
suspend_backoff();
suspend_short_count = 0;
}
} else {
suspend_short_count = 0;
}
if (current_event_num == entry_event_num) {
if (debug_mask & DEBUG_SUSPEND)
pr_info("suspend: pm_suspend returned with no event\n");
wake_lock_timeout(&unknown_wakeup, HZ / 2);
}
}
suspend函數中,通過pm_suspend(requested_suspend_state)進入suspend操作。這個裡面也有喚醒操作,只有等喚醒後才會跳出pm_suspend,跳出後會打印log:suspend:exit suspend, ret =pm_suspend就是判斷傳入的state是否符合suspend,符合就調用enter_state(state),到現在開始才進入了linux標准的suspend流程。
pm_suspend的路徑:kernel/kernel/power/suspend.c
[html] view plaincopyprint?
int pm_suspend(suspend_state_t state)
{
if (state > PM_SUSPEND_ON && state < PM_SUSPEND_MAX)
return enter_state(state);
return -EINVAL;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(pm_suspend);
int pm_suspend(suspend_state_t state)
{
if (state > PM_SUSPEND_ON && state < PM_SUSPEND_MAX)
return enter_state(state);
return -EINVAL;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(pm_suspend);
enter_state這個函數主要有三個函數調用,分別是suspend_prepare,suspend_devices_and_enter,suspend_finish。
[html] view plaincopyprint?
/**
* enter_state - Do common work of entering low-power state.
* @state: pm_state structure for state we're entering.
*
* Make sure we're the only ones trying to enter a sleep state. Fail
* if someone has beat us to it, since we don't want anything weird to
* happen when we wake up.
* Then, do the setup for suspend, enter the state, and cleaup (after
* we've woken up).
*/
int enter_state(suspend_state_t state)
{
int error;
if (!valid_state(state))
return -ENODEV;
if (!mutex_trylock(&pm_mutex))
return -EBUSY;
printk(KERN_INFO "PM: Syncing filesystems ... ");
sys_sync();
printk("done.\n");
pr_debug("PM: Preparing system for %s sleep\n", pm_states[state]);
error = suspend_prepare();
if (error)
goto Unlock;
if (suspend_test(TEST_FREEZER))
goto Finish;
pr_debug("PM: Entering %s sleep\n", pm_states[state]);
pm_restrict_gfp_mask();
error = suspend_devices_and_enter(state);
pm_restore_gfp_mask();
Finish:
pr_debug("PM: Finishing wakeup.\n");
suspend_finish();
Unlock:
mutex_unlock(&pm_mutex);
return error;
}
/**
* enter_state - Do common work of entering low-power state.
* @state: pm_state structure for state we're entering.
*
* Make sure we're the only ones trying to enter a sleep state. Fail
* if someone has beat us to it, since we don't want anything weird to
* happen when we wake up.
* Then, do the setup for suspend, enter the state, and cleaup (after
* we've woken up).
*/
int enter_state(suspend_state_t state)
{
int error;
if (!valid_state(state))
return -ENODEV;
if (!mutex_trylock(&pm_mutex))
return -EBUSY;
printk(KERN_INFO "PM: Syncing filesystems ... ");
sys_sync();
printk("done.\n");
pr_debug("PM: Preparing system for %s sleep\n", pm_states[state]);
error = suspend_prepare();
if (error)
goto Unlock;
if (suspend_test(TEST_FREEZER))
goto Finish;
pr_debug("PM: Entering %s sleep\n", pm_states[state]);
pm_restrict_gfp_mask();
error = suspend_devices_and_enter(state);
pm_restore_gfp_mask();
Finish:
pr_debug("PM: Finishing wakeup.\n");
suspend_finish();
Unlock:
mutex_unlock(&pm_mutex);
return error;
}
suspend_prepare做一些睡眠的准備工作
suspend_devices_and_enter就是真正的設備進入睡眠
suspend_finish喚醒後進行的操作。
下面來一個一個分析:
suspend_prepare中首先通過pm_prepare_console,給suspend分配一個虛擬終端來輸出信息;接著通過pm_notifier_call_chain來廣播一個系統進入suspend的通報;關閉用戶態的helper進程;最後通過suspend_freeze_processes來凍結用戶態進程,最後會嘗試釋放一些內存。在suspend_freeze_processes()函數中調用了freeze_processes()函數,而freeze_processes()函數中又調用了try_to_freeze_tasks()來完成凍結任務。在凍結過程中,會判斷當前進程是否有wake_lock,若有,則凍結失敗,函數會放棄凍結。
執行完上面的操作後再次回到enter_state函數中,下面開始調用suspend_devices_and_enter()函數讓外設進入休眠。在suspend_devices_and_enter()中首先調用關於平台的suspend_ops->begin,接著通過suspend_console來關閉console,也可以通過改變一個flag來使這個函數無效。接著調用dpm_suspend_start。dpm_suspend_start中會執行device_prepare和device_suspend,這兩個函數都是調用pm接口裡的prepare和suspend函數(其實這裡就開始通過總線的接口來執行驅動的suspend函數了,通過bus->pm->suspend)。接著回到suspend_devices_and_enter中調用suspend_enter(state);在suspend_enter中,首先調用平台相關的suspend_ops->prepare,接著執行dpm_suspend_noirq()調用pm接口裡的pm->suspend_noirq,回到suspend_enter,接著調用suspend_ops->prepare_late,接下來多cpu中非啟動的cpu通過函數disable_nonboot_cpus()被關閉,然後通過調用arch_suspend_disable_irqs()關閉本地中斷。再後來才到睡眠設備的操作,sysdev_suspend(PMSG_SUSPEND),這樣就會進入sysdev_driver.suspend階段。最後調用suspend_ops->enter(),這裡就開始執行到睡眠的最後一步了,執行平台相關的睡眠。在平台睡眠的代碼中主要是通過suspend_in_iram(suspend_param1)來執行一段匯編代碼,最終在匯編中睡死。喚醒的步驟與睡眠的步驟相反,cpu有電後會首先從匯編中起來,接著回到suspend_enter函數中,執行suspend_ops->enter()返回後的一些喚醒代碼,這邊就不再去說了,基本是按照上面的逆序來操作的。
上面的過程在我看來還是很復雜的,power management 要好好研究一下了
resume的過程
喚醒的時候,程序從suspend_devices_and_enter函數中出來後,開始執行suspend_finish,接著就會從enter_state中退出來,返回pm_suspend,然後又從pm_suspend返回到wakelock.c中的suspend(),在這裡接下來就會打印出”suspend:exit suspend, ret“這些log。
 Android 進階 - ActivieyManagerService簡介
Android 進階 - ActivieyManagerService簡介
在前面多篇文章中,都有提到ActivityManagerService,它是在系統啟動時加載的一個服務線程,運行於system_server進程中,主要負責管理系統中的A
 android中使用jni對字符串加解密實現分析
android中使用jni對字符串加解密實現分析
android中使用jni對字符串加解密實現分析 最近項目有個需求,就是要對用戶的敏感信息進行加密處理,比如用戶的賬戶密碼,手機號等私密信息。在java中,就對字符串
 Android照片牆完整版,完美結合LruCache和DiskLruCache
Android照片牆完整版,完美結合LruCache和DiskLruCache
在上一篇文章當中,我們學習了DiskLruCache的概念和基本用法,但僅僅是掌握理論知識顯然是不夠的,那麼本篇文章我們就來繼續進階一下,看一看在實戰當中應
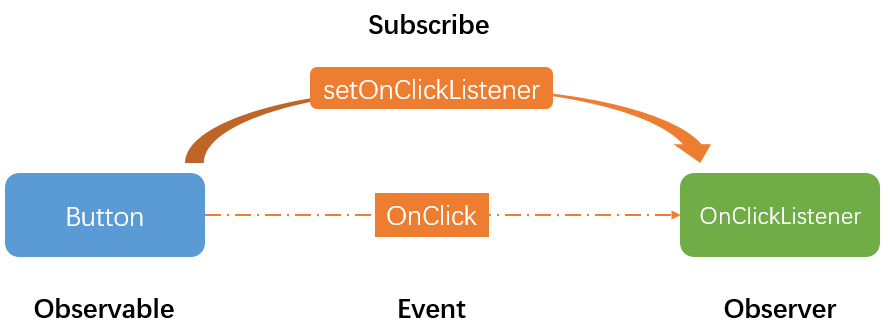 RxJava入門之介紹與基本運用
RxJava入門之介紹與基本運用
前言因為這個RxJava內容不算少,而且應用場景非常廣,所以這個關於RxJava的文章我們會陸續更新,今天就來先來個入門RxJava吧初識RxJava什麼是Rx很多教程在